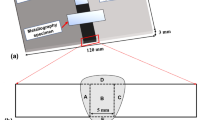
Abstract
Welding experiments were carried out on AISI 316 austenitic stainless steel by vacuum electron beam welding (VEBW) machine at different welding beam currents (IW = 70 mA, 80 mA, 90 mA and 100 mA). Different vacuum electron beam welding beam current on AISI 316 austenitic stainless steel microstructure and mechanical properties were analyzed by optical microscopy (OM), electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) and mechanical stretching machines, combined with digital image correlation (DIC) stretching. The results show that the elongation and tensile strength of AISI 316 austenitic stainless steel increases and then decreases with the increase of IW. The base material (BM) consists of fine austenite grains, while the weld material (WM) is characterized by fine equiaxed austenite grains scattered between elongated columnar austenite grains. No coarse austenite grains are observed in the heat affected zone (HAZ). The proper distribution of narrower HAZ and WM elongated columnar crystals ensures high yield strength (278 MPa), tensile strength (589 MPa) and good plasticity (88% total elongation) of the welded joints. The welded specimens are in ductile fracture mode and the fracture consists of various tough nests in different regions. The increase in elongation is attributed to the weakening of the thin lamellar grain structure and Cube texture {001} < 100 > formed byVEBW, which enhances the deformation coordination of dislocation slippage.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Speidel MO. Nitrogen containing austenitic stainless steels. Materialwiss Werkstofftech. 2006;37:875–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/mawe.200600068.
Cruces AS, Garcia-Gonzalez A, Moreno B, Itoh T, Lopez-Crespo P. Critical plane based method for multiaxial fatigue analysis of 316 stainless steel. Theor Appl Fract Mech. 2022;118: 103273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2022.103273.
Ha HY, Lee TH, Kim SJ. Role of nitrogen in the active–passive transition behavior of binary Fe–Cr alloy system. Electrochim Acta Mater. 2012;80:432–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.07.056.
Berns H. Manufacture and application of high nitrogen steels. ISIJ Int. 1996;36:909–14. https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.36.909.
Simmons JW. Overview: High-nitrogen alloying of stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng A. 1996; 207:159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(95)09991-3.
Katada Y, Sagara M, Kobayashi Y, Kodama T. Fabrication of high strength high nitrogen stainless steel with excellent corrosion resistance and its mechanical properties. Mater Manuf Processes. 2004;19:19–30. https://doi.org/10.1081/AMP-120027495.
Yang K, Ren Y. Nickel-free austenitic stainless steels for medical applications. Adv Mater Technol. 2010;11(1): 014105. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/11/1/014105.
Krichel T, Olschok S, Reisgen U. Comparison of penetration depth in bead-on-plate welds of thick-walled steel sheets with Laser Beam Welding in Vacuum and Electron Beam Welding. Vacuum. 2022;203: 111314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2022.111314.
Woo I, Kikuchi Y. Weldability of high nitrogen stainless steel. ISIJ Int. 2002;42(12):1334–43. https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.42.1334.
Zhang X, Zhou Q, Wang K, Peng P, Ding J, Kong J, Williams S. Study on microstructure and tensile properties of high nitrogen Cr-Mn steel processed by CMT wire and arc additive manufacturing. Mater Des. 2019;166: 107611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.107611.
**a X, Wu J, Liu Z, Shen X, Ma J, Liu Z. Study of microstructure difference properties of electron beam welds with beam oscillation of 50 mm 316L in CFETR. Fusion Eng Des. 2019;138:339–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2018.12.011.
Kar J, Roy SK, Roy GG. Effect of beam oscillation on microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 316L electron beam welds. Metall Mater Trans A. 2017;48:1759–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-3976-2.
Zhao L, Tian Z, Peng Y, Qi Y, Wang Y. Influence of nitrogen and heat input on weld metal of gas tungsten arc welded high nitrogen steel. J Iron Steel Res Int. 2007;14(5):259–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60090-4.
Liu S, Cui B, Bai D, Yan S, Zhang H. Effect of N2 shielding gas flow rate on microstructure and weld surface corrosion resistance of high nitrogen steel by laser-arc hybrid welding. Mater. Res Express.2019;6(8): https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab29b7.
