Abstract
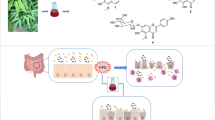
Macleaya cordata (Willd.) R.Br., Papaveraceae, is a traditional Chinese herb, and it has been proven to have good antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antidiarrheal properties. However, its antidiarrheal constituents and mechanism have not been clarified yet and therefore need to be determined. In this paper, the antidiarrheal activity and active fraction of Macleaya cordata ethanol extract were evaluated based on a series of in vivo assays involving castor oil-induced diarrhea, intestinal transit, and enteropooling. The chemical constituents of the antidiarrheal fraction were analyzed by UPLC-ESI–MS, and the binding affinities with the target proteins of the cAMP/cGMP-regulated cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), aquaporin 4 (AQP4), Na+/H+ exchanger 1 (NHE1), Na+/H+ exchanger 3 (NHE3), and Na+/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) were elucidated in an in silico study. Moreover, the screened compound was separated by silica gel chromatography and tested based on the castor oil-induced diarrhea model. In the antidiarrheal investigation, the dichloromethane fraction at 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg inhibited intestinal transit and decreased intraluminal fluid accumulation in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, UPLC-ESI–MS analysis of the chemical composition of the active fraction revealed that 6-methoxydemethylatedsanguinarine, ethoxychelerthrine, 6-methoxyldihydrochelerythrine, dihydrochelerythrine, and dihydrosanguinarine were the main components. Molecular docking results showed the main active components with strong binding affinity for the ion channels. The best binding component, dihydrosanguinarine, exerts its antidiarrheal activity in a dose-dependent manner at 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg. Real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) experiments showed that dihydrosanguinarine could downregulate the expression of the CFTR and upregulate the expression of AQP4, NHE1, NHE3, and SGLT1 to reduce fecal frequencies. Therefore, the most predominant component of Macleaya cordata against diarrhea was dihydrosanguinarine, which exerts an antidiarrheal effect by regulating the activity of ion channels, supporting the traditional use of Macleaya cordata in the treatment of diarrhea.
Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbor GA, Longo F, Makong EA, Tarkang PA (2014) Evaluation of the antidiarrheal and antioxidant properties of Justicia hypocrateriformis. Pharm Biol 52:1128–1133. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2013.879189
Akah PA, Aguwa CN, Agu RU (1999) Studies on the antidiarrhoeal properties of Pentaclethra macrophylla leaf extracts. Phytother Res 13:292–295. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1573(199906)13:4<292::AID-PTR415>3.0.CO;2-N
Bawazeer S, Rauf A, Bawazeer S (2020) Gastrointestinal motility, muscle relaxation, antipyretic and acute toxicity screening of amyrin type triterpenoid (daturaolone) isolated from Datura metel Linnaeus (Angel’s Trumpet) fruits. Front Pharmacol 11:544794. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.544794
Chen J, Li Y, Yu B, Chen D, Mao X, Zheng P, Luo J, He J (2018) Dietary chlorogenic acid improves growth performance of weaned pigs through maintaining antioxidant capacity and intestinal digestion and absorption function. J Anim Sci 96:1108–1118. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skx078
Choudhary MI, Hussain A, Ali Z, Adhikari A, Sattar SA, Ayatollahi SA, Al-Majid AM (2012) Diterpenoids including a novel dimeric conjugate from Salvia leriaefolia. Planta Med 78:269–275. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1280454
Dong SJ, Gao CS, Wang QR, Ge YQ, Cheng RB (2020) Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Macleaya cordata and its phylogenomic position within the subfamily Papaveroideae. Mitochond DNA B 5:1714–1715. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2020.1749172
Duan T, Cil O, Thiagarajah JR, Verkman AS (2019) Intestinal epithelial potassium channels and CFTR chloride channels activated in ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor diarrhea. JCI Insight 4:126444. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.126444
Duke JA, Ayenus ES (1984) Medicinal plants of China. Reference Publications, Inc., Algonac
Gong Y, Hou ZQ, Gao YX, Xue YS, Liu X, Liu GM (2012) Optimization of extraction parameters of bioactive components from defatted marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) residue using response surface methodology. Food Bioprod Process 90:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2010.12.004
Grieve M (1984) A modern herbal. Penguin Books, Middlesex
Hiki K, Asahina K, Kato K, Yamagishi T, Omagari R, Iwasaki Y, Watanabe H (2021) Acute toxicity of a tire rubber-derived chemical, 6PPD quinone, to freshwater fish and crustacean species. Environ Sci Tech Let 8:779–784. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.1c00453
Hou F, Yu Z, Cheng Y, Liu Y, Liang S, Zhang F (2022) Deciphering the pharmacological mechanisms of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi on oral leukoplakia by combining network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental evaluations. Phytomedicine 103:154195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154195
Hunan Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine (1962) Hunan Yao Wu Zhi. Hunan Sci Technol Pubi House, Chnagsha
Iba H, Shimohata T, Kido J, Hatayama S, Uebanso T, Mawatari K, Takahashi A (2021) Vibrio parahaemolyticus induces inflammation-associated fluid accumulation via activation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J Med Invest 68:59–70. https://doi.org/10.2152/jmi.68.59
