Abstract
Long noncoding RNAs are thought to regulate gene expression by organizing protein complexes through unclear mechanisms. XIST controls the inactivation of an entire X chromosome in female placental mammals. Here we develop and integrate several orthogonal structure-interaction methods to demonstrate that XIST RNA-protein complex folds into an evolutionarily conserved modular architecture. Chimeric RNAs and clustered protein binding in fRIP and eCLIP experiments align with long-range RNA secondary structure, revealing discrete XIST domains that interact with distinct sets of effector proteins. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated permutation of the **st A-repeat location shows that A-repeat serves as a nucleation center for multiple **st-associated proteins and m6A modification. Thus modular architecture plays an essential role, in addition to sequence motifs, in determining the specificity of RBP binding and m6A modification. Together, this work builds a comprehensive structure-function model for the XIST RNA-protein complex, and suggests a general strategy for mechanistic studies of large ribonucleoprotein assemblies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play essential roles in many aspects of gene expression in development and disease1. lncRNAs control X chromosome inactivation (XCI), genome imprinting, immune response, cell-cycle regulation, genome stability, lineage commitment, and embryonic stem cell (ESC) pluripotency2,3,4,5,6,7,35) and WDR5 (low read numbers). The bar graph on the right side shows the fraction of long-distance read pairs pulled down each protein relative to total mapped reads (see numbers in Supplementary Fig. 1a). n = 3 biologically independent samples. Data are presented as mean values +/− standard deviation in the bar graph. i PCA analysis of profiles in 100-nt windows. The numbers on the right are variation explained by each component. Source data are provided as a Source data file.
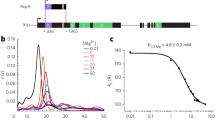
During the experiments, two adapters were ligated to the purified RNA fragments. In addition, endogenous (in lysate) or the added RNA ligases (in purified RNA) can join two fragments that are crosslinked together, resulting in chimeras. Subsequent paired end sequencing captures the two ends of, and we developed a pipeline to identify, such chimeras (Fig. 1b). Short-distance pairs indicate single fragments, while long-distance pairs indicate two proximally ligated fragments. Distance distribution between paired-end tags (inclusive) is mostly between 100 and 400 nts (Fig. 1c, left side panels, see complete data in Supplementary Fig. 1). In addition, discrete clusters of long-distance reads are detected up to 10 kb for most proteins, including input control (Fig. 1c, right panels). Five major long-distance groups (LGs) were identified in XIST. The discrete distribution suggests that the ligation reactions are highly specific for certain positions along the XIST RNA dictated by spatial proximity.
To determine the nature of these LGs, we compared them to the PARIS-derived XIST structure27 (Fig. 1d). The first four major LGs are mapped to the Exon6 domain, primarily among three anchor points, while LG5 is mapped to the large BCD domain (Fig. 1e). LG1–4 overlap RNA duplexes from PARIS (Fig. 1f); the sequencing tags extended to the approximate length of the RNA fragments clearly overlaps the two arms of the PARIS duplex (Fig. 1g). LG5 does not directly overlap duplexes in PARIS but is consistent with the overall shape of the BCD domain. Together, these long-distance crosslinking data support the XIST domain architecture.
fRIP-seq reveals spatial partition of XIST-associated proteins
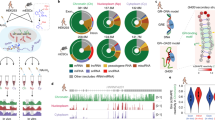
To understand how XIST-associated proteins are assembled, we normalized all 74 fRIP samples (including input) against the average of input controls in 100-nt windows (see “Methods,” the 25th percentile set to 0.1 for each fRIP-seq profile), and clustered enrichment profiles (Fig. 1h, see Supplementary Fig. 1 for all tracks). Several patterns emerged, including the selective enrichment in the A-repeat domain (DNMT1, CBX3, and phosphorylated CBX3 (pCBX3)), F domain (DNMT1, CBX3, pCBX3, and HNRNPH), BCD domain (HNRNPU, which is also in the Exon6 domain), and E domain (CHD4, EZH2, SUZ12, DNMT1, and pCBX3), which is coupled to the end of the transcript. The enrichment on the two ends of the Exon6 domain correlate with the higher percentages of long-distance read pairs (Fig. 1h, bar graph, and Supplementary Fig. 1d), providing further support for the bona fide long-range interactions. Together, these data show clear spatial separation of the XIST-associated proteins.
