Abstract
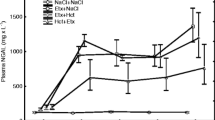
This work studied the effects of hydrocortisone treatment in experimental acute pancreatitis on cytokines, phospholipase A2, and breakdown products of arachidonic acid and survival. Edematous and necrotizing pancreatitis were induced in Wistar rats by cerulein hyperstimulation and retrograde intraductal infusion of sodium taurocholate, respectively. Hydrocortisone (10 mg/kg) was administered intravenously 10 minutes after induction of acute pancreatitis. Serum was assayed for phospholipase A2; interleukin (IL) 1β, IL-6, IL-10, thromboxane B2; Prostaglandin E2; and leukotriene B4 at five different time points. A significant release of inflammatory mediators was seen only in the severe model. Hydrocortisone powerfully suppressed arachidonic acid breakdown products and only mildly attenuated the systemic increase of phospholipase A2 and pro- and antiinflammatory cytokines. The mortality rate after 72 hr in the severe model was 86%. Hydrocortisone treatment reduced mortality to 13% (P = 0.001; Fisher's exact test). Hydrocortisone seems to be effective in the treatment of the early systemic inflammatory response syndrome associated with severe acute pancreatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Uhl W, Isenmann R, Curti G, Vogel R, Beger HG, Buchler MW: Influence of etiology on the course and outcome of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 13:335–343, 1996
British Society of Gastroenterology: United Kingdom guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Gut 42:S1–S13, 1998
Norman JG, Fink GW, Denham W, Yang J, Carter G, Sexton C, Falkner J, Gower WR, Franz MG: Tissue-specific cytokine production during experimental acute pancreatitis. A probable mechanism for distant organ dysfunction. Dig Dis Sci 42:1783–1788, 1997
Norman JG: New approaches to acute pancreatitis: Role of inflammatory mediators. Digestion 60:57–60, 1999
Gloor B, Reber HA: Effects of cytokines, and other inflammatory mediators on human acute pancreatitis. J Intens Care Med 13:305–312, 1998
Osman MO, Jensen SL. Acute pancreatitis: The pathophysiological role of cytokines and integrins. Dig Surg 16:347–362, 1999
Norman J, Franz M, Fink G, Messina J, Fabri P, Gower W, Carey L: Decreased mortality of severe acute pancreatitis after proximal cytokine blockade. Ann Surg 221:625–631, 1995
Gloor B. Todd KE, Lane JS, Lewis MPN, Reber HA: Hepatic Kupffer cell blockade reduces mortality in acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis in mice. J Gastrointest Surg 2:430–435, 1998
Leser HG, Gross V, Scheibenbogen C, Heinisch A, Salm R, Lausen M, Ruckauer K, Andreesen R, Farthmann EH, Scholmerich J: Elevation of serum interleukin-6 concentration precedes acute-phase response and reflects severity in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 101:782–785, 1991
Heath DI, Cruickshank A, Gudgeon M, Jehanli A, Shenkin A, Imrie CW: Role of interleukin-6 in mediating the acute phase protein response and potential as an early means of severity assessment in acute pancreatitis. Gut 34:41–45, 1993
Gross V, Andreesen R, Leser H, Ceska M, Liehl E, Lausen M. Farthmann E, Schoelmerich J: Interleukin-8 and neutrophil activation in acute pancreatitis. Eur J Clin Invest 22:200–203, 1992
Gloor B, Todd KE, Lane JS, Rigberg DA, Reber HA: Mechanism of increased lung injury after acute pancreatitis in IL-10 knockout mice. J Surg Res 80:110–114, 1998
Hughes CB, Gaber LW, Kotb M, Mohey el-Din AB, Pabst M, Gaber AO: Induction of acute pancreatitis in germ-free rats: Evidence of a primary role for tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Surgery 117:201–205, 1995
Buchler M, Malfertheiner P, Schadlich H, Nevalainen TJ, Friess H, Beger HG: Role of phospholipase A2 in human acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 97:1521–1526, 1989
Uhl W, Schrag HJ, Schmitter N, Aufenanger J, Nevalainen TJ, Buchler MW: Experimental study of a novel phospholipase A2 inhibitor in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg 85:618–623, 1998
Uhl W, Schrag HJ, Schmitter N, Nevalainen TJ, Aufenanger J, Wheatley AM, Buchler MW: Pathophysiological role of secre-tory type I and II phospholipase A2 in acute pancreatitis: An experimental study in rats. Gut 40:386–392, 1997
Zhou W, Levine BA, Olson MS: Lipid mediator production in acute and chronic pancreatitis in the rat. J Surg Res 56:37–44, 1994
Manabe T, Steer ML: Protective effects of PGE2 on dietinduced acute pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology 78:777–781, 1980
Yamanaka K, Saluja AK, Brown GE, Yamaguchi Y, Hofbauer B, Steer ML: Protective effects of prostaglandin E1 on acute lung injury of caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Am J Physiol 272:G23–G30, 1997
Closa D, Rosello-Catafau J, Martrat A, Hotter G, Bulbena O, Fernandez-Cruz L, Gelpi E: Changes of systemic prostacyclin and thromboxane A2 in sodium taurocholate-and ceruleininduced acute pancreatitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci 38:33–38, 1993
