Abstract
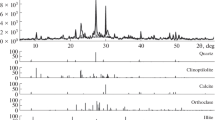
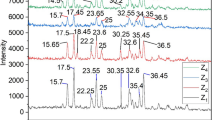
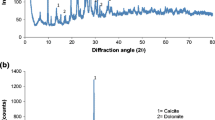
Research works on the removal of mercury from water by zeolitic mineralshow that small quantities of this element are sorbed. In this work the mercury sorption from aqueous solutions in the presence and absence of Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) onto a Mexican zeolitic mineral unmodified and modified with cysteamine hydrochloride or cystamine dihydrochloride was investigated in acidic pH. The zeolitic minerals were characterized by thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction and FTIR. The sorption kinetics behavior and the retention isotherms for mercury were determined in the natural and treated zeolitic mineral samples. It was found that the amounts of sulfur on the modified zeolitic minerals were 0.375 (cysteamine hydrochloride) and 0.475 (cystamine dihydrochloride) mmol g-1, which were not saturated to their total capacities of adsorption for the maximum concentration used (0.310 mM). Under the experimental conditions, the retention of mercury was the highest for the zeolitic minerals treated with the organic compounds, with adsorption capacities ranging from 0.0107 to 0.0509 mmol Hg g-1.The retention was not affected by the presence of others heavy metals studied in this work as expected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanchard, G., Maunaye, M. and Martin, G.: 1984, ‘Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites’, Water Res. 18, 1501-1507.
Bowman, R. S., Li, Z., Roy, S. J., Burt, T., Johnson, T. L. and Johnson, R. L.: 2001, in Smith and Burns (eds), Physicochemical Groundwater Remediation, Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, Chapter 8.
Breck, W.: 1974, Zeolite Molecular Sieves, Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Celis, R., Hermosin, M. C. and Cornejo, J.: 2000, ‘Heavy metal adsorption by functionalized clays’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 4593-4599.
Chiarle, S., Ratto, M. and Rovatti, M.: 2000, ‘Mercury removal from water by ion exchange resins adsorption’, Water Res. 34, 2971-2978.
Curkovic, L., Cerjan-Stefanovic, S. and Filipan, T.: 1997, ‘Metal ion exchange by natural and modified zeolites’, Water Res. 31, 1379-1382.
Flanigen, E. M. and Khatami H.: 1971, Molecular Sieve Zeolites, American Chemical Society, 1, Washington.
Haile, T., Olguín, M. T. and Solache-Ríos, M.: 2001, ‘—Zeolita Natural Mexicana para la Remoción de Mercurio del Agua’ Memorias del 2º Congreso Mexicano de Zeolitas Naturales, Ed. UAM-Azcapozalco, pp. 153-156.
Huheey, J. E.: 1978, Inorganic Chemistry: Principles and Structures of Reactivity, Happer & Row.
Khalid, N., Ahmad, S., Naseer, S. K and Ahmed, J.: 1999, ‘Removal of mercury from aqueous solutions by adsorption to rice husks’, Separat. Sci. Technol. 34, 3139-3153.
Lagadic, I. L., Mitchell, M. K. and Payne, B. D.: 2001, ‘Highly effective adsorption of heavy metal ions by a thiol-functionalized magnesium phyllosilicate clay’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 984- 990.
Li, Z. and Bowman, R. S.: 1997, ‘Counterion effects on the sorption of cationic surfactant and chromate on natural clinoptilolite’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 2407-2412.
Mercier, L. and Pinnavaia, T. J.: 1998, ‘Heavy metal ion adsorbents formed by grafting of a thiol functionality to mesoporous silica molecular sieves: Factor affecting Hg(II) uptake’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 2749-1754.
Mumpton, F. A. and Ormsby, W. C.: 1976, ‘Morphology of zeolites in sedimentary rocks by scanning electron microscopy’, Clay and Clay Minerals 24, 1-23.
Nooney, R. I., Kalyanaraman, M., Kennedy, G. and Maginn, E. J.: 2001, ‘Heavy metal remediation using functionalized mesoporous silicas with controlled macrostructure’, Langmuir 17, 528-533.
Olguín, M. T., Solache, M., Asomoza, M., Acosta, D., Bosch, P. and Bulbulian, S.: 1994, ‘UO 2+2 sorption in natural Mexican erionite and Y zeolite’, Separat. Sci. Technol. 29, 2161-2178.
Olguín, M. T., García-Sosa, I. and Solache-Ríos M.: 1996, ‘Sorption of strontium by Mexican erionite’, J. Radioanalyt. Nucl. Chem. Articles 204, 415-422.
Pabalan, R. T. and Bertetti, F. P.: 2001, in D. L. Bish and D. W. Ming (eds), Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, Mineralogical Society of America, Chapter 14.
Pavon-Silva, T. B., Campos, E. and Olguín, M. T.: 2000, ‘—Remoción de níquel, cadmio y zinc del agua, utilizando clinoptilolita heulandita’, Ciencia Ergo Sum 7, 251-258.
Puigdomenech, I.: Program MEDUSA (Make Equilibrium Diagrams Using Sophisticated Algorithms), http://www.inorg.Kth.se/Ignasi/Index.html.
Ritchie, S. M. C., Kissick, K. E., Bachas, L. G., Sikdar, S. K., Parikh, C. and Bhattacharyya, D.: 2001, ‘Polycysteine and other polyamino acid functionalized microfiltration membranes for heavy metal capture’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 3252-3258.
Rivera-Garza, M., Olguín, M. T., García-Sosa, I., Alcántara, D. and Rodríguez-Fuente: 2000, ‘Silver supported on natural Mexican zeolite as an antibacterial material’, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 39, 431-444.
Roque-Malherbe R.: 2001, in H. S. Nalwa (ed.), Handbook of Surfaces and Interfaces of Materials, Academic Press, Chapter 12, pp. 495-522.
Shubha, K. P., Raji, C. and Anirudhan, T. S.: 2001, ‘Immobilization of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using polyacrylamide grafted hydrous Tin(IV) oxide gel having carboxylate functional groups’, Water Res. 35, 300-310.
Sullivan, E. J., Hunter, D. B. and Bowman, R. S.: 1997, ‘Topological and thermal properties of surfactant-modified clinoptilolite studied by tap**-mode atomic force microscopy and highresolution thermogravimetric analysis’, Clays and Clay Minerals 45, 42-53.
Tiwari, D. P., Sing., D. K. and Saksena, D. N.: 1995, ‘Hg(II) adsorption from aqueous solutions using rice-husk ash’, J. Environ. Engineer. 121, 479-481.
Tsitsivilli, G. V., Andronikashvili, T. G., Kirov, G.N., Felizova, L. D.: 1992, Natural Zeolites, Ellis Horwood, U.K.
Zamzow, M. J., Eichbaum, B. R., Sandgren, K. R. and Shanks, D. E.: 1990, ‘Removal of heavy metals and other cations from wastewater using zeolites’, Separat. Sci. Technol. 25, 1555-1569.
Zamzow, M. J. and Murphy, J. E.: 1992, ‘Removal of metal cations from water using zeolites’, Separat. Sci. Technol. 27, 1967-1984.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gebremedhin-Haile, T., Olguín, M.T. & Solache-Ríos, M. Removal of Mercury Ions from Mixed Aqueous Metal Solutions by Natural and Modified Zeolitic Minerals. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 148, 179–200 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025474001939
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025474001939