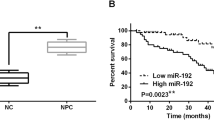
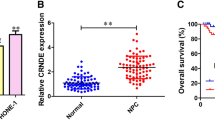
Abstract
Abnormal interaction between non-coding RNAs has been demonstrated to be a common molecular event in various human cancers, but its significance and underlying mechanisms have not been well documented. RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are key regulators of RNA transcription and post-transcriptional processing. In this study, we found that RNA-binding protein 24 (RBM24) was frequently downregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). The restoration of RBM24 expression suppressed NPC cellular proliferation, migration and invasion and impeded metastatic colonization in mouse models. Microarray analyses revealed that miR-25 expression was upregulated by RBM24 expression in NPC cells. Similarly, ectopic miR-25 expression suppressed NPC cellular growth and motility by targeting the pro-oncogenic lncRNA MALAT1, and the knockdown of MALAT1 expression exhibited similar effects as RBM24 restoration in NPC cells. Overall, these findings suggest a novel role of RBM24 as a tumor suppressor. Mechanistically, RBM24 acts at least in part through upregulating the expression of miR-25, which in turn targets MALAT1 for degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a highly malignant cancer that often invades adjacent regions and metastasizes to regional lymph nodes and distant organs. Although early-stage NPC is highly radiocurable, the treatment results of locoregionally advanced NPC have been disappointing.1, 2 Therefore, elucidation of the molecular mechanisms underlying the tumorigenicity, invasion and metastasis of NPC is very important for the treatment of this disease.
Recently, comprehensive microarray analysis has revealed a microRNA (miRNA) signature that is significantly associated with the prognosis and progression of NPC.3, 4, 5 Among the numerous differentially expressed miRNAs in NPC, three miRNAs, including miR-29c, miR-9 and miR-26a, have been shown to be significantly downregulated and have been extensively studied in association with this disease.5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 Accumulating evidence indicates that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are frequently deregulated in the malignant transformation and progression of various types of cancer, including NPC.13, 14, 15, 16, 53, 54 Briefly, 2.5 μg total RNA was labeled with pCp-DY647 (Dharmacon, Lafayette, CO, USA). After hybridization, the arrays were scanned with a LuxScan 10 K Microarray Scanner (CapitalBio, Bei**g, China), and the resulting images were analyzed with GenePix Pro 6.0 software (Axon Instruments, Foster City, CA, USA).
In vivo experiments
Female 4- to 5-week-old athymic mice were purchased (BALB/c nu/nu; Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center, Guangzhou, China) and were maintained under a specific pathogen-free environment. All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. For the tumor xenograft experiments, tumor cells (5 × 104 or 1 × 106 cells/tumor in 100 μl of serum-free culture medium) were suspended in 200 μl RPMI 1640 complete culture medium with 25% Matrigel (BD Biosciences, Bedford, MA, USA) and inoculated subcutaneously into the right flanks of the nude mice. The mice were monitored daily for palpable tumor formation, and tumors were measured using a Vernier caliper, weighed and photographed. Tumor width (W) and length (L) were measured every 2 days. RBM24 expression was repressed by the addition of doxycycline (1 g/l) to the drinking water until the mice were killed at 3 (5 × 104 cells/tumor, n=16) or 9 weeks (1 × 106 cells/tumor, n=22) after inoculation. Then, the tumors were isolated and weighed. Tumor volumes were calculated using the formula V=1/2 (L × W2).
Accession numbers
The Gene Expression Omnibus database accession number for the miRNA array data reported in this paper is GSE66878.
Statistical analysis
All in vitro experiments were repeated at least three times unless stated otherwise. Differences among the groups and treatments were determined by Student’s t-test unless stated otherwise. Kaplan–Meier survival analyses were performed to compare the survival times between the RBM24-induced and non-induced mice, and the log-rank test was used to generate P-values. The differences were considered significant at a P<0.05.
Accession codes
Abbreviations
- RBPs:
-
RNA-binding proteins
- RBM24:
-
RNA-binding protein 24
- RRM:
-
RNA recognition motif
- Dox:
-
Doxycycline
- WT:
-
Wild type
- Ago2:
-
Argonaute2
- lncRNAs:
-
long noncoding RNAs
- MALAT1:
-
metastasis associated in lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1
- NPC:
-
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
References
Hong RL, Ting LL, Ko JY, Hsu MM, Sheen TS, Lou PJ et al. Induction chemotherapy with mitomycin, epirubicin, cisplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin followed by radiotherapy in the treatment of locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 4305–4313.
Lin JC, Jan JS, Hsu CY, Liang WM, Jiang RS, Wang WY . Phase III study of concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: positive effect on overall and progression-free survival. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 631–637.
Liu N, Chen NY, Cui RX, Li WF, Li Y, Wei RR et al. Prognostic value of a microRNA signature in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol 2012; 13: 633–641.