To automatically derive the domain definitions from the high-dimension data, we applied principal component analysis (PCA; Fig. 1i). The first 4 principal components (PCs) account for 86% of all variation, while the first 7 PCs account for >90% of all variation. The major domains are all detectable. For example, PC1 contains the coupled E-repeat and the feet of the Exon6 domain. PC2 primarily shows the different enrichment patterns in A and F domains. PC5 shows the differential enrichment in the largest BCD domain. Together these data not only confirm the XIST RNA structure but also reveal patterns of protein binding on the XIST RNA.
Modular assembly of the XIST RNP based on eCLIP
To further understand the organization of the XIST RNP complex, we used published RNA–protein UV crosslinking data (eCLIP) to map the binding sites of XIST-associated proteins36. Yeo and colleagues published a large set of RBP eCLIP data that maps the binding sites to nt resolution. The original analysis revealed enrichment of only four proteins on the transcript level, including HNRNPM, HNRNPK, RBM15, and PTBP1, whereas many other XIST-associated proteins did not pass the stringent enrichment threshold. Out of the 81 proteins previously detected by ** of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat. Methods 12, 767–772 (2015)." href="/article/10.1038/s41467-020-20040-3#ref-CR47" id="ref-link-section-d72439055e1189">47. m6A sites closely follows RBM15/RBM15B occupancy, which recruit the METTL3/14 methyltransferase complex, suggesting that these two adapter proteins guide the modification. Patil et al. proposed a model where the location of RBM15/15B proteins determines m6A modification sites. Close examination of CLIP data showed that the RBM15/RBM15B-binding sites are primarily clustered in the A-repeat domain and the other sites are much weaker, raising the question of how m6A is placed at distal locations on XIST RNA over 10,000 bases away. Instead, we noticed that all m6A modification sites, as well as the RBM15/RBM15B-binding sites, are in close spatial proximity when the XIST RNA is folded (Fig. 4a). The consensus m6A motif DRACH is nearly uniformly distributed along the XIST RNA transcript in both human and mouse, with the exception of the pyrimidine-rich E repeat, and at a density of one motif every ~54 nts (Fig. 4a). The discrepancy between m6A motifs and modification sites suggests that the folding of the XIST RNA into compact modular domains contribute to the specificity of m6A modifications. Here we propose two hypotheses to explain the pattern of m6A modifications. First, the compact folding of the large BCD and Exon6 domains exclude the m6A methylase complex. Second, the folding of the XIST RNA creates local proximity among the modification sites with the A-repeat domain. These two possibilities are not mutually exclusive. Altering the overall structure of the XIST RNA is challenging because all the base pairing interactions contribute to the whole transcript structure; disruption of a small number of base pairs is unlikely to cause global changes.
a m6A on the human mature XIST RNA. K562 RBM15 eCLIP was normalized against input in 100-nt windows36 and plotted in two scales to highlight the differences in binding the 5’ end and other regions. HEK293 cell m6A iCLIP track was from ref. 47. m6A motif density was calculated in 300-nt windows and 50-nt steps. b Gene structure for the alleles. WT and ΔSX (~900 bp deletion in ** the human miRNA interactome by CLASH reveals frequent noncanonical binding. Cell 153, 654–665 (2013)." href="/article/10.1038/s41467-020-20040-3#ref-CR51" id="ref-link-section-d72439055e1694">51,52. In this work, the crosslink and proximity ligation principle that has been successfully employed in the analysis of chromatin structures and RNA interactions and structures can be extended to the analysis of other RBPs on any RNA of interest, as long as these proteins are crosslinkable. The application of these methods will be instrumental in the analysis of other RNP complexes. More importantly, the discovery of compact RNP domains set the stage for focused in vitro studies of these domains through purification reconstitution and structure analysis using physical methods53.
