Abstract
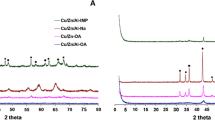
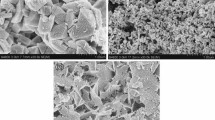
The highly selective reaction concerning catalytic glycerol dehydration to acetol was studied using Zn, Al and Cu oxide catalysts. The diffractograms and Raman spectroscopy revealed the presence of Al2O3, ZnO, CuO, ZnAl2O4 and CuAl2O4 phases with crystallite nanometer size (8–22 nm). AlNMR profiles showed the octahedral, pentacoordinate and tetrahedral coordination of the Al species The redox properties obtained by TPR indicated that at 250 °C, due to SMSI effects, the copper phase is reduced and ZnO is more resistant to reduction while alumina is metastable. The N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms exhibited the formation of materials in the micro-mesopore range with specific surface area between 90 and 224 m2 g−1. The SEM micrographs showed a sponge-like morphology with cavity sizes between 60 and 70 nm. The best catalytic performance occurred with average yield and selectivity to acetol of 26% and 97%, respectively. The catalyst was quite selective to acetol during reuse tests and was almost completely reactivated after regeneration. The ex-situ analyzes investigated the changes that occurred in the Cun+ sites during the reaction, which confirmed the sintering of the copper species by increasing the crystallite size from 25.3 to 36.3 nm. The simple computational theoretical study identified the most exposed sites in planes (hkl), supporting the proposed mechanism. Considering that they are little explored, a brief discussion on the mechanisms involved in the catalyst deactivation by coke was also proposed. Thus, the presence of Cu0 and Cu+ sites combined with Zn–Al species and their synergy enhances the high selectivity and yield to acetol, while unreduced Cu2+ has inferior catalytic performance.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be provided when requested from the authors.
References
Abrahami ST, Chiter F, Klein LH, Maurice V, Terryn H, Costa D, Marcus P (2019) J Phys Chem C 123:22228–22238
Ahmed SF, Debnath JC, Mehejabin F, Islam N, Tripura R, Mofijur M, Hoang AT, Rasul MG, Vo D-VN (2023) Sustain Energy Technol Assessments 55:102894
Alhanash A, Kozhevnikova EF, Kozhevnikov IV (2010) Appl Catal A Gen 378:11–18
Arjmand M, Azad A-M, Leion H, Mattisson T, Lyngfelt A (2012) Ind Eng Chem Res 51:13924–13934
Attarbachi T, Kingsley MD, Spallina V (2023) Fuel 340:127485
A.V. Azaroff, Elements of X-ray crystallography, vol. 26 (1968)
Bao Q, Bu T, Yan J, Zhang C, Ning C, Zhang Y, Hao M, Zhang W, Wang Z (2017) Catal Letters 147:1540–1550
Basu S, Shree V, Sen AK (2022) J Rare Earths 40:63–72
Bayramoğlu D, Gürel G, Sinağ A, Güllü M (2014) Turk J Chem 38:661–670
Bouriakova A, Mendes PSF, Katryniok B, De Clercq J, Thybaut JW (2020) Catal Commun 146:106134
Braga TP, Essayem N, Valentini A (2015) RSC Adv 5:93394–93402
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319
Chagas P, Oliveira CC, Leitão AA, Lima LL, Portilho MF, Oliveira LCA (2022) J Environ Chem Eng 10:107286
Chaminand J, Auren Djakovitch L, Gallezot P, Marion P, Pinel C, Rosier C (2004) Green Chem 6:359
Chang T-C, Lu Y-T, Lee C-H, Gupta JK, Hardwick LJ, Hu C-C, Chen H-YT (2021) ACS Omega 6:9692–9699
Checa M, Nogales-Delgado S, Montes V, Encinar JM (2020) Catalysts 10:1279