Peng Y, Song L, Zhao L, Ma C, Zhao H, Tian Z. Research Status of Weldability of Advanced Steel. Acta Metall Sin. 2020;56(04):601–618. https://doi.org/10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00369.Elmer,
Jaypuria S, Bondada V, Gupta SK, Pratihar DK, Chakrabarti D, Jha MN. Prediction of electron beam weld quality from weld bead surface using clustering and support vector regression. Expert Syst Appl. 2023;211: 118677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118677.
Elmer JW, Allen SM, Eagar TW. Microstructural development during solidification of stainless steel alloys. Metall Trans A. 1989;20(10):2117–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650298.
Miyano Y, Fujii H, Sun Y, Katada Y, Kuroda S, Kamiya O. Mechanical properties of friction stir butt welds of high nitrogen-containing austenitic stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2011;528(6): 2917–2921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.12.071.
Zhao Y, Sato Y, Kokawa H, Wu A. Microstructure and properties of friction stir welded high strength Fe–36 wt%Ni alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 2011;528(25–26):7768–7773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.06.082.
Alali M, Todd I, Wynne B P. Through-thickness microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded 20 mm thick AISI 316L austenitic stainless steel. Mater Des. 2017;130,:488–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.05.080.
Geng Y, Jiang P, Liu X, Liu Z, **ong J. Microstructure and mechanical property of the 30mm-thickness stainless steel welded joint by the electron beam welding technique. Electric Welding Machine. 2016;46(07):50–54. https://doi.org/10.7512/j.issn.1001-2303.2016.07.12
**a M, Tian Z, Peng Y, Ma C. Nitrogen content in the fusion weldment of high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel. Mater Rep. 2006;02:61–5. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0887-381X(2006)20:1(20).
Yan Z, Wang K. Researching on microstructural properties of HNS Cr22Mn18NiN welded joints. Mech Manuf Auto. 2017;46(05); 45–47.https://doi.org/10.19344/j.cnki.issn1671-5276.2017.05.012
El-Batahgy AM, Miura T, Ueji R, Hidetoshi F. Investigation into feasibility of FSW process for welding 1600MPa quenched and tempered steel. Mater Sci Eng., A. 2016;651:904–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.11.054.
Ran MM, Sun FF, Li GQ, Kanvinde A, Wang YB, **ao RY.Experimental study on the behavior of mismatched butt welded joints of high strength steel. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019;153(FEB.):196–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2018.10.003.
Alali M, Todd I, Wynne BP. Through-thickness microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded 20 mm thick AISI 316L austenitic stainless steel. Mater Des. 2017;130(15):488–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.05.080.
Cao R, Zhu SS, Feng W, Peng Y, Jiang F, Du WS, Tian ZL, Chen JH. Effects of weld metal property and fraction on the toughness of welding joints of a 8 %Ni 980 MPa high strength steel. J Mater Process Technol. 2011;211(4):759–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.12.011.
Bringa EM, Traiviratana S, Meyers MA. Void initiation in fcc metals: Effect of loading orientation and nanocrystalline effects. Acta Mater. 2010;58(13):4458–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.04.043.
Chen JH, Cao R. Chapter 8—Special case studies. Micromechanism of Cleavage Fracture of Metals. 2015;307–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800765-5.00008-3.
Yang L,Sun G, Wang J, Huan L. Study on Laser Welding of A304 Stainless Steel Sheet. Electric welding machine. 2011;41:66–69.https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-2303.2011.01.016
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by the Shanxi Science and Technology Achievement Transformation Guidance Fund (202204021301057), Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (20210302123207 and 20210302124009 ), Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (2021L292), Taiyuan University of Science and Technology Scientific Research Initial Funding (20212026), the Shanxi Outstanding Doctorate Award Funding Fund (20222042), Taiyuan University of Science and Technology Graduate Innovation Project (BY2022004 and SY2022088), Shanxi Province Scientific Research Innovation Project (2023KY651) and the Coordinative Innovation Center of Taiyuan Heavy Machinery Equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants and/or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Huang, F., Li, J. et al. Electron beam welding beam current on microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 316 austenitic stainless steel. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 23, 259 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-023-00802-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-023-00802-8