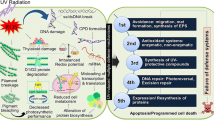
Abstract
Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn., Polygonaceae) exhibits potential bioactivities and pharmacological activities. Tartary buckwheat extract shows photoprotective properties by absorbing ultraviolet radiation and preventing light damage to human skin. In this study, a multicellular model of Caenorhabditis elegans was used to evaluate the UVB photoprotective effect of tartary buckwheat flavone, and the sun protection factor values of the lotions containing 0.5% tartary buckwheat flavone were evaluated using the in vitro sun protection factor 290AS instrument method via comparison to7.5% octyl methoxycinnamate. The lifespan, swallowing rate, cuticle morphology, the reactive oxygen species, and malondialdehyde values of C. elegans treated with tartary buckwheat flavone were characterized using a fluorescence microscope, a scanning electron microscope, a fluorescence spectrophotometer, and a UV–vis spectrophotometer. The results indicate that tartary buckwheat extract can ameliorate the vital indicators of C. elegans and improve the sun protection factor value of a sunscreen lotion under UVB exposure. Tartary buckwheat extract can be used as an effective compound to prevent UVB light from damaging the skin, making it a potential natural sunscreen ingredient.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altaei T (2012) The treatment of melasma by silymarin cream. BMC Dermatol 12:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-5945-12-18
Back P, Braeckman BP, Matthijssens F (2012) ROS in aging Caenorhabditis elegans: damage or signaling? Oxi Med Cell Longev 2012:608478. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/608478
Bartwal A, Mall R, Lohani P, Guru S, Arora S (2013) Role of secondary metabolites and brassinosteroids in plant defense against environmental stresses. J Plant Growth Regul 32:216–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-012-9272-x
Bhattacharya S, Sherje AP (2020) Development of resveratrol and green tea sunscreen formulation for combined photoprotective and antioxidant properties. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 60:102000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102000
Bryden AM, Moseley H, Ibbotson SH, Chowdhury MMU, Beck MH, Bourke J, English J, Farr P, Foulds IS, Gawkrodger DJ (2006) Photopatch testing of 1155 patients: results of the UK multicentre photopatch study group. Br J Dermatol 155:737–747. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07458.x
Chen Y, Wang J, Wan D (2010) Determination of total flavonoids in three Sedum crude drugs by UV–Vis spectrophotometry. Pharmacogn Mag 6:259–263. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.71784
Chow DK, Glenn CF, Johnston JL, Goldberg IG, Wolkow CA (2006) Sarcopenia in the Caenorhabditis elegans pharynx correlates with muscle contraction rate over lifespan. Exp Gerontol 41:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2005.12.004
Correa L, de Carvalho MG, Balestrin L, de Souza PO, Moreira JCF, Schuh RS, Bidone J, von Poser GL, Teixeira HF (2020) In vitro protective effect of topical nanoemulgels containing Brazilian red propolis benzophenones against UV-induced skin damage. Photochem Photobiol Sci 19:1460–1469. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0pp00243g
da Silva ACP, Paiva JP, Diniz RR, dos Anjos VM, Silva ABSM, Pinto AV, dos Santos EP, Leitão AC, Cabral LM, Rodrigues CR, de Pádula M, Santos BAMC (2019) Photoprotection assessment of olive (Olea europaea L.) leaves extract standardized to oleuropein: in vitro and in silico approach for improved sunscreens. J Photoch Photobiol B 193:162–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.03.003
D’Autréaux B, Toledano MB (2007) ROS as signalling molecules: mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:813–824. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2256
de Gruijl FR (2002) Photocarcinogenesis: UVA vs. UVB radiation. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 15:316–320. https://doi.org/10.1159/000064535
Detoni CB, Souto GD, da Silva ALM, Pohlmann AR, Guterres SS (2012) Photostability and skin penetration of different E-resveratol-loaded supramolecular structures. Photochem Photobiol 88:913–921. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.2012.01147.x
Downs CA, Kramarsky-Winter E, Segal R, Fauth J, Knutson S, Bronstein O, Ciner FR, Jeger R, Lichtenfeld Y, Woodley CM (2016) Toxicopathological effects of the sunscreen UV filter, oxybenzone (benzophenone-3), on coral planulae and cultured primary cells and its environmental contamination in Hawaii and the US Virgin Islands. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 70:265–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0227-7
Fabjan N, Rode J, Košir IJ, Wang Z, Zhang Z, Kreft I (2003) Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn.) as a source of dietary rutin and quercitrin. J Agric Food Chem 51:6452–6455. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf034543e
He F (2011) BCA (bicinchoninic acid) protein assay. Bio-protocol 101:44. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.44
Heinrich U, Gärtner C, Wiebusch M, Eichler O, Sies H, Tronnier H, Stahl W (2003) Supplementation with β-carotene or a similar amount of mixed carotenoids protects humans from UV-induced erythema. J Nutr 133:98–101. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/133.1.98
