Abstract
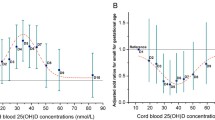
The concentration of micronutrients impacts fetal development and pregnancy outcome and has been suggested to be negatively correlated with the body-mass index (BMI). We evaluated the relationship between BMI and the serum folate concentration in 802 and 660 Korean pregnant women in mid- and late pregnancy, respectively, who participated in a multicenter prospective study. There was a significant negative correlation between BMI value and the serum folate concentration at mid- and late pregnancy (P for trend 0.001 and 0.024, respectively). A general linear model confirmed this correlation at both time points after adjusting for gestational age and total folate intake. These findings are important as the serum folate concentration is a rate-limiting factor for placental folate transport to the fetus, and an inadequate folate supply may cause various malformations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldenberg RL, Tamura T, Neggers Y, Copper RL, Johnston KE, DuBard MB et al. (1995). The effect of zinc supplementation on pregnancy outcome. JAMA 274, 463–468.
Kant AK (2003). Interaction of body mass index and attempt to lose weight in a national sample of US adults: association with reported food and nutrient intake, and biomarkers. Eur J Clin Nutr 57, 249–259.
Kim H, Hwang JY, Ha EH, Park H, Ha M, Lee SJ et al. (2011). Association of maternal folate nutrition and serum C-reactive protein concentrations with gestational age at delivery. Eur J Clin Nutr 65, 350–356.
Lawrence JM, Watkins ML, Chiu V, Erickson JD, Petitti DB. (2006). Do racial and ethnic differences in serum folate values exist after food fortification with folic acid? Am J Obstet Gynecol 194, 520–526.
Li Y, Wang C, Zhu K, Feng RN, Sun CH (2010). Effects of multivitamin and mineral supplementation on adiposity, energy expenditure and lipid profiles in obese Chinese women. Int J Obes 34, 1070–1077.
Mills JL, Troendle J, Conley MR, Carter T, Druschel CM (2010). Maternal obesity and congenital heart defects: a population-based study. Am J Clin Nutr 91, 1543–1549.
Rasmussen SA, Chu SY, Kim SY, Schmid CH, Lau J (2008). Maternal obesity and risk of neural tube defects: a metaanalysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198, 611–619.
Tamura T, Goldenberg RL, Johnston KE, Chapman VR (2004). Relationship between pre-pregnancy BMI and plasma zinc concentrations in early pregnancy. Br J Nutr 91, 773–777.
Tamura T, Picciano MF (2006). Folate and human reproduction. Am J Clin Nutr 83, 993–1016.
Werler MM, Louik C, Shapiro S, Mitchell AA (1996). Prepregnant weight in relation to risk of neural tube defects. JAMA 275, 1089–1092.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Mothers and Children's Environmental Health (MOCEH) Project of the Ministry of Environment, and the 2nd stage of Brain Korea 21 project, Republic of Korea. The visiting research professorship (Tsunenobu Tamura) was supported by the Korea Research Foundation and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies Grant funded by the Korea Government (MOEHRD, Basic Research Promotion Fund; 091S-4-3-0222).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Contributors: TT and NC designed the research; HK, E-HH, HP, MH, K-YL, and Y-CH conducted the research; HK analyzed the data; HK, J-YH, K-NK, TT and NC wrote the manuscript; and NC was primarily responsible for the final content. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Hwang, JY., Kim, KN. et al. Relationship between body-mass index and serum folate concentrations in pregnant women. Eur J Clin Nutr 66, 136–138 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2011.160
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2011.160
- Springer Nature Limited