Abstract
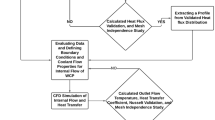
An acrylic suspension furnace was used to study the flow structure of air and rice husk. The standard k–ε model with standard wall function was employed in the simulation study while the cold test experiment, for results validation, utilized onionskin (thin oil paper) and rice husk itself. From the simulation, both air and rice husk flows are in swirling mode due to the tangential air. The cold test experiment strengthened that swirl flow of air is indicated by the onionskin movement upward and downward forming a curve and circular directions. On the other hand, swirl flow of rice husk is visualized by the sinusoidal peaks and valleys. In addition, the contribution of secondary air generates recirculation flow at the bottom area of the furnace. Also, there are backflow phenomena that occur, and yet, the revalidation study revealed that modification of tangential air pipes angle with a longer burner length can overcome the problem. Finally, this model can predict the flow structure in a good compliment to the cold test experiment results. Moreover, the less-intensive computation load with a shorter computation time makes it in demand for the design purpose and performance evaluation of process equipment.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANSYS (2019) ANSYS fluent theory guide 2019 R3. ANSYS Inc
Bhuiyan AA, Naser J (2015) CFD modelling of co-firing of biomass with coal under oxy-fuel combustion in a large scale power plant. Fuel 159:150–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.06.058
Bindar Y (2017) Computational engineering on multidimensional turbulent flows (Rekayasa Komputasi Aliran Turbulen Multidimensi). ITB Press, New York
Bindar Y et al (2022) Large-scale pyrolysis of oil palm frond using two-box chamber pyrolyzer for cleaner biochar production. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02842-1
Blissett R et al (2017) Valorisation of rice husks using a TORBED® combustion process. Fuel Process Technol 159:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.01.046
Cardoso J et al (2019) Comparative 2D and 3D analysis on the hydrodynamics behaviour during biomass gasification in a pilot-scale fluidized bed reactor. Renew Energy 131:713–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.07.080
Chokphoemphun S et al (2019) Rice husk combustion characteristics in a rectangular fluidized-bed combustor with triple pairs of chevron-shaped discrete ribbed walls. Case Stud Therm Eng 14(July):100511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2019.100511
Costa JAS, Paranhos CM (2018) Systematic evaluation of amorphous silica production from rice husk ashes. J Clean Prod 192:688–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.028
Defraeye T (2014) Advanced computational modelling for drying processes—a review. Appl Energy 131(Supplement C):323–344
Duan F et al (2013) Experimental study on rice husk combustion in a vortexing fluidized-bed with flue gas recirculation (FGR). Biores Technol 134:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.125
Fang M et al (2004) Experimental study on rice husk combustion in a circulating fluidized bed. Fuel Process Technol 85(11):1273–1282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2003.08.002
Fernandes IJ et al (2016) Characterization of rice husk ash produced using different biomass combustion techniques for energy. Fuel 165:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.10.086
Gao X et al (2018) CFD modeling of sawdust gasification in a lab-scale entrained flow reactor based on char intrinsic kinetics. Part 1: model development. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 125(December 2017):280–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2018.02.017
Gomes GMF et al (2016) Rice husk bubbling fluidized bed combustion for amorphous silica synthesis. J Environ Chem Eng 4(2):2278–2290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.03.049
Guan Y et al (2014) Three-dimensional CFD simulation of hydrodynamics in an interconnected fluidized bed for chemical loo** combustion. Powder Technol 268:316–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.08.046
Haider A, Levenspiel O (1989) Drag coefficient and terminal velocity of spherical and nonspherical particles. Powder Technol 58(1):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-5910(89)80008-7
Hernowo P et al (2022a) Nature of mathematical model in lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis process kinetic using volatile state approach. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 139:104520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2022.104520
Hernowo P et al (2022b) Chemicals component yield prediction and kinetic parameters determination of oil palm shell pyrolysis through volatile state approach and experimental study. J Anal Appl Pyrol 161:105399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105399
Hoekstra AJ (2000) Gas flow field and collection efficiency of cyclone separators. Dissertation, Technische Universiteit Delft