Ichihashi M, Ueda M, Budiyanto A, Bito T, Oka M, Fukunaga M, Tsuru K, Horikawa T (2003) UV-induced skin damage. Toxicology 189:21–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-483X(03)00150-1
Janjua NR, Kongshoj B, Andersson AM, Wulf HC (2008) Sunscreens in human plasma and urine after repeated whole-body topical application. J Eur Acad Dermatol 22:456–461. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02492.x
Kapoor MP, Sugita M, Fukuzawa Y, Timm D, Ozeki M, Okubo T (2021) Green tea catechin association with ultraviolet radiation-induced erythema: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Molecules 26:3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123702
Kawakami CM, Gaspar LR (2015) Mangiferin and naringenin affect the photostability and phototoxicity of sunscreens containing avobenzone. J Photoch Photobiol B 151:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.08.014
Kim S, Choi K (2014) Occurrences, toxicities, and ecological risks of benzophenone-3, a common component of organic sunscreen products: a mini-review. Environ Int 70:143–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.05.015
Korkina LG, Pastore S, De Luca C, Kostyuk VA (2008) Metabolism of plant polyphenols in the skin: beneficial versus deleterious effects. Curr Drug Metab 9:710–729. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920008786049267
Levine A (2020) Sunscreen use and awareness of chemical toxicity among beach goers in Hawaii prior to a ban on the sale of sunscreens containing ingredients found to be toxic to coral reef ecosystems. Mar Policy 117:103875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2020.103875
Li J, Yang P, Yang Q, Gong X, Ma H, Dang K, Chen G, Gao X, Feng B (2019) Analysis of flavonoid metabolites in buckwheat leaves using UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Moleclues 24:1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071310
Lin JY, Selim MA, Shea CR, Grichnik JM, Omar MM, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Pinnell SR (2003) UV photoprotection by combination topical antioxidants vitamin C and vitamin E. JAAD 48:866–874. https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2003.425
Lin C, Zhang X, Su Z, **ao J, Lv M, Cao Y, Chen Y (2019) Carnosol improved lifespan and healthspan by promoting antioxidant capacity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Oxi Med Cell Longev 2019:2999296. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5958043
Melo CPB, Saito P, Vale DL, Rodrigues CCA, Pinto IC, Martinez RM, Bezerra JR, Baracat MM, Verri WA Jr, Fonseca-Bazzo YM, Georgetti SR, Casagrande R (2021) Protection against UVB deleterious skin efects in a mouse model: efect of a topical emulsion containing Cordia verbenacea extract. Photochem Photobiol Sci 20:1033–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-021-00079-x
Miller IB, Pawlowski S, Kellermann MY, Petersen-Thiery M, Moeller M, Nietzer S, Schupp PJ (2021) Toxic efects of UV flters from sunscreens on coral reefs revisited: regulatory aspects for “reef safe” products. Environ Sci Eur 33:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-021-00515-w
Miranda-Vizuete A, Veal EA (2017) Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for understanding ROS function in physiology and disease. Redox Biol 11:708–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.020
Mishra AK, Mishra A, Chattopadhyay P (2011) Herbal cosmeceuticals for photoprotection from ultraviolet B radiation: a review. Trop J Pharm Res 10:351–360. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v10i3.7
Ngoc LTN, Tran VV, Moon J-Y, Chae M, Park D, Lee Y-C (2019) Recent trends of sunscreen cosmetic: an update review. Cosmetics 6:64. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics6040064
Njom VS, Winks T, Diallo O, Lowe A, Behnke J, Dickman MJ, Duce I, Johnstone I, Buttle DJ (2021) The effects of plant cysteine proteinases on the nematode cuticle. Parasit Vectors 14:302. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-021-04800-8
Pallela R, Na-Young Y, Kim SK (2010) Anti-photoaging and photoprotective compounds derived from marine organisms. Mar Drugs 8:1189–1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8041189
Parrado C, Nicolas J, Juarranz A, Gonzalez S (2020) The role of the aqueous extract Polypodium leucotomos in photoprotection. Photochem Photobiol Sci 19:831–843. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0pp00124d
Peng LX, Zou L, Zhao JL, **ang DB, Zhu P, Zhao G (2013) Response surface modeling and optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of three flavonoids from tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). Pharmacogn Mag 9:210–215. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.113266
Pourang A, Dourra M, Ezekwe N, Kohli I, Hamzavi I, Lim HW (2021) The potential efect of Polypodium leucotomos extract on ultraviolet- and visible light-induced photoaging. Photochem Photobiol Sci 20:1229–1238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-021-00087-x
Prasanth MI, Santoshram GS, Balamurugan BJP, K, (2016) Ultraviolet-A triggers photoaging in model nematode Caenorhabditis elegans in a DAF-16 dependent pathway. Age 38:27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-016-9889-y
Prasanth MI, Gayathri S, Bhaskar JP, Krishnan V, Balamurugan K (2020) Understanding the role of p38 and JNK mediated MAPK pathway in response to UV-A induced photoaging in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Photoch Photobiol B 205:111844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2020.111844
