Abstract
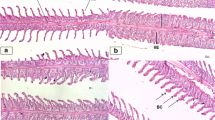
Tilapia rendalli was exposed to various siltconcentrationsfor different exposure periods to determine LC50 andsublethalconcentration ranges. The extent of damaging effects, if any,ofsuspended silt on the exposed fish, were investigated by meansofscanning electron microscopy. The LC50 values rangedbetween21 to 24 g l™1 and 42–48 g l™1 for juveniles andadultsrespectively. The silt concentrations tolerated by the testfisheswere above those found in most natural waters. The resultstherefore support the hypothesis that suspended silt is lethaltofish at concentrations higher than those naturally observed insurface water. The observed mortalities can be attributed tothecombined physical effects of high silt concentrations andassociated reduction in dissolved oxygen levels. To preventfishmortalities and other impacts on biota, anthropogenicactivitiesthat affect the natural variation in suspended siltconcentrationsin surface water should be carefully monitored and, wherepossible,be restricted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alabaster, J. S., 1972. Suspended solids and fisheries. Proc. r. Soc. Lond. 180: 395–406.
Alabaster, J. S. & R. Lloyd, 1980. Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Fish. FAO, United Nations, Butterworths, London, 297 pp.
Anderson, T. F., 1969. Electron microscopy of micro-organisms. In Oster, G. & A. W. Pollister (eds), Physical Techniques in Biological Research. Vol. 3(A), Academic Press, NewYork: 178–237.
Buermann, Y., H. H. Du Preez, G. J. Steyn, J. Harmse & A. Deacon, 1995. Suspended silt concentrations in the lower Olifant River (Mpumalanga) and the impact of silt releases from the Phalaborwa Barrage on water quality and fish survival. Koedoe 38: 11–34.
Bruton, M. N., 1985. The effects of suspensiods on fish. Hydrobiologia 125: 221–241.
Canadian Guidelines, 1987. Canadian water quality guidelines. Report prepared by the Task Force on water quality guidelines of the Canadian Council of Resource and Environment Ministry. Canada: 407 pp.
Chilton, E. W., 1991. System for maintaining sediment suspensions during larval fish studies. Prog. Fish. Cult. 53: 28–33.
Crouse, M. R., C. A. Callahan & K. W. Malueg, 1981. Effects of fine sediment on growth of juvenile Coho salmon in laboratory streams. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 110: 281-186.
Day, J. H., 1981. Estuarine Ecology with particular reference to Southern Africa. A. A. Balkema, Cape Town, 411 pp.
Department of Water Affairs and Forestry (DWA & F), 1993. South African Water Quality Guidelines. Pretoria, RSA. Volumes 1–4.
Ellis, M. M., 1937. Detection and measurement of stream pollution. US Bur. Fish. Bull. 22: 365–437.
European Inland Fisheries Advisory Commission, 1965. Water quality criteria for European freshwater fish. Report on finely divided solids and inland fisheries. E.I.F.A.C. Tech. Paper 1. Air Water Pollut. 91: 151–168.
Goldes, S. A., H. W. Ferguson, R. D. Moccia & P. Y. Daoust, 1988. Histological effects of the inert suspended clay kaolin on the gills of juvenile rainbow trout, Samo gairdneri, Richardson. J. Fish Dis. 11: 23–33.
Herbert, D. W. M., 1980. Finely divided solids. In Alabaster, J. S. & Lloyd (eds), Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Fish. Butterworths, Toronto: 1–20.
Horkel, J. D. & W. D. Pearson, 1976. Effects of turbidity on ventilation rates and oxygen consumption of green sunfish, Lepomis cyanellus. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 1: 107–113.
Muir, B. S., 1969. Gill dimensions as a function of fish size. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 26: 165–170.
O’Connor, J. M., D. A. Neumann & J. A. Sherk (Jr)., 1976. Lethal effects of suspended sediments on estuarine fish. US Army, Corps of Engineers, Coastal Engineering Research Centre. Tech. Paper 76–200: 1–40.
O’Connor, J.M., D. A. Neumann & J. A. Sherk (Jr)., 1977. Sublethal effects of suspended sediments on estuarine fish. US Army, Corps of Engineers, Coastal Engineering Research Centre. Techn Paper No. 77-3.
Ritchie, J. C., 1972. Sediment, fish and fish habitat. J. Soil Water Conserv. 27: 124.
Rogers, B. A., 1969. Tolerance levels of four species of Estuarine fishes to suspended mineral solids. M.Sc. Thesis, Univ. Rhode Island.
Scott, A. L. & W. A. Rogers, 1980. Histological effects prolonged sublethal hypoxia on channel catfish. Ictalurus punctatus. J.Fish. Dis. 3: 305.
Seymore, T., H. H. Du Preez, J. H. J. Van Vuren, A. Deacon & G. Strydom, 1994. Variations in selected water quality variables and metal concentrations in the sediment of the lower Olifants and Selati Rivers, South Africa. Koedoe 37: 1–18.
Sherk, J. A., J. M. O’Conner & D. A. Neumann, 1975. Effects of suspended and deposited sediments on estuarine environments. In Cronin, L. E. (ed.), Estuarine Research, Vol. 2, Academic Press, New York: 541–588.
Stern, E. M. & W. B. Stickel, 1978. Effect of turbidity and suspended material in aquatic environments. US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment station. Tech. Report No. 0-78-21-76-84.
Wilber, C. G., 1983. Turbidity in the aquatic environment. An environmental factor in fresh and oceanic waters. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, 133 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buermann, Y., Du Preez, H.H., Steyn, G.J. et al. Tolerance levels of redbreast tilapia, Tilapia rendalli (Boulenger, 1896) to natural suspended silt. Hydrobiologia 344, 11–18 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002985707694
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002985707694