Kantas D, Papatsiros VG, Tassis PD, Athanasiou L, Tzika VD (2015) The effect of a natural feed additive (Macleaya cordata), containing sanguinarine, on the performance and health status of weaning pigs. Anim Sci J 86:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/asj.12240
Khadem A, Soler L, Everaert N, Niewold TA (2014) Growth promotion in broilers by both oxytetracycline and Macleaya cordata extract is based on their anti-inflammatory properties. Brit J Nutr 112:1110–1118. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114514001871
Kroser JA, Metz DC (1996) Evaluation of the adult patient with diarrhea. Prim Care 23:629–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0095-4543(05)70352-3
Liu G, Guan G, Fang J, Martinez Y, Chen S, Bin P, Duraipandiyan V, Gong T, Tossou MC, Al-Dhabi NA, Yin Y (2016) Macleaya cordata extract decreased diarrhea score and enhanced intestinal barrier function in growing piglets. Biomed Res Int 2016:1069585. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1069585
Moran AW, Al-Rammahi MA, Daly K, Grand E, Ionescu C, Bravo DM, Wall EH, Shirazi-Beechey SP (2020) Consumption of a natural high-intensity sweetener enhances activity and expression of rabbit intestinal Na (+)/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) and improves colibacillosis-induced enteric disorders. J Agr Food Chem 68:441–450. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04995
Qian WD, Yang M, Li XC, Sun ZH, Li YD, Wang XJ, Wang T (2020) Anti-microbial and anti-biofilm activities of combined chelerythrine-sanguinarine and mode of action against candida albicans and cryptococcus neoformans in vitro. Colloid Surface B 191:111003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111003
Qnais EY, Elokda AS, Abu Ghalyun YY, Abdulla FA (2007) Antidiarrheal activity of the aqueous extract of Punica granatum (pomegranate) peels. Pharm Biol 45:715–720. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880200701575304
Robert A, Nezamis JE, Lancaster C, Hanchar AJ, Klepper MS (1976) Enteropooling assay: a test for diarrhea produced by prostaglandins. Prostag Oth Lipid M 11:809–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-6980(76)90189-1
Soler L, Hermes R, Niewold TA (2016) Macleaya cordata extract reduces inflammatory responses of intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Am J Plant Sci 7:1531–1537. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2016.711144
Sullivan S, Alex P, Dassopoulos T, Zachos NC, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Donowitz M, Brant SR, Cuffari C, Harris ML, Datta LW, Conklin LY, Chen YP, Li XH (2009) Downregulation of sodium transporters and NHERF proteins in IBD patients and mouse colitis models: potential contributors to IBD-associated diarrhea. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15:261–274. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.20743
Sunil MA, Sunitha VS, Ashitha A, Neethu S, Midhun SJ, Radhakrishnan EK, Jyothis M (2019) Catechin rich butanol fraction extracted from Acacia catechu L. (a thirst quencher) exhibits immunostimulatory potential. J Food Drug Anal 27:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2018.06.010
Teke GN, Kuiate JR, Ngouateu OB, Gatsing D (2007) Antidiarrhoeal and antimicrobial activities of Emilia coccinea (Sims) G Don extracts. J Ethnopharmacol 112:278–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.03.007
Thiagarajah JR, Donowitz M, Verkman AS (2015) Secretory diarrhoea: mechanisms and emerging therapies. Nat Rev Gastro Hepat 12:446–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2015.111
WHO (2017) Diarrheal Disease. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diarrhoeal disease/(Accessed 10 March 2022).
Xu GJ, Wang Q, Yu BM (1997) Color illustrations of antitumor traditional Chinese medicine. Fujian Sci Technol Publ House, Fuzhou
Xu QQ, Shen ZQ, Wang YB, Guo SJ, Li F, Wang YP, Zhou CF (2013) Anti-diarrhoeal and anti-microbial activity of Flos populi (male inflorescence of Populus tomentosa Carriere) aqueous extracts. J Ethnopharmacol 148:640–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.021
Zhang Y, Wang X, Sha S, Liang S, Zhao L, Liu L, Chai N, Wang H, Wu K (2012) Berberine increases the expression of NHE3 and AQP4 in sennosideA-induced diarrhoea model. Fitoterapia 83:1014–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2012.05.015
Zhang D, Yang L, Su W, Zhao Y, Ma X, Zhou H, Xu B, Zhang K, Ma H (2017) Aquaporin-4 is downregulated in the basolateral membrane of ileum epithelial cells during enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli induced diarrhea in mice. Front Microbiol 8:02655. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02655
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31572559) and the Postdoctoral Scientific Research Developmental Fund of Heilongjiang Province (Grant No. LBH- Q18020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LG and ZS conceived and designed the study. LG and LA performed the experiments. FY, WL, WH, and XZ acquired the data. LG, LA, FY, and CG analyzed the data. LG drafted and critically revised the article. LG, LA, FY, WL, XZ, WH, and ZS approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The authors declare that the procedures followed were in accordance with the regulations of the relevant clinical research ethics committee and with those of the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki).
Right to Privacy and Consent to Participate
The authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Confidentiality of Data
The authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, L., Ai, L., Yang, F. et al. Assessment of the Antidiarrheal Activity and Chemical Composition of Dichloromethane Extract from Macleaya Cordata. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 32, 1009–1020 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-022-00337-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-022-00337-8