Multiple previous studies have analyzed the XIST RNA, either in part or in its entirety, using various methodsmeRIP-seq in mESCs Total mES RNA was subjected to one round of Poly(A)Purist MAG treatment to enrich for polyadenylated RNAs as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Ambion). RNA was then fragmented to 100-nt median-sized fragments using RNA Fragmentation Reagents (Ambion) and subjected to one round of m6A immunoprecipitation. For immunoprecipitation of RNA, 5 μg of m6A antibody (Millipore) was coupled to 40 μl Protein A Dynabeads (Novex) in 100 μl 1× IPP Buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5; 150 mM NaCl; 0.1% NP-40; 5 mM EDTA) overnight at 4 C. Beads were then washed twice in 1× IPP Buffer. Fragmented RNA was denatured at 70 °C for 2 min, cooled on ice, and bound to antibody beads in 185 μl 1× IPP Buffer for 3 h at 4 °C. Beads were then washed sequentially with (2×) 500 μl 1× IPP Buffer, (2×) 500 μl Low Salt Buffer (0.25× SSPE; 1 mM EDTA; 0.05% Tween-20; 37.5 mM NaCl), (2×) 500 μl High Salt Buffer (0.25× SSPE; 1 mM EDTA; 0.05% Tween-20; 137.5 mM NaCl), (1×) 500 μl TET Buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 1 mM EDTA; 0.05% Tween-20). Beads were eluted with 50 μl RLT Buffer (Qiagen RNeasy Mini Kit) and incubated at 25 °C for 5 min and recovered with the RNeasy Mini Kit followed by concentrating with Zymo RNA Clean & Concentrator in 10 μl water. Ten nanograms of input RNA (before immunoprecipitation) and 10 ng of immunoprecipitated RNA were then used to prepare sequencing libraries using the SMARTer Stranded RNA-Seq Kit—Pico Input Mammalian (Clontech #634411), as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Sequencing libraries were pooled and sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq (files named *mar08* and *apr26*) and NextSeq (files named *jun24*). See Supplementary Note 6 for details of the global analyses of meRIP-seq data and targeted analysis of ** of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat. Methods 12, 767–772 (2015)." href="/article/10.1038/s41467-020-20040-3#ref-CR47" id="ref-link-section-d72439055e2104">47
The miCLIP bedgraph files in GSE63753 were downloaded from GEO and lifted to hg38 using the liftOver tool from UCSC genome brower47. Then the data were lifted to the mature XIST transcript coordinates (without introns) using custom python scripts.
irCLIP analysis of SPEN and LBR
The irCLIP experiments were performed as described previously60. Briefly, mESCs with engineered **st mutations were cultured with standard conditions and induced to express **st (see earlier description on cell culture). Afterwards, cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated with antibodies for these RBPs and treated with S1 nuclease. RNP complexes were resolved on denatured polyacrylamide gels and regions above the protein size were excised for RNA extraction and library preparation.
Sequencing output reads were processed by bbmap to remove duplication on fastq level. Remained reads were trimmed off the 3’ solexa adapter and against sequencing quality q20 by cutadapt (version 2.4). Trimmed reads were mapped first to RNA biotypes with high repetitiveness by bowtie2 (version 2.2.9) to our custom-built indexes: rRNAs (rRNAs downloaded from Ensembl GRCm38.p6/mm10 and a full, non-repeat masked mouse rDNA repeat from GenBank accession No. BK000964), snRNAs (from Ensembl GRCm38.p6/mm10), miscRNAs (from Ensembl GRCm38.p6/mm10), tRNAs (from UCSC table browser GRCm38.p6/mm10), RetroGenes V6 (from UCSC table browser GRCm38.p6/mm10), and RepeatMasker (from UCSC table browser GRCm38.p6/mm10). Remained reads were mapped to mouse genome GRCm38/mm10 by STAR (version 2.7.1a) with junction file generated from mRNAs and lncRNAs by Genocode GRCm38.p6/mm10 GTF file. Only reads uniquely mapped to the mouse genome were included in the downstream analysis. The RBP-binding loci as suggested by the irCLIP method, was defined as 1-nt shift to the 5’ end of each mapped read. Each locus was extended 5 nts upstream and downstream to shape a local interval; only intervals overlapped between two replicates were included. Then five nts were trimmed from each side of the overlapped interval to shape the final cluster. Cluster annotation was processed against the Genocode GRCm38.p6/mm10 GTF file. Reads annotated to **st gene were re-mapped to the **st mini-genome. Normalization on **st was processed in the same way as for m6A data.
