Abstract
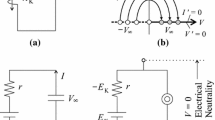
The mechanism of directional propagation of action potential throughout a single cell was examined using a liquid-membrane model cell system. In the experiments on the liquid-membrane model cell system, liquid-membrane cells were constructed to mimic the function of K+ and voltage-gated Na+ channels, which play important roles in action potential propagation. These channel-mimicking cells were connected electrically, and a model cell system was composed of four parts within the one cell. When one voltage-gated Na+ channel-mimicking cell was connected to form the action potential and generated the inflow current at the one part, action potential occurred in the surrounding area due to the local circulating current and propagated to the other parts. The action potential propagation throughout the cell by a brief electrical stimulus (10 ms) was easier than that by a long electrical stimulus (2 s). The long electric stimulus thus caused hyperpolarized region within the cell. Moreover, the increase in resistance corresponding to the extracellular fluid weakened the action potential propagation. In the simulation experiments using the software LTspice, the characteristics of K+ and Na+ channel-mimicking cells were reproduced in the electrical circuit also. A model cell aggregate consisting of closely packed three model cells and the extracellular fluid was constructed in the electric circuit. When one cell fired, the electrical signal propagated to the neighboring cells through the intercellular and extracellular fluids. This result suggests that electrical propagation can occur between independent cells in closely packed tissues without chemical transmission or direct propagation across the gap junctions.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
B. Alberts, A. Johnson, J. Lewis, D. Morgan, M. Raff, K. Robert, P. Walter, Molecular Biology of the Cell, 6th edn. (W. W. Norton & Company, New York, 2014)
B. Alberts, K. Hopkin, A.D. Johnson, D. Morgan, M. Raff, K. Roberts, P. Walter, Essential Cell Biology-An Introduction to the Molecular Biology-, 5th edn. (W. W. Norton & Company, New York, 2018)
W. Lim, B. Mayer, T. Pawson, Cell Signaling-Principles and Mechanisms, Garland Science (Taylor & Francis Group, LLC., New York, 2015)
M.J. Berridge, J. Physiol. 586, 5047 (2008)
R.E. Haddock, C.E. Hill, J. Physiol. 566, 645 (2005)
M.S. Nielsen, L.N. Axelsen, P.L. Sorgen, V. Verma, M. Delmar, N.H. Holstein-Rathlou, Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2 (1981)
S. Rohr, Cardiovasc. Res. 62, 309 (2004)
G.S. Goldberg, V. Valiunas, P.R. Brink, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1662, 96 (2004)
D.A. Goodenough, D.L. Paul, Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 1, a002576 (2009)
C. Mahapatra, K.L. Brain, R. Manchanda, PLoS ONE 13, e0200712 (2018)
P.M. Hopkins, Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 6, 1 (2006)
A.L. Hodgkin, A.F. Huxley, Bull. Math. Biol. 52, 25 (1990)
N. Ueya, O. Shirai, Y. Kushida, S. Tsujimura, K. Kano, J. Electroanal. Chem. 673, 8 (2012)
Y. Kushida, O. Shirai, Y. Kitazumi, K. Kano, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 87, 110 (2014)
Y. Kushida, O. Shirai, Y. Kitazumi, K. Kano, Electroanalysis 2014, 26 (1858)
Y. Kushida, O. Shirai, Y. Takano, Y. Kitazumi, K. Kano, Anal. Sci. 31, 677 (2015)
Y. Takano, O. Shirai, Y. Kitazumi, K. Kano, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 12689 (2016)
Y. Takano, O. Shirai, Y. Kitazumi, K. Kano, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 5310 (2017)
O. Shirai, Y. Kitazumi, K. Kano, Electroanalysis 29, 2656 (2017)
M. Kaji, O. Shirai, Y. Kitazumi, K. Kano, Electrochim. Acta 282, 80 (2018)
M. Kaji, Y. Kitazumi, K. Kano, O. Shirai, Bioelectrochemistry 128, 155 (2019)
M. Kaji, Y. Yamada, Y. Kitazumi, O. Shirai, Electroanalysis 34, 1299 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202100508
I. Kasai, Y. Kitazumi, K. Kano, O. Shirai, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 21288 (2020)
B. Hille, Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes, 3rd edn. (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, 2001)
A. Feigenspan, K. Dedek, K. Schlich, R. Weiler, S. Thanos, Investig. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 51, 1789 (2010)
T. Akaishi, Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 244, 151 (2018)
S.D. Beagle, S.W. Lockless, Nature 527, 44 (2015)
A. Prindle, J. Liu, M. Asally, S. Ly, J. Garcia-Ojalvo, G.M. Süel, Nature 527, 59 (2015)
J. Humphries, L. **ong, J. Liu, A. Prindle, F. Yuan, H.A. Arjes, L. Tsimring, G.M. Süel, Cell 168, 200 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Enago (www. Enago.jp) for English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Morishita, R., Sowa, K., Kitazumi, Y. et al. Directional propagation of action potential within a single cell and intercellular conduction within a cell aggregate using model cell systems. ANAL. SCI. 39, 945–955 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00302-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00302-y