Wang LJ, Chou YF, Chen PR, Su B, Hsu YC, Chang CH et al. Differential miRNA expression in repeated recurrence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett 2014; 344: 188–194.
Sengupta S, den Boon JA, Chen IH, Newton MA, Stanhope SA, Cheng YJ et al. MicroRNA 29c is down-regulated in nasopharyngeal carcinomas, up-regulating mRNAs encoding extracellular matrix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 5874–5878.
Zhang JX, Qian D, Wang FW, Liao DZ, Wei JH, Tong ZT et al. MicroRNA-29c enhances the sensitivities of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma to cisplatin-based chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Cancer Lett 2013; 329: 91–98.
Lu J, Xu X, Liu X, Peng Y, Zhang B, Wang L et al. Predictive value of miR-9 as a potential biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis. Br J Cancer 2014; 110: 392–398.
Lu J, Luo H, Liu X, Peng Y, Zhang B, Wang L et al. miR-9 targets CXCR4 and functions as a potential tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2014; 35: 554–563.
Gao F, Zhao ZL, Zhao WT, Fan QR, Wang SC, Li J et al. miR-9 modulates the expression of interferon-regulated genes and MHC class I molecules in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 431: 610–616.
Yu L, Lu J, Zhang B, Liu X, Wang L, Li SY et al. miR-26a inhibits invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal cancer by targeting EZH2. Oncol Lett 2013; 5: 1223–1228.
Alajez NM, Shi W, Hui AB, Bruce J, Lenarduzzi M, Ito E et al. Enhancer of Zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is overexpressed in recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma and is regulated by miR-26a, miR-101, and miR-98. Cell Death Dis 2010; 1: e85.
Lu J, He ML, Wang L, Chen Y, Liu X, Dong Q et al. MiR-26a inhibits cell growth and tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through repression of EZH2. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 225–233.
Schmitt AM, Chang HY . Gene regulation: long RNAs wire up cancer growth. Nature 2013; 500: 536–537.
Prensner JR, Chinnaiyan AM . The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov 2011; 1: 391–407.
Mitra SA, Mitra AP, Triche TJ . A central role for long non-coding RNA in cancer. Front Genet 2012; 3: 17.
Yang QQ, Deng YF . Genome-wide analysis of long non-coding RNA in primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma by microarray. Histopathology 2015; 66: 1022–1030.
Gong Z, Zhang S, Zeng Z, Wu H, Yang Q, **ong F et al. LOC401317, a p53-regulated long non-coding RNA, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line HNE2. PLoS One 2014; 9: e110674.
Gao W, Chan JY, Wong TS . Differential expression of long noncoding RNA in primary and recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Biomed Res Int 2014; 2014: 404567.
Nie Y, Liu X, Qu S, Song E, Zou H, Gong C . Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and survival. Cancer Sci 2013; 104: 458–464.
Ren S, Liu Y, Xu W, Sun Y, Lu J, Wang F et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is a new potential therapeutic target for castration resistant prostate cancer. J Urol 2013; 190: 2278–2287.
Fan Y, Shen B, Tan M, Mu X, Qin Y, Zhang F et al. TGF-beta-induced upregulation of malat1 promotes bladder cancer metastasis by associating with suz12. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: 1531–1541.
Zhao Z, Chen C, Liu Y, Wu C . 17beta-Estradiol treatment inhibits breast cell proliferation, migration and invasion by decreasing MALAT-1 RNA level. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014; 445: 388–393.
**e L, Hu Z, Wang X, Li Z . Expression of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 gene in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines and its biological significance. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2013; 33: 692–697.
Gutschner T, Hammerle M, Diederichs S . MALAT1 – a paradigm for long noncoding RNA function in cancer. J Mol Med (Berl) 2013; 91: 791–801.
Terami H, Hidaka K, Shirai M, Narumiya H, Kuroyanagi T, Arai Y et al. Efficient capture of cardiogenesis-associated genes expressed in ES cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007; 355: 47–53.
** D, Hidaka K, Shirai M, Morisaki T . RNA-binding motif protein 24 regulates myogenin expression and promotes myogenic differentiation. Genes Cells 2010; 15: 1158–1167.
Poon KL, Tan KT, Wei YY, Ng CP, Colman A, Korzh V et al. RNA-binding protein RBM24 is required for sarcomere assembly and heart contractility. Cardiovasc Res 2012; 94: 418–427.
Grifone R, **e X, Bourgeois A, Saquet A, Duprez D, Shi DL . The RNA-binding protein Rbm24 is transiently expressed in myoblasts and is required for myogenic differentiation during vertebrate development. Mech Dev 2014; 134: 1–15.
Yang J, Hung LH, Licht T, Kostin S, Looso M, Khrameeva E et al. RBM24 is a major regulator of muscle-specific alternative splicing. Dev Cell 2014; 31: 87–99.
Jiang Y, Zhang M, Qian Y, Xu E, Zhang J, Chen X . Rbm24, an RNA-binding protein and a target of p53, regulates p21 expression via mRNA stability. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 3164–3175.