Chen X, Shen Y-F, Suib SL, O’Young CL (2002) Chem Mater 14:940–948
Cherubini F (2010) Energy Convers Manag 51:1412–1421
Chimentão RJ, Hirunsit P, Torres CS, Ordoño MB, Urakawa A, Fierro JLG, Ruiz D (2021) Catal Today 367:58–70
Choma J, Kloske M, Jaroniec M (2003) J Colloid Interface Sci 266:168–174
Colmenares-Zerpa J, Gajardo J, González G, Fierro JLG, Peixoto AF, Junkaew A, Suthirakun S, Santos JBO, Picinini M, Urquieta-Gonzalez EA, Hirunsit P, Chimentão RJ (2023) Catal Today 423:114275
Cristino AF, Matias IAS, Bastos DEN, Galhano dos Santos R, Ribeiro APC, Martins LMDRS (2020) Catalysts 10:1406
Dalil M, Carnevali D, Edake M, Auroux A, Dubois J-L, Patience GS (2016) J Mol Catal A Chem 421:146–155
Danov S, Esipovich A, Belousov A, Rogozhin A (2015) Chinese J. Chem Eng 23:1138–1146
Dasari MA, Kiatsimkul P-P, Sutterlin WR, Suppes GJ (2005) Appl Catal A Gen 281:225–231
Derrouiche S, La Fontaine C, Thrimurtulu G, Casale S, Delannoy L, Lauron-Pernot H, Louis C (2016) Catal Sci Technol 6:6794–6805
Dieuzeide ML, Jobbagy M, Amadeo N (2016) Ind Eng Chem Res 55:2527–2533
Donphai W, Piriyawate N, Witoon T, Jantaratana P, Varabuntoonvit V, Chareonpanich M (2016) J CO2 Util 16:204–211
Estevez, Aguado-Deblas, Luna, Bautista (2019) Energies 12:2364
Fabián M, Bottke P, Girman V, Düvel A, Da Silva KL, Wilkening M, Hahn H, Heitjans P, Šepelák V (2015) RSC Adv 5:54321–54328
Fang J, Xuan Y (2017) RSC Adv 7:56023–56033
Farnetti E, Crotti C (2016) Catal Commun 84:1–4
Fernandes Barbosa F, Pinheiro Braga T (2022). ChemCatChem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202200950
Fierro G, Lo Jacono M, Inversi M, Porta P, Cioci F, Lavecchia R (1996) Appl Catal A Gen 137:327–348
Flores JH, Pais da Silva MI (2008) Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 322:113–123
Gandarias I, Requies J, Arias PL, Armbruster U, Martin A (2012) J Catal 290:79–89
Gillman IG, Kistler KA, Stewart EW, Paolantonio AR (2016) Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 75:58–65
Guisnet M, Costa L, Ribeiro FR (2009) J Mol Catal A Chem 305:69–83
Hirunsit P, Luadthong C, Faungnawakij K (2015) RSC Adv 5:11188–11197
Ionescu M, Petrović ZS (2018). Eur J Lipid Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201800004
Ivanova AS, Korneeva EV, Bondareva VM, Glazneva TS (2015) J Mol Catal A Chem 408:98–106
Jiang XC, Zhou CH, Tesser R, Di Serio M, Tong DS, Zhang JR (2018) Ind Eng Chem Res 57:10736–10753
Kanai R, Yagi F, Omata K, Miura H, Shishido T (2023) Mol Catal 550:113588
Katryniok B, Paul S, Bellière-Baca V, Rey P, Dumeignil F (2010) Green Chem 12:2079–2098
Kim YT, Jung K-D, Park ED (2011) Appl Catal A Gen 393:275–287
Koranian P, Huang Q, Dalai AK, Sammynaiken R (2022) Catalysts 12:897
Kunthakudee N, Khemthong P, Luadthong C, Panpranot J, Mekasuwandumrong O, Witoon T, Faungnawakij K (2022) Mol Catal 523:111426
Kwak BK, Park DS, Yun YS, Yi J (2012) Catal Commun 24:90–95
B. Lafuente, R.T. Downs, H. Yang and N. Stone, The power of databases: The RRUFF project (2016)
Lari GM, Pastore G, Haus M, Ding Y, Papadokonstantakis S, Mondelli C, Pérez-Ramírez J (2018) Energy Environ Sci 11:1012–1029
Larina OV, Kyriienko PI, Balakin DY, Vorokhta M, Khalakhan I, Nychiporuk YM, Matolín V, Soloviev SO, Orlyk SM (2019) Catal Sci Technol 9:3964–3978
V.D.R.B.A.C. Larson, Los Alamos Natl. Lab. Rep., (2016) https://doi.org/10.4135/9781483371283.n174.