Beutler B, Krochin N, Milsark IW, Luedke C, Cerami A: Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science 232:977–980, 1986
Zanker B, Walz G, Wieder KJ, Strom TB: Evidence that glucocorticosteroids block expression of the human interleukin-6 gene by accessory cells. Transplantation 49:183–185, 1990
Abe R, Shimosegawa T, Kimura K, Abe T, Kashimura J, Koizumi M, Toyota T: The role of endogenous glucocorticoids in rat experimental models of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 109:933–943, 1995
Kimura K, Shimosegawa T, Sasano H, Abe R, Satoh A, Masamune A, Koizumi M, Nagura H, Toyota T: Endogenous glucocorticoids decrease the acinar cell sensitivity to apoptosis during cerulein pancreatitis in rats. Gastroenterology 114:372–381, 1998
Briegel J, Kellermann W, Forst H, Haller M, Bittl M, Hoffmann GE, Buchler M, Uhl W, Peter K: Low-dose hydrocortisone infusion attenuates the systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Clin Invest 72:782–787, 1994
Aufenanger J, Zimmer W, Kattermann R: Characteristics and clinical application of a radiometric Escherichia coli-based phospholipase A2 assay modified for serum analysis. Clin Chem 39:605–613, 1993
Rongione AJ, Kusske AM, Kwan K, Ashley SW, Reber HA, McFadden DW: Interleukin 10 reduces the severity of acute pancreatitis in rats. Gastroenterology 112:960–967, 1997
Spormann H, Sokolowski A, Letko G: Experimental acute pancreatitis-a quantification of dynamics at enzymic and histomorphologic levels. Pathol Res Pract 185:358–362, 1989
van Ooijen B, Kort WJ, Tinga CJ, Wilson JH: Significance of thromboxane A2 and prostaglandin I2 in acute necrotizing pancreatitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci 35:1078–1084, 1990
van Ooijen B, Ouwendijk RJ, Kort WJ, Zijlstra FJ, Vincent JE, Wilson JH, Westbroek DL: Raised plasma thromboxane B2 levels in experimental acute necrotizing pancreatitis in rats. The effects of flunarizine, dazoxiben, and indomethacin, Scand J Gastroenterol 23:188–92, 1988
Folch E, Prats N, Hotter G, Lopez S, Gelpi E, Rosello-Catafau J, Closa D: P-selectin expression and Kupffer cell activation in rat acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 45:1535–1544, 2000
de Dios I, San Roman JI, Manso M, Calvo JJ, Lopez MA: Glucocorticoids effects on exocrine pancreatic secretion in caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Arch Int Physiol Biochim 98:361–369, 1990
Abe R, Shimosegawa T, Kikuchi Y, Kimura K, Nagasaki Y, Koizumi M, Toyota T: The role of pituitary-adrenal counterregulation of inflammation in cerulein-induced pancreatitis: A comparison between Fischer and Lewis rats. Pancreas 12:280–285, 1996
Norman J: The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Am J Surg 175:76–83, 1998
Osman MO, Jacobsen NO, Kristensen JU, Larsen CG, Jensen SL: Beneficial Effects of Hydrocortisone in a model of experimental acute pancreatitis. Dig Surg 16:214–221, 1999
Tcholakov O, Uhl W, Gloor B, Bischofberger H, Müller CA, Büchler MW: Role of arachidonic acid metabolism and its inhibition by hydrocortisone in experimental acute pancreatitis. Eur Surg Res 31:79–80, 1999
Bone RC, Fisher CJ, Clemmer TP, Slotman GJ, Metz CA, Balk RA: A controlled clinical trial of high-dose methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 317:653–658, 1987
Manso MA, Rebollo A, Pescador R, de Dios I. Action of CCK on CDE diet-induced acute pancreatitis in rats treated with hydrocortisone. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 111:257–263, 1995
Gomez G, Townsend CMJ, Green D, Rajaraman S, Uchida T, Thompson JC: Involvement of cholecystokinin receptors in the adverse effect of glucocorticoids on diet-induced necrotizing pancreatitis. Surgery 106:230–238, 1989
Guice KS, Oldham KT, Remick DG, Kunkel SL, Ward PA: Anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody augments edema formation in caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. J Surg Res 51:495–499, 1991
Lazar G Jr, Varga J, Lazar G, Duda E, Takacs T, Balogh A, Lonovics J: The effects of glucocorticoids and a glucocorticoid antagonist (RU 38486) on experimental acute pancreatitis in rat. Acta Chir Hung 36:190–191, 1997
van den Bosch H, Schalkwijk C, Pfeilschifter J, Märki F: The induction of cellular group II phospholipase A2 by cytokines and its prevention by dexamethasone. Adv Exp Med Biol 318:1–10, 1992
Dinarello CA, Wolff SM: Pathogenesis of fever. In Infectious Diseases. GL Mandell, RG Douglas, JA Bennett (eds). New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1990, pp 462–467
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gloor, B., Uhl, W., Tcholakov, O. et al. Hydrocortisone Treatment of Early SIRS in Acute Experimental Pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 46, 2154–2161 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011902729392
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011902729392