Quantification and statistical analysis
In the relevant figures, figure legends denote the statistical details of experiments, including statistical tests used, kind of replicates, and the value of n. Asterisks define degree of significance as described in the figure legends. All Student’s t test and Mann–Whitney U test were analyzed as two sided. All the sequencing data were aligned to mouse and human genomes (mm10 and hg38) or custom-made mini-genomes (mm**st and hsXIST). Statistical analyses and graphics were performed using Python, R, and Microsoft Excel.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
The data that support this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. Conservation plot is imported from “100 vertebrates Basewise Conservation by PhyloP” at UCSC genome browser. The custom IGV genome for human XIST mature transcript is available in the same folder as well. All raw sequencing reads and raw count matrices generated in this study are available through Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) with accession number GSE126715 (m6A RIP-seq and irCLIP on A-repeat relocation alleles) and GSE126716 (PARIS in mouse ES cells). Source data are provided with this paper.
Code availability
All softwares used in this study are as follows: STAR 2.7.1a61 https://github.com/alexdobin/STAR, Samtools v1.162 http://samtools.sourceforge.net/, Bedtools v2.22.063 https://bedtools.readthedocs.io/, m6aViewer v1.6.164 http://dna2.leeds.ac.uk/m6a/, PARIS27 https://github.com/qczhang, IGV65 http://broadinstitute.org/software/igv, Vienna RNA Package66 https://www.tbi.univie.ac.at/RNA/, Kent Utilities67 https://genome.ucsc.edu/util.html, Trimmomatic v0.3.268 http://www.usadellab.org/cms/?page=trimmomatic, Python (Van Rossum, 1995) https://www.python.org/, Cluster68 http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster/software.htm, Java Treeview69 http://jtreeview.sourceforge.net/, Fastqc70 https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/, and Custom scripts https://github.com/zhipenglu.
References
Wang, K. C. & Chang, H. Y. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 43, 904–914 (2011).
Lu, Z., Carter, A. C. & Chang, H. Y. Mechanistic insights in X-chromosome inactivation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 372, 20160356 (2017).
Lee, S. et al. Noncoding RNA NORAD regulates genomic stability by sequestering PUMILIO proteins. Cell 164, 69–80 (2016).
Gomez, J. A. et al. The NeST long ncRNA controls microbial susceptibility and epigenetic activation of the interferon-gamma locus. Cell 152, 743–754 (2013).
Brannan, C. I., Dees, E. C., Ingram, R. S. & Tilghman, S. M. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10, 28–36 (1990).
Guttman, M. et al. lincRNAs act in the circuitry controlling pluripotency and differentiation. Nature 477, 295–300 (2011).
Tichon, A. et al. A conserved abundant cytoplasmic long noncoding RNA modulates repression by Pumilio proteins in human cells. Nat. Commun. 7, 12209 (2016).
Brockdorff, N. et al. Conservation of position and exclusive expression of mouse **st from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 351, 329–331 (1991).
Brown, C. J. et al. A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 349, 38–44 (1991).
Quinn, J. J. & Chang, H. Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 17, 47–62 (2016).
Ransohoff, J. D., Wei, Y. & Khavari, P. A. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 143–157 (2018).
Zappulla, D. C. & Cech, T. R. Yeast telomerase RNA: a flexible scaffold for protein subunits. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 10024–10029 (2004).
Tsai, M. C. et al. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 329, 689–693 (2010).
Lu, Z. & Chang, H. Y. Decoding the RNA structurome. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 36, 142–148 (2016).
Somarowthu, S. et al. HOTAIR forms an intricate and modular secondary structure. Mol. Cell 58, 353–361 (2015).
Hawkes, E. J. et al. COOLAIR antisense RNAs form evolutionarily conserved elaborate secondary structures. Cell Rep. 16, 3087–3096 (2016).
Xue, Z. et al. A G-rich motif in the lncRNA braveheart interacts with a zinc-finger transcription factor to specify the cardiovascular lineage. Mol. Cell 64, 37–50 (2016).
Smola, M. J. et al. SHAPE reveals transcript-wide interactions, complex structural domains, and protein interactions across the **st lncRNA in living cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 10322–10327 (2016).
Fang, R., Moss, W. N., Rutenberg-Schoenberg, M. & Simon, M. D. Probing **st RNA structure in cells using targeted structure-seq. PLoS Genet. 11, e1005668 (2015).
Eddy, S. R. How do RNA folding algorithms work?. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 1457–1458 (2004).
Mathews, D. H., Moss, W. N. & Turner, D. H. Folding and finding RNA secondary structure. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2, a003665 (2010).
Chu, C. et al. Systematic discovery of **st RNA binding proteins. Cell 161, 404–416 (2015).