Lei N, Miao Z, Liu F, Wang H, Pan X, Wang A, Zhang T (2020) Chinese. J Catal 41:1261–1267
Li L, Korányi TI, Sels BF, Pescarmona PP (2012) Green Chem 14:1611
Li X, Xu P, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Jia H, Yu H, Li X (2022) Anal Chem 94:16502–16509
Liotta LF, Longo A, Macaluso A, Martorana A, Pantaleo G, Venezia AM, Deganello G (2004) Appl Catal B Environ 48:133–149
List B (2000) J Am Chem Soc 122:9336–9337
Liu Y, Guo X, Rempel G, Ng F (2019) Catalysts 9:412
Liu Y, Mai CTQ, Ng FTT (2021) Catalysts 11:110
Liu Y, Zheng J, Yan T, Deng J, Fang J, Zhang D (2023) New J Chem 47:10604–10612
Lizana I, Colmenares-Zerpa J, Pecchi G, Chimentão RJ, Delgado EJ (2021) J King Saud Univ - Sci 33:101597
Luciani G, Ruoppolo G, Landi G, Gargiulo V, Alfè M, Di Benedetto A (2022) Catalysts 12:72
Luque R, Budarin V, Clark JH, Macquarrie DJ (2008) Appl Catal B Environ 82:157–162
Mane RB, Rode CV (2012) Green Chem 14:2780
Maniammal K, Madhu G, Biju V (2017) Phys E Low-Dimens Syst Nanostruct 85:214–222
Marchi AJ, Fierro JLG, Santamaría J, Monzón A (1996) Appl Catal A Gen 142:375–386
Mazarío J, Raad Z, Concepción P, Cerdá-Moreno C, Domine ME (2020a) Catal. Sci Technol 10:8049–8063
Mazarío J, Concepción P, Ventura M, Domine ME (2020b) J Catal 385:160–175
Mazarío J, Cecilia JA, Rodríguez-Castellón E, Domine ME (2023) Appl Catal A Gen 652:119029
B.A.T. Mehrabadi, S. Eskandari, U. Khan, R.D. White and J.R. Regalbuto, pp. 1–35 (2017)
Meima GR, Menon PG (2001) Appl Catal A Gen 212:239–245
Miranda BC, Chimentão RJ, Santos JBO, Gispert-Guirado F, Llorca J, Medina F, Bonillo FL, Sueiras JE (2014) Appl Catal B Environ 147:464–480
Miranda BC, Chimentão RJ, Szanyi J, Braga AH, Santos JBO, Gispert-Guirado F, Llorca J, Medina F (2015) Appl Catal B Environ 166–167:166–180
Momma K, Izumi F (2011) J Appl Crystallogr 44:1272–1276
Nimbalkar AS, Oh K, Han SJ, Yun G, Cha SH, Upare PP, Awad A, Hwang DW, Hwang YK (2023). Chemsuschem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202301315
Notz W, List B (2000) J Am Chem Soc 122:7386–7387
O’Neill HStC, James M, Dollase WA, Redfern SAT (2005) Eur J Mineral 17:581–586
Oliveira YL, Gouveia AF, Costa MJS, Lopes FHP, Sczancoski JC, Longo E, Luz GE Jr, Santos RS, Cavalcante LS (2022) Mater Sci Energy Technol 5:125–144
Pan C-J, Tsai M-C, Su W-N, Rick J, Akalework NG, Agegnehu AK, Cheng S-Y, Hwang B-J (2017) J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 74:154–186
Pandey DK, Singh SP, Dalai AK, Biswas P (2022). Catal Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2022.03.021
Panyad S, Jongpatiwut S, Sreethawong T, Rirksomboon T, Osuwan S (2011) Catal Today 174:59–64
Park H, Yun YS, Kim TY, Lee KR, Baek J, Yi J (2015) Appl Catal B Environ 176–177:1–10
Pinheiro Pires AP, Arauzo J, Fonts I, Domine ME, Fernández Arroyo A, Garcia-Perez ME, Montoya J, Chejne F, Pfromm P, Garcia-Perez M (2019) Energy Fuels 33:4683–4720
Popova M, Lazarova H, Kalvachev Y, Todorova T, Szegedi Á, Shestakova P, Mali G, Dasireddy VDBC, Likozar B (2017) Catal Commun 100:10–14
Posada JA, Rincón LE, Cardona CA (2012) Bioresour Technol 111:282–293
Restrepo JB, Bustillo JA, Bula AJ, Paternina CD (2021) Processes 9:479