Hoekstra AJ, Derksen JJ, Van Den Akker HEA (1999) An experimental and numerical study of turbulent swirling flow in gas cyclones. Chem Eng Sci 54:2055–2065. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(98)00373-X
Huang Q et al (2010) CFD simulation of hydrodynamics and mass transfer in an internal airlift loop reactor using a steady two-fluid model. Chem Eng Sci 65(20):5527–5536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2010.07.021
Kapur PC, Singh R, Srinivasan J (1984) Tube-in-basket burner for rice husk. I: properties of husk as a fuel and basic design considerations. Sadhana 7(4):291–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811369
Khosravi Nikou MR, Ehsani MR (2008) Turbulence models application on CFD simulation of hydrodynamics, heat and mass transfer in a structured packing. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 35(9):1211–1219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2008.05.017
Koksal M (2001) Gas mixing and flow dynamics in circulating fluidized beds with secondary air injection. National Library of Canada
Kuprianov VI et al (2010) Combustion and emission characteristics of a swirling fluidized-bed combustor burning moisturized rice husk. Appl Energy 87(9):2899–2906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.09.009
Li Z et al (2019) CFD simulation of a fluidized bed reactor for biomass chemical loo** gasification with continuous feedstock. Energy Convers Manag 201(September):112143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112143
Lin CH, Teng JT, Chyang CS (1997) Evaluation of the combustion efficiency and emission of pollutants by coal particles in a vortexing fluidized bed. Combust Flame 110(1–2):163–172
Malekjani N, Jafari SM (2018) Simulation of food drying processes by computational fluid dynamics (CFD): recent advances and approaches. Trends Food Sci Technol 78:206–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.06.006
Malik R et al (2010) Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) based simulated study of multi-phase fluid flow. Defect Diffus Forum 307:1–11. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/DDF.307.1
Mohammed RH et al (2018) Physical properties and adsorption kinetics of silica-gel/water for adsorption chillers. Appl Therm Eng 137:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.03.088
Nakhaei M et al (2020) CFD modeling of gas–solid cyclone separators at ambient and elevated temperatures. Processes 8(228):1–26. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020228
Nemoda S et al (2005) Experimental and numerical investigation of gaseous fuel combustion in swirl chamber. Int J Heat Mass Transf 48(21–22):4623–4632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2005.04.004
Norton T, Tiwari B, Sun DW (2013) Computational fluid dynamics in the design and analysis of thermal processes: a review of recent advances. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 53(3):251–275
Nunes LJR, Matias JCO, Catalão JPS (2014) Mixed biomass pellets for thermal energy production: a review of combustion models. Appl Energy 127:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.04.042
Panneerselvam R, Savithri S, Surender GD (2009) CFD simulation of hydrodynamics of gas–liquid–solid fluidised bed reactor. Chem Eng Sci 64(6):1119–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2008.10.052
Panuju DR, Mizuno K, Trisasongko BH (2013) The dynamics of rice production in Indonesia 1961–2009. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 12(1):27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2012.05.002
Park HC, Choi HS (2019) Numerical study of the segregation of pyrolyzed char in a bubbling fluidized bed according to distributor configuration. Powder Technol 355:637–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.07.084
Pashtrapanska M et al (2006) Turbulence measurements in a swirling pipe flow. Exp Fluids 41(5):813–827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-006-0206-x
Pasymi P, Budhi YW, Bindar Y (2017) The effect of inlet aspect ratio (RIA) to the three dimensional mixing characteristics in tangential burner. ARPN J Eng Appl Sci 12(18):5300–5306
Pasymi P, Budhi YW, Bindar Y (2020a) Experimental and numerical investigations of fluid flow behaviors in a biomass cyclone burner. ASEAN J Chem Eng 20(1):88–98. https://doi.org/10.22146/ajche.56708
Pasymi P, Budhi YW, Bindar Y (2020b) Intrinsic parameters of dry chopped miscanthus for cold particle dynamic modeling. J Teknol 82(5):91–100. https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v82.13534
Prasara AJ, Gheewala SH (2017) Sustainable utilization of rice husk ash from power plants: a review. J Clean Prod 167:1020–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.11.042
Ramli Y et al (2022) Simulation study of bamboo leaves valorization to small-scale electricity and bio-silica using ASPEN PLUS. BioEnergy Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-022-10403-7
Rozainee M (2007) Production of amorphous silica from rice husk in fluidised bed system. Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Rozainee M et al (2010) Computational fluid dynamics modeling of rice husk combustion in a fluidised bed combustor. Powder Technol 203(2):331–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2010.05.026
