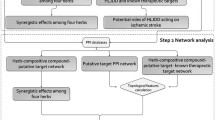
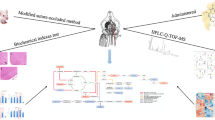
Abstract
Ginsenoside Rc is one of the active components of “nao-mai-tong,” which is a traditional Chinese medicine prescription widely used in the treatment of cerebral ischemia. Ginsenoside Rc has remarkable effects on the protection of the nervous system, but the molecular mechanism underlying its neuroprotective activity remains unclear. Thus, we aimed to integrate serum and network pharmacology to investigate the neuroprotective effect and potential mechanism of this ginsenoside for ischemic stroke. In this study, ginsenoside Rc was identified by liquid chromatography–Orbitrap tandem mass spectrometry system in the “nao-mai-tong” decoction. Network pharmacology and molecular docking simulation were employed to predict the potential targets and pharmacological mechanisms of ginsenoside Rc. Finally, oxygen-glucose deprivation reperfusion model of neuronal damage was induced in PC12 cells for verification of the decoction activity. Ginsenoside Rc was identified in “nao-mai-tong”-containing plasma and the analysis of bioinformatics indicated its key targets to be TNF-α and DRP-1. Besides, ginsenoside Rc reversed the alterations of TNF-α and DRP-1 level after oxygen-glucose deprivation reperfusion injury in a dose-dependent manner as indicated by experiments with antagonists.

Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed T, Raza SH, Maryam A, Setzer WN, Braidy N, Nabavi SF, Oliveira MR, Nabavi SM (2016) Ginsenoside Rb1 as a neuroprotective agent: a review. Brain Res Bull 125:30–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.04.002
Armahizer M, Blackman A, Plazak M, Brophy GM (2020) Early acute ischemic stroke management for pharmacists. Hosp Pharm 55:12–25. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018578718791504
Barone FC, Arvin B, White RF, Miller A, Webb CL, Willette RN, Lysko PG, Feuerstein GZ (1997) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke 28:1233–1244. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.28.6.1233
Chasman DI, Schürks M, Anttila V, de Vries B, Schminke U, Launer LJ, Terwindt GM, van den Maagdenberg AMJM, Fendrich K, Völzke H, Ernst F, Griffiths LR, Buring JE, Kallela M, Freilinger T, Kubisch C, Ridker PM, Palotie A, Ferrari MD, Hoffmann W, Zee RYL, Kurth T (2011) Genome-wide association study reveals three susceptibility loci for common migraine in the general population. Nat Genet 43:695–698. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.856
Choi RJ, Roy A, Jung HJ, Ali MY, Min BS, Park CH, Yokozawa T, Fan TP, Choi JS, Jung HA (2016) BACE1 molecular docking and anti-Alzheimer’s disease activities of ginsenosides. J Ethnopharmacol 190:219–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEP.2016.06.013
Cleves AE, Jain AN (2015) Knowledge-guided docking: accurate prospective prediction of bound configurations of novel ligands using Surflex-Dock. J Comput Aided Mol Des 29:485–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10822-015-9846-3
Duan Y, Cheng S, Jia L, Zhang Z, Chen L (2020) PDRPS7 protects cardiac cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through inactivation of JNKs. FEBS Open Bio 10:593–606. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.12822
Emberson J, Lees KR, Lyden P, Blackwell L, Albers G, Bluhmki E, Brott T, Cohen G, Davis S, Donnan G, Grotta J, Howard G, Kaste M, Koga M, von Kummer R, Lansberg M, Lindley RI, Murray G, Olivot JM, Parsons M, Tilley B, Toni D, Toyoda K, Wahlgren N, Wardlaw J, Whiteley W, del Zoppo GJ, Baigent C, Sandercock P, Hacke W, Stroke Thrombolysis Trialists’ Collaborative Group (2014) Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 384:1929–1935. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60584-5
Fatani SH, ALrefai AA, Al-Amodi HS, Kamel HF, Al-Khatieb K, Bader H (2018) Assessment of tumor necrosis factor alpha polymorphism TNF-α-238 (rs 361525) as a risk factor for development of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Mol Biol Rep 45:839–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4230-8
Hu C, Huang Y, Li L (2017) Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission plays critical roles in physiological and pathological progresses in mammals. Int J Mol Sci 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS18010144
** R, Yang G, Li G (2010) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: role of inflammatory cells. J Leukoc Biol 87:779–789. https://doi.org/10.1189/JLB.1109766
Kim DH, Park CH, Park D, Choi YJ, Park MH, Chung KW, Kim SR, Lee JS, Chung HY (2014) Ginsenoside Rc modulates Akt/FoxO1 pathways and suppresses oxidative stress. Arch Pharm Res 37:813–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0223-2