Rouquerol J, Rouquerol F (2014). In: Rouquerol F, Rouquerol J, Sing KSW, Llewellyn P, Maurin G (eds) Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids (Second Edition). Academic Press, Oxford, pp 57–104
Sagar GV, Rao PVR, Srikanth CS, Chary KVR (2006) J Phys Chem B 110:13881–13888
Santibáñez C, Varnero MT, Bustamante M (2011) Chil J Agric Res 71:469–475
Sasaki S, Kurniawan E, Sato K, Matsusaka K, Kojima T, Hara T, Yamada Y, Sato S (2024) Appl Catal A Gen 671:119561
Sato S, Akiyama M, Takahashi R, Hara T, Inui K, Yokota M (2008) Appl Catal A Gen 347:186–191
Sato S, Sakai D, Sato F, Yamada Y (2012) Chem Lett 41:965–966
Šepelák V, Bergmann I, Indris S, Feldhoff A, Hahn H, Becker KD, Grey CP, Heitjans P (2011) J Mater Chem 21:8332
Shaikh RR, Damruang S, Khan RA, Praserthdam S, Praserthdam P (2024) J Energy Chem 94:486–507
Shozi ML, Dasireddy VDBC, Singh S, Mohlala P, Morgan DJ, Iqbal S, Friedrich HB (2017) Sustain. Energy Fuels 1:1437–1445
Slaa JC, Weierink GJM, van Ommen JG, Ross JRH (1992) Catal Today 12:481–490
Song TT, Yang M, Chai JW, Callsen M, Zhou J, Yang T, Zhang Z, Pan JS, Chi DZ, Feng YP, Wang SJ (2016) Sci Rep 6:29221
Stokes AR, Wilson AJC (1944) Proc Phys Soc 56:174–181
Streimikiene D, Kyriakopoulos GL (2023) Energies 16:610
Sun JT, Metcalfe IS, Sahibzada M (1999) Ind Eng Chem Res 38:3868–3872
Sun D, Yamada Y, Sato S (2014) Appl Catal A Gen 475:63–68
Suprun W, Lutecki M, Haber T, Papp H (2009) J Mol Catal A Chem 309:71–78
Taarning E, Madsen AT, Marchetti JM, Egeblad K, Christensen CH (2008) Green Chem 10:408
Talebian-Kiakalaieh A, Amin NAS, Hezaveh H (2014) Renew Sustain Energy Rev 40:28–59
M. Thommes, K. Kaneko, A.V. Neimark, J.P. Olivier, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, J. Rouquerol and K. S. W. Sing, Pure Appl. Chem (2015)
Thongratkaew S, Kiatphuengporn S, Junkaew A, Kuboon S, Chanlek N, Seubsai A, Rungtaweevoranit B, Faungnawakij K (2022) Catal Commun 169:106468
Toby BH (2001) J Appl Crystallogr 34:210–213
Villarroel Rocha J, Barrera D, Sapag K (2011) Top Catal 54:121–134
Villarroel-Rocha J, Barrera D, Sapag K (2014) Microporous Mesoporous Mater 200:68–78
Vogt ETC, Fu D, Weckhuysen BM (2023). Angew Chemie Int Ed. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202300319
Young RA, Sakthivel A, Moss TS, Paiva-Santos CO (1995) J Appl Crystallogr 28:366–367
Zhao L, Zhang Y, Bi S, Liu Q (2019) RSC Adv 9:19236–19242
Zhao H, Zheng L, Li X, Chen P, Hou Z (2020) Catal Today 355:84–95
Zhou J, Zhao J, Zhang J, Zhang T, Ye M, Liu Z (2020) Chinese. J Catal 41:1048–1061
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support of the Coordination of Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES, acronym in Portuguese) and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq, acronym in Portuguese). Thank Johnny Villarroel-Rocha for hel** us obtain the pore distribution curves using the VBS method.
Funding
CNPq,CAPES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barbosa, F.F., Pergher, S.B.C. & Braga, T.P. Synergistic effects on Cu, Zn and Al-based catalyst: tracking the change of active sites during glycerol dehydration. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43153-024-00480-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43153-024-00480-w