Singh RI, Brink A, Hupa M (2013) CFD modeling to study fluidized bed combustion and gasification. Appl Therm Eng 52(2):585–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2012.12.017
Steven S et al (2021) Influences of pretreatment, extraction variables, and post treatment on bench-scale rice husk black ash (RHBA) processing to bio-silica. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 16(5):e2694. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.2694
Steven S, Restiawaty E et al (2022a) Digitalized turbulent behaviors of air and rice husk flow in a vertical suspension furnace from computational fluid dynamics simulation. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.2805
Steven S, Friatnasary DL et al (2022b) High cell density submerged membrane photobioreactor (SMPBR) for microalgae cultivation. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 963(1):012034. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/963/1/012034
Steven S, Windari L et al (2022c) Investigation of air and rice husk cold flow structures in the suspension furnace chamber through a simulation study. Int J Thermofluid Sci Technol 9(5):2090501. https://doi.org/10.36963/IJTST.2022090501
Steven S, Hernowo P et al (2022d) Thermodynamics simulation performance of rice husk combustion with a realistic decomposition approach on the devolatilization stage. Waste Biomass Valoriz 13(5):2735–2747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01657-x
Steven S, Restiawaty E, Bindar Y (2022e) Operating variables on production of high purity bio-silica from rice hull ash by extraction process. J Eng Technol Sci 54(3):220304. https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2022.54.3.4
Steven S, Restiawaty E, Bindar Y (2022f) Simple mass transfer simulation using a single-particle heterogeneous reaction approach in rice husk combustion and rice husk ash extraction. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 963(1):012050. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/963/1/012050
Steven, S, Restiawaty, E, et al (2022g) Three-dimensional flow modelling of air and particle in a low-density biomass combustor chamber at various declination angles of tangential and secondary air pipes. Powder Technol 410:117883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2022.117883
Stroh A et al (2015) 3-D numerical simulation for co-firing of torrefied biomass in a pulverized-fired 1 MWth combustion chamber. Energy 85:105–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.03.078
Suranani S, Goli VR (2012) Modeling fluidized bed combustion of rice husk. Int Conf Chem Civil Environ Eng 2012:305–308
Sylvia N et al (2019) A computational fluid dynamic comparative study on CO2 adsorption performance using activated carbon and zeolite in a fixed bed reactor. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 536(1):012042. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/536/1/012042
Wang T et al (2019) Combustion behavior of refuse-derived fuel produced from sewage sludge and rice husk/wood sawdust using thermogravimetric and mass spectrometric analyses. J Clean Prod 222(2019):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.016
Werther J et al (2000) Combustion of agricultural residues. Prog Energy Combust Sci 26(1):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1285(99)00005-2
Yang S et al (2019) Eulerian–Lagrangian simulation of air-steam biomass gasification in a three-dimensional bubbling fluidized gasifier. Energy 181:1075–1093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.06.003
Yang S et al (2020) Particle-scale characteristics of the three distinct regions in the multi-chamber slot-rectangular spouted bed. Powder Technol 360:658–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.10.038
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Riset Unggulan PT grants funding, Indonesian Ministry of Research and Technology/National Research and Innovation Agency for the full financial support to this study. Thanks to Mr. Imam Mardhatillah Fajri who has sincerely helped us in manufacturing the suspension furnace 3D design as seen in the Supplementary File. We also greatly thank Akrilik Cipta Jaya (Bandung, Indonesia) for their endeavor to fabricate the acrylic suspension furnace equipped with the cyclone with satisfying results. Finally, a special thank is addressed to Mr. Harben (Biomass Technology Workshop ITB Jatinangor) for his great notion about the acrylic furnace and blower frames as well as his kindness and patient assistance when installing all of the frames.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Steven, S., Restiawaty, E., Pasymi, P. et al. Revealing flow structure of air and rice husk in the acrylic suspension furnace: simulation study and cold test experiment. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 40, 733–748 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43153-022-00274-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43153-022-00274-y