Lee MS, Hwang JT, Kim SH, Yoon S, Kim MS, Yang HJ, Kwon DY (2010) Ginsenoside Rc, an active component of Panax ginseng, stimulates glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes through an AMPK-dependent mechanism. J Ethnopharmacol 127:771–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEP.2009.11.022
Lee BY, Chon J, Kim HS, Lee JH, Yun DH, Yoo SD, Kim DH, Lee SA, Han YJ, Lee H, Kim JC, Soh Y, Chung JH, Kim SK, Park HJ (2017) Association between a polymorphism in CASP3 and CASP9 genes and ischemic stroke. Ann Rehabil Med 41:197–203. https://doi.org/10.5535/ARM.2017.41.2.197
Liu J, Chen F, Yin J, Bu F, Zheng B, Yang M, Wang Y, Sun D, Meng Q (2015) The effects of ginsenosides to amyloid fibril formation by RCMκ-casein. Int J Biol Macromol 79:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.04.046
Maneechote C, Palee S, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N (2017) Roles of mitochondrial dynamics modulators in cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury. J Cell Mol Med 21:2643–2653. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13330
Morris G, Walker AJ, Berk M, Maes M, Puri BK (2018) Cell death pathways: a novel therapeutic approach for neuroscientists. Mol Neurobiol 55:5767–5786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0793-y
Nabavi SF, Sureda A, Habtemariam S, Nabavi SM (2015) Ginsenoside Rd and ischemic stroke; a short review of literatures. J Ginseng Res 39:299–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2015.02.002
Phipps MS, Cronin CA (2020) Management of acute ischemic stroke. BMJ 368:l6983. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l6983
Pinzi L, Rastelli G (2019) Molecular docking: shifting paradigms in drug discovery. Int J Mol Sci 20:4331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184331
Rong Y, Feng S, Wu C, Wang S, Liang S, Liu D (2017) LC-high-resolution-MS/MS analysis of chemical compounds in rat plasma after oral administration of Nao-Mai-Tong and its individual herbs. Biomed Chromatogr 31. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.3920
Saito M, Chen-Yoshikawa TF, Suetsugu K, Okabe R, Takahagi A, Masuda S, Date H (2019) Pirfenidone alleviates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 158:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.08.098
Savitz SI, Baron JC, Yenari MA, Sanossian N, Marc F (2017) Reconsidering Neuroprotection in the Reperfusion Era. Stroke 48:3413–3419. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017283
Shen YL, Shi YZ, Chen GG, Wang LL, Zheng MZ, ** HF, Chen YY (2018) TNF-α induces Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fragmentation during inflammatory cardiomyocyte injury. Int J Mol Med 41. https://doi.org/10.3892/IJMM.2018.3385
Su M, Guo C, Liu M, Liang X, Yang B (2019a) Therapeutic targets of vitamin C on liver injury and associated biological mechanisms: a study of network pharmacology. Int Immunopharmacol 66. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INTIMP.2018.11.048
Su J, Zhou R-R, Guo F-F, Zhou Q-W, Xu H-Y (2019b) Molecular mechanism of Shuguan Granules in treating angina based on integrative pharmacology. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 44:1425–1435. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190111.001
Vakili A, Mojarrad S, Akhavan MM, Rashidy-Pour A (2011) Pentoxifylline attenuates TNF-α protein levels and brain edema following temporary focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1377:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BRAINRES.2011.01.001
Wang P, Dai L, Zhou W, Meng J, Zhang M, Wu Y, Huo H, **ong X, Sui F (2019) Intermodule coupling analysis of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction on stroke. Front Pharmacol 10:1288. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01288
Wu C, Zhao L, Rong Y, Zhu G, Liang S, Wang S (2016) The pharmacokinetic screening of multiple components of the Nao Mai Tong formula in rat plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry combined with pattern recognition method and its application to comparative pharmacokinetics. J Pharm Biomed Anal 131. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPBA.2016.09.011
Xu HY, Zhang YQ, Liu ZM, Chen T, Lv CY, Tang SH, Zhang XB, Zhang W, Li ZY, Zhou RR, Yang HJ, Wang XJ, Huang LQ (2019) ETCM: An encyclopaedia of traditional Chinese medicine. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D976–D982. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky987
