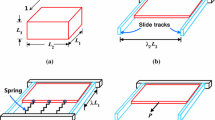
Abstract
The performance of dielectric elastomer (DE) transducers is significantly affected by viscoelastic relaxation-induced electromechanical dissipations. This paper presents an experimental study to obtain the rate dependent stress-stretch relation of DE membranes (VHB™9473) subjected to pure shear like loading and electric loading simultaneously. Stretching rate dependent behavior is observed. The results also show that the tensile force decreases as the voltage increases. The observations are compared with predictions by a viscoelastic model of DE. This experiment may be used for further studies of dynamic electromechanical coupling properties of DEs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirai, T., Nemoto, H., Hirai, M. and Hayashi, S., Electrostriction of highly swollen polymer gel: Possible application for gel actuator. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1994, 53(1): 79–84.
Heydt, R., Kornbluh, R., Pelrine, R. and Mason, V., Design and performance of an electrostrictive-polymer-film acoustic actuator. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1998, 215(2): 297–311.
Pelrine, R.E., Kornbluh, R.D. and Joseph, J.P., Electrostriction of polymer dielectrics with compliant electrodes as a means of actuation. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 1998, 64(1): 77–85.
Zanna, J.J., Nguyen, H.T., Parneix, J.P., Ruffie, G. and Mauzac, M., Dielectric properties of side chain liquid crystalline elastomers: influence of crosslinking on side chain dynamics. The European Physical Journal B—Condensed Matter and Complex Systems, 1999, 10(2): 345–351.
Liang, C., Sun, F.P. and Rogers, C.A., Coupled electro-mechanical analysis of adaptive material systems — determination of the actuator power consumption and system energy transfer. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 1994, 5(1): 12–20.
Pelrine, R., Kornbluh, R., Pei, Q. and Joseph, J., High-speed electrically actuated elastomers with strain greater than 100%. Science, 2000, 287(5454): 836–839.
Pelrine, R., Kornbluh, R., Joseph, J., Heydt, R., Pei, Q. and Chiba, S., High-field deformation of elastomeric dielectrics for actuators. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2000, 11(2): 89–100.
Pelrine, R., Kornbluh, R. and Kofod, G., High-strain actuator materials based on dielectric elastomers. Advanced Materials, 2000, 12(16): 1223–1225.
Wissler, M. and Mazza, E., Electromechanical coupling in dielectric elastomer actuators. Sensors and Actuators a-Physical, 2007, 138: 384–393.
Moscardo, M., Zhao, X., Suo, Z. and Lapusta, Y., On designing dielectric elastomer actuators. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 104(9): 093503.
O’Halloran, A., O’Malley, F. and McHugh, P., A review on dielectric elastomer actuators, technology, applications, and challenges. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 104(7): 071101.
Koh, S.J.A., Zhao, X. and Suo, Z., Maximal energy that can be converted by a dielectric elastomer generator. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(26): 262902.
Brochu, P. and Pei, Q., Advances in dielectric elastomers for actuators and artificial muscles. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2010, 31(1): 10–36.
Koh, S.J.A., Li, T., Zhou, J., Zhao, X., Hong, W., Zhu, J. and Suo, Z., Mechanisms of large actuation strain in dielectric elastomers. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 2011, 49(7): 504–515.
Qiang, J.H., Chen, H.L. and Li, B., Experimental study on the dielectric properties of polyacrylate dielectric elastomer. Smart Materials and Structures, 2012, 21(2): 025006.
Goulbourne, N., Mockensturm, E. and Frecker, M., A nonlinear model for dielectric elastomer membranes. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2005, 72(6): 899–906.
Dorfmann, A. and Ogden, R.W., Nonlinear electroelasticity. Acta Mechanica, 2005, 174(3): 167–183.
Suo, Z., Zhao, X. and Greene, W.H., A nonlinear field theory of deformable dielectrics. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2008, 56(2): 467–486.
Trimarco, C., On the Lagrangian electrostatics of elastic solids. Acta Mechanica, 2009, 204(3): 193–201.
Suo, Z., Theory of dielectric elastomers. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2010, 23(6): 549–578.
Plante, J.S. and Dubowsky, S., Large-scale failure modes of dielectric elastomer actuators. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2006, 43(25–26): 7727–7751.
Foo, C.C., Cai, S., Koh, S.J.A., Bauer, S. and Suo, Z., Model of dissipative dielectric elastomers. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111(3): 034102.
Huang, J., Li, T., Foo, C.C., Zhu, J., Clarke, D.R. and Suo, Z., Giant, voltage-actuated deformation of a dielectric elastomer under dead load. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 100(4): 041911.
Zhao, X.H., Koh, S.J.A. and Suo, Z.G., Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of dielectric elastomers. International Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2011, 3(2): 203–217.
Where do the ‘Pure’ and ‘Shear’ Come From in the Pure Shear Test? In: Fatigue Life Simulation for Rubber. www.endurica.com
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 10832009), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-08-0480), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. Z1110057), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, S., Li, K., Li, T. et al. Rate Dependent Stress-Stretch Relation of Dielectric Elastomers Subjected to Pure Shear Like Loading and Electric Field. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 25, 542–549 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-9166(12)60048-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-9166(12)60048-2