Minajigi, A. et al. Chromosomes. A comprehensive **st interactome reveals cohesin repulsion and an RNA-directed chromosome conformation. Science 349, aab2276 (2015).
Moindrot, B. et al. A pooled shRNA screen identifies Rbm15, Spen, and Wtap as factors required for **st RNA-mediated silencing. Cell Rep. 12, 562–572 (2015).
Monfort, A. et al. Identification of Spen as a crucial factor for **st function through forward genetic screening in haploid embryonic stem cells. Cell Rep. 12, 554–561 (2015).
McHugh, C. A. et al. The **st lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3. Nature 521, 232–236 (2015).
Lu, Z. et al. RNA duplex map in living cells reveals higher-order transcriptome structure. Cell 165, 1267–1279 (2016).
Patil, D. P. et al. m(6)A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature 537, 369 (2016).
Chen, C. K. et al. **st recruits the X chromosome to the nuclear lamina to enable chromosome-wide silencing. Science 354, 468–472 (2016).
Hasegawa, Y. et al. The matrix protein hnRNP U is required for chromosomal localization of **st RNA. Dev. Cell 19, 469–476 (2010).
Sakaguchi, T. et al. Control of chromosomal localization of **st by hnRNP U family molecules. Dev. Cell 39, 11–12 (2016).
Ridings-Figueroa, R. et al. The nuclear matrix protein CIZ1 facilitates localization of **st RNA to the inactive X-chromosome territory. Genes Dev. 31, 876–888 (2017).
Sunwoo, H., Colognori, D., Froberg, J. E., Jeon, Y. & Lee, J. T. Repeat E anchors **st RNA to the inactive X chromosomal compartment through CDKN1A-interacting protein (CIZ1). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 10654–10659 (2017).
Kolpa, H. J., Fackelmayer, F. O. & Lawrence, J. B. SAF-A requirement in anchoring XIST RNA to chromatin varies in transformed and primary cells. Dev. Cell 39, 9–10 (2016).
Hendrickson, D. G., Kelley, D. R., Tenen, D., Bernstein, B. & Rinn, J. L. Widespread RNA binding by chromatin-associated proteins. Genome Biol. 17, 28 (2016).
Van Nostrand, E. L. et al. Robust transcriptome-wide discovery of RNA-binding protein binding sites with enhanced CLIP (eCLIP). Nat. Methods 13, 508–514 (2016).
Fang, J. et al. Functional classification of noncoding RNAs associated with distinct histone modifications by PIRCh-seq. Genome Biol. 20, 292 (2019).
Minkovsky, A. et al. A high-throughput screen of inactive X chromosome reactivation identifies the enhancement of DNA demethylation by 5-aza-2’-dC upon inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase. Epigenetics Chromatin 8, 42 (2015).
Lee, H. J. et al. En bloc and segmental deletions of human XIST reveal X chromosome inactivation-involving RNA elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, 3875–3887 (2019).
Wutz, A., Rasmussen, T. P. & Jaenisch, R. Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of **st RNA. Nat. Genet. 30, 167–174 (2002).
Royce-Tolland, M. E. et al. The A-repeat links ASF/SF2-dependent **st RNA processing with random choice during X inactivation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 948–954 (2010).
Bousard, A. et al. The role of **st-mediated Polycomb recruitment in the initiation of X-chromosome inactivation. EMBO Rep. 20, e48019 (2019).
Caparros, M. L., Alexiou, M., Webster, Z. & Brockdorff, N. Functional analysis of the highly conserved exon IV of XIST RNA. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 99, 99–105 (2002).
Dominguez, D. et al. Sequence, structure, and context preferences of human RNA binding proteins. Mol. Cell 70, 854.e9–867.e9 (2018).
Van Nostrand, E. L. et al. A large-scale binding and functional map of human RNA binding proteins. Nature 583, 711–719 (2020).
Elisaphenko, E. A. et al. A dual origin of the **st gene from a protein-coding gene and a set of transposable elements. PLoS ONE 3, e2521 (2008).
Linder, B. et al. Single-nucleotide-resolution map** of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat. Methods 12, 767–772 (2015).
Sarma, K., Levasseur, P., Aristarkhov, A. & Lee, J. T. Locked nucleic acids (LNAs) reveal sequence requirements and kinetics of **st RNA localization to the X chromosome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 22196–22201 (2010).