Yang JW, Kim SS (2015) Ginsenoside Rc promotes anti-adipogenic activity on 3T3-L1 adipocytes by down-regulating C/EBPα and PPARγ. Molecules 20:1293–1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES20011293
Youle RJ, van der Bliek AM (2012) Mitochondrial fission, fusion, and stress. Science 337:1062–1065. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.1219855
Yu T, Yang Y, Kwak Y-S, Song GG, Kim M-Y, Rhee MH, Cho JY (2017) Ginsenoside Rc from Panax ginseng exerts anti-inflammatory activity by targeting TANK-binding kinase 1/interferon regulatory factor-3 and p38/ATF-2. J Ginseng Res 41:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2016.02.001
Yuan Y, Men W, Shan X, Zhai H, Qiao X, Geng L, Li C (2020) Baicalein exerts neuroprotective effect against ischaemic/reperfusion injury via alteration of NF-kB and LOX and AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Inflammopharmacology 28:1327–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10787-020-00714-6
Zheng M, **n Y, Li Y, Xu F, ** X, Guo H, Cui X, Cao H, Zhang X, Han C (2018) Ginsenosides: a potential neuroprotective agent. Biomed Res Int 2018:8174345–8174311. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8174345
Zheng P-F, Liao F-J, Yin R-X, Chen L-Z, Li H, Nie R-J, Wang Y, Liao P-J (2020) Genes associated with inflammation may serve as biomarkers for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease and ischaemic stroke. Lipids Health Dis 19:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-020-01217-7
Zhou M, Wang H, Zhu J, Chen W, Wang L, Liu S, Li Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Yin P, Liu J, Yu S, Tan F, Barber RM, Coates MM, Dicker D, Fraser M, González-Medina D, Hamavid H, Hao Y, Hu G, Jiang G, Kan H, Lopez AD, Phillips MR, She J, Vos T, Wan X, Xu G, Yan LL, Yu C, Zhao Y, Zheng Y, Zou X, Naghavi M, Wang Y, Murray CJL, Yang G, Liang X (2016) Cause-specific mortality for 240 causes in China during 1990-2013: a systematic subnational analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 387:251–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00551-6
Zhou K, Chen J, Wu J, Wu Q, Jia C, Xu YXZ, Chen L, Tu W, Yang G, Kong J, Kou J, Jiang S (2019) Atractylenolide III ameliorates cerebral ischemic injury and neuroinflammation associated with inhibiting JAK2/STAT3/Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission in microglia. Phytomedicine 59. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYMED.2019.152922
Zhu B, Zhang W, Lu Y, Hu S, Gao R, Sun Z, Chen X, Ma J, Guo Z, Du S, Li P (2018) Network pharmacology-based identification of protective mechanism of Panax notoginseng saponins on aspirin induced gastrointestinal injury. Biomed Pharmacother 105:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2018.04.054
Acknowledgements
Technology Funds were obtained from the Key Unit of Chinese Medicine Digitalization Quality Evaluation of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. We thank Haibin Luo from Sun Yat-sen University for technical assistance in SYBYL.
Funding
This research is supported by Projects of The National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81773884, 81473413, and 81274060), the National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for “Significant New Drugs Development” during the Thirteenth Five – year Plan Period (grant numbers 2017ZX09301077), and the Science and Technology Plan Project of Guangzhou (grant number 201803010115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MX and SW conceived and designed the idea; KL and MH performed the experiments; MH analyzed the data; SC, KZ, and QL performed network pharmacology analysis; MX and MH wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Animal Ethical Approval
Animal studies were carried out in accordance with the Guidelines for Animal Experimentation of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, and the protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of this institution (protocol number: gdpulac2017130).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 395 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, M., Chen, S., Zheng, K. et al. Integrated LC-MS/MS Method and Network Pharmacology for Exploring the Mechanism of Neuroprotective Effect of Ginsenoside Rc in Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion Injury. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 31, 207–216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00145-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00145-6