Procházková D, Boušová I, Wilhelmová N (2011) Antioxidant and prooxidant properties of flavonoids. Fitoterapia 82:513–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2011.01.018
Raffa RB, Pergolizzi JV Jr, Taylor R Jr, Kitzen JM, Group NR (2019) Sunscreen bans: coral reefs and skin cancer. J Clin Pharm Ther 44:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpt.1277
Saewan N, Jimtaisong A (2013) Photoprotection of natural flavonoids. J Appl Pharm Sci 3:129–141. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2013.3923
Saewan N, Jimtaisong A (2015) Natural products as photoprotection. J Cosmet Dermatol 14:47–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12123
Santamaría CG, Abud JE, Porporato MM, Meyer N, Zenclussen A, Kass L, Rodriguez HA (2019) The UV filter benzophenone 3, alters early follicular assembly in rat whole ovary cultures. Toxicol Lett 303:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.12.016
Schreiner M, Mewis I, Huyskens-Keil S, Jansen M, Zrenner R, Winkler J, O’brien N, Krumbein A (2012) UV-B-induced secondary plant metabolites-potential benefits for plant and human health. Crit Rev Plant Sci 31:229–240. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2012.664979
Sharma P, Montes de Oca MK, Alkeswani AR, McClees SF, Das T, Elmets CA, Afaq F (2018) Tea polyphenols for the prevention of UVB-induced skin cancer. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 34:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/phpp.12356
Shen P, Yue Y, Park Y (2018) A living model for obesity and aging research: Caenorhabditis elegans. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:741–754. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1220914
Suh S, Pham C, Smith J, Mesinkovska NA (2020) The banned sunscreen ingredients and their impact on human health: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol 59:1033–1042. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.14824
Thaler AKV, Kamenisch Y, Berneburg M (2010) The role of ultraviolet radiation in melanomagenesis. Exp Dermatol 19:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2009.01025.x
Tienaho J, Silvan N, Muilu-Mäkelä R, Kilpeläinen P, Poikulainen E, Sarjala T (2021) Ultraviolet absorbance of Sphagnum magellanicum, S. fallax and S. fuscum extracts with seasonal and species-specifc variation. Photochem Photobiol Sci 20:379–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-021-00026-w
Torun AN, Kulaksizoglu S, Kulaksizoglu M, Pamuk BO, Isbilen E, Tutuncu NB (2009) Serum total antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation marker malondialdehyde levels in overt and subclinical hypothyroidism. Clin Endocrinol 70:469–474. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2008.03348.x
Wang L, Yang X, Qin P, Shan F, Ren G (2013) Flavonoid composition, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of tartary buckwheat bran extract. Ind Crops Prod 49:312–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.04.039
Widsten P (2020) Lignin-based sunscreens—state-of-the-art, prospects and challenges. Cosmetics 7:85. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7040085
Wlaschek M, Tantcheva-Poór I, Naderi L, Ma W, Schneider LA, Razi-Wolf Z, Schüller J, Scharffetter-Kochanek K (2001) Solar UV irradiation and dermal photoaging. J Photoch Photobiol B 63:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1011-1344(01)00201-9
Yuan Y, Kang N, Li Q, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Tan P (2019) Study of the effect of neutral polysaccharides from Rehmannia glutinosa on lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 24:4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244592
Zhang W, Zheng B, Na D, Wang H, Li T, Liu R (2020) Effects of ethyl acetate fractional extract from Portulaca oleracea L. (PO-EA) on lifespan and healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Food Sci 85:4367–4376. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15507
Zielińska D, Turemko M, Kwiatkowski J, Zieliński H (2012) Evaluation of flavonoid contents and antioxidant capacity of the aerial parts of common and tartary buckwheat plants. Molecules 17:9668–9682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17089668
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M, Sollott S (2006) Mitochondrial ROS-induced ROS release: an update and review. BBA-Bioenergetics 1757:509–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.04.029
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Shanghai Affiliate Program from Shanghai Promotion Association for transformation of scientific and technological achievements (LM201825). The authors also thank C. elegans Genetics Center (CGC, Minneapolis, USA) that provided the C. elegans (Bristol N2).
Funding
This research was supported by Shanghai Affiliate Program from Shanghai Promotion Association for transformation of scientific and technological achievements (LM201825).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SZ: project administration, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing. BW: methodology; writing—original draft; validation; visualization. XZ: methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Wang, B. & Zheng, X. The Effect of Tartary Buckwheat Extract on Caenorhabditis elegans Exposed to UVB Light and Its Sunscreen Protection Factor in Sunscreen Formulation. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 32, 921–930 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-022-00315-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-022-00315-0