Heather, C. et al. The role of the **st 5’ m6A region and RBM15 in X chromosome inactivation [version 1; peer review: 1 approved, 2 approved with reservations]. Wellcome Open Res. 5, 31 (2020).
Spitale, R. C. et al. Structural imprints in vivo decode RNA regulatory mechanisms. Nature 519, 486–490 (2015).
Helwak, A., Kudla, G., Dudnakova, T. & Tollervey, D. Map** the human miRNA interactome by CLASH reveals frequent noncanonical binding. Cell 153, 654–665 (2013).
Grosswendt, S. et al. Unambiguous identification of miRNA:target site interactions by different types of ligation reactions. Mol. Cell 54, 1042–1054 (2014).
Lu, Z. & Chang, H. Y. The RNA base-pairing problem and base-pairing solutions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 10, a034926 (2018).
Liu, F., Somarowthu, S. & Pyle, A. M. Visualizing the secondary and tertiary architectural domains of lncRNA RepA. Nat. Chem. Biol. 13, 282–289 (2017).
Metkar, M. et al. Higher-order organization principles of pre-translational mRNPs. Mol. Cell 72, 715.e3–726.e3 (2018).
Duszczyk, M. M., Wutz, A., Rybin, V. & Sattler, M. The **st RNA A-repeat comprises a novel AUCG tetraloop fold and a platform for multimerization. RNA 17, 1973–1982 (2011).
Maenner, S. et al. 2-D structure of the A region of **st RNA and its implication for PRC2 association. PLoS Biol. 8, e1000276 (2010).
Rivas, E., Clements, J. & Eddy, S. R. A statistical test for conserved RNA structure shows lack of evidence for structure in lncRNAs. Nat. Methods 14, 45–48 (2017).
Engreitz, J. M. et al. The **st lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome architecture to spread across the X chromosome. Science 341, 1237973 (2013).
Zarnegar, B. J. et al. irCLIP platform for efficient characterization of protein-RNA interactions. Nat. Methods 13, 489–492 (2016).
Dobin, A. et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29, 15–21, (2013).
Li, H. et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25, 2078–2079 (2009).
Quinlan, A. R. & Hall, I. M. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26, 841–842 (2010).
Antanaviciute, A. et al. m6aViewer: software for the detection, analysis, and visualization of N(6)-methyladenosine peaks from m(6)A-seq/ME-RIP sequencing data. RNA 23, 1493–1501 (2017).
Robinson, J. T. et al. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 24–26 (2011).
Lorenz, R. et al. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 6, 26 (2011).
Fujita, P. A. et al. The UCSC Genome Browser database: update 2011. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, D876–882 (2011).
Bolger, A. M., Lohse, M. & Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30, 2114–2120 (2014).
Saldanha, A. J. Java Treeview-extensible visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics 20, 3246–3248 (2004).
Andrews, S. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (2010).
Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 573–580 (1999).
de Hoon, M. J., Imoto, S., Nolan, J. & Miyano, S. Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics 20, 1453–1454 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank CK Chen and M Guttman for help with LBR and SPEN CLIP. This work was supported by NIH R01-HG004361 and RM1-HG007735 (to H.Y.C.) and King Abdulaziz University (to H.C., H.Y.C.). Z.L. was a Layton Family Fellow of the Damon Runyon-Sohn Foundation Pediatric Cancer Fellowship Award (DRSG-14-15) and supported by Stanford Jump Start Award of Excellence in Postdoctoral Research and the Pathway to Independence Award from NHGRI (1R00HG009662). We also acknowledge the USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center (P30CA014089) for their support of our research. H.Y.C. is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. and H.Y.C.; methodology, Z.L., J.K.G., F.L., and Q.M.; investigation, Z.L., J.K.G., D.R.D., B.Z., F.L., H.C., Q.M., R.L., and P.A.K.; data analysis: Z.L., Y.W., Y.Z., and F.L.; writing, Z.L. and H.Y.C.; funding acquisition, Z.L. and H.Y.C.; resources, Z.L., H.Y.C., H.C., and P.A.K. supervision, Z.L. and H.Y.C.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
H.Y.C. is affiliated with Accent Therapeutics, Boundless Bio, 10x Genomics, Arsenal Biosciences, and Spring Discovery. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks Sven Diederichs and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Z., Guo, J.K., Wei, Y. et al. Structural modularity of the XIST ribonucleoprotein complex. Nat Commun 11, 6163 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20040-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20040-3
- Springer Nature Limited