Xu E, Zhang J, Zhang M, Jiang Y, Cho SJ, Chen X . RNA-binding protein RBM24 regulates p63 expression via mRNA stability. Mol Cancer Res 2014; 12: 359–369.
Yuan L, Liu ZH, Lin ZR, Xu LH, Zhong Q, Zeng MS . Recurrent FGFR3-TACC3 fusion gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 2014; 15: 1613–1621.
van Kouwenhove M, Kedde M, Agami R . MicroRNA regulation by RNA-binding proteins and its implications for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2011; 11: 644–656.
Liu B, Sun L, Liu Q, Gong C, Yao Y, Lv X et al. A cytoplasmic NF-kappaB interacting long noncoding RNA blocks IkappaB phosphorylation and suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell 2015; 27: 370–381.
Moore MJ, Proudfoot NJ . Pre-mRNA processing reaches back to transcription and ahead to translation. Cell 2009; 136: 688–700.
Glisovic T, Bachorik JL, Yong J, Dreyfuss G . RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene regulation. FEBS Lett 2008; 582: 1977–1986.
Keene JD . RNA regulons: coordination of post-transcriptional events. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 533–543.
Sharp PA . The centrality of RNA. Cell 2009; 136: 577–580.
Licatalosi DD, Darnell RB . RNA processing and its regulation: global insights into biological networks. Nat Rev Genet 11: 75–87.
Ciafre SA, Galardi S . microRNAs and RNA-binding proteins: a complex network of interactions and reciprocal regulations in cancer. RNA Biol 2013; 10: 935–942.
Kan T, Sato F, Ito T, Matsumura N, David S, Cheng Y et al. The miR-106b-25 polycistron, activated by genomic amplification, functions as an oncogene by suppressing p21 and Bim. Gastroenterology 2009; 136: 1689–1700.
Li BS, Zuo QF, Zhao YL, **ao B, Zhuang Y, Mao XH et al. MicroRNA-25 promotes gastric cancer migration, invasion and proliferation by directly targeting transducer of ERBB2, 1 and correlates with poor survival. Oncogene 2015; 34: 2556–2565.
Xu FX, Su YL, Zhang H, Kong JY, Yu H, Qian BY . Prognostic implications for high expression of MiR-25 in lung adenocarcinomas of female non-smokers. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014; 15: 1197–1203.
Su ZX, Zhao J, Rong ZH, Geng WM, Wu YG, Qin CK . Upregulation of microRNA-25 associates with prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol 2014; 9: 47.
Wang X, Meng X, Li H, Liu W, Shen S, Gao Z . MicroRNA-25 expression level is an independent prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 2014; 16: 954–958.
Li Q, Zou C, Zou C, Han Z, **ao H, Wei H et al. MicroRNA-25 functions as a potential tumor suppressor in colon cancer by targeting Smad7. Cancer Lett 2013; 335: 168–174.
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH . starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42: D92–D97.
Liu J, Carmell MA, Rivas FV, Marsden CG, Thomson JM, Song JJ et al. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science 2004; 305: 1437–1441.
Leucci E, Patella F, Waage J, Holmstrom K, Lindow M, Porse B et al. microRNA-9 targets the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 for degradation in the nucleus. Sci Rep 2013; 3: 2535.
Wang X, Li M, Wang Z, Han S, Tang X, Ge Y et al. Silencing of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 by miR-101 and miR-217 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 2015; 290: 3925–3935.
Song LB, Zeng MS, Liao WT, Zhang L, Mo HY, Liu WL et al. Bmi-1 is a novel molecular marker of nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and immortalizes primary human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 6225–6232.
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, Feng Y, Yu CP, Hu LJ et al. The polycomb group protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 3626–3636.
Wang HY, Luo M, Tereshchenko IV, Frikker DM, Cui X, Li JY et al. A genoty** system capable of simultaneously analyzing >1000 single nucleotide polymorphisms in a haploid genome. Genome Res 2005; 15: 276–283.
Wang H, Ach RA, Curry B . Direct and sensitive miRNA profiling from low-input total RNA. Rna 2007; 13: 151–159.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2012CB967003 and 2015AA020931) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91440106, 81230045 and 81202137).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by G Calin
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Disease website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Cell Death and Disease is an open-access journal published by Nature Publishing Group. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, WF., Zhong, Q., **a, TL. et al. RBM24 suppresses cancer progression by upregulating miR-25 to target MALAT1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 7, e2352 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.252
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.252
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Systematic analysis of the function and prognostic value of RNA binding protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology (2022)
-
RBM24 exacerbates bladder cancer progression by forming a Runx1t1/TCF4/miR-625-5p feedback loop
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
The molecular march of primary and recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Oncogene (2021)
-
Blocking long noncoding RNA MALAT1 restrained the development of laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinoma
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology (2020)
-
Long non-coding RNA implicated in the invasion and metastasis of head and neck cancer: possible function and mechanisms
Molecular Cancer (2018)