Abstract
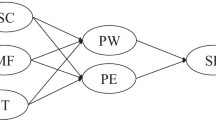
Academic buoyancy has been shown to contribute to adaptive emotional, motivational, and academic outcomes. Previous work suggests that students’ emotional intelligence, self-compassion, and achievement goals are key determinants of academic buoyancy. However, to date, no study has examined the combined influence of these factors on students’ academic buoyancy. Thus, this study investigated if the relationship between emotional intelligence and academic buoyancy is mediated by self-compassion and achievement goals in a serial fashion. University students (N = 498, 87.6% female, 67.6% white, \(\overline{X }\) age = 28.10 ± 9.46) completed the following instruments: Brief Emotional Intelligence Scale, Self-Compassion Scale–Short Form, 3 × 2 Achievement Goal Questionnaire, and Academic Buoyancy Scale. Using mediation techniques, we determined that the relationship between emotional intelligence and academic buoyancy was mediated by both self-compassion and specific achievement goal constructs. Specifically, the indirect effect of emotional intelligence was shown to decrease academic buoyancy when the mediation pathway included self-compassion followed by Task-Approach, Other-Approach, or Task-Avoidance goals. The unexpected indirect relationships between emotional intelligence and academic buoyancy resulted from a negative association between self-compassion and the achievement goal constructs. Thus, although emotional intelligence enhanced self-compassion, self-compassion was shown to undermine academic goal striving and subsequent academic buoyancy. This study broadens our understanding of the factors influencing academic buoyancy and underscores the potential drawbacks of excessive self-compassion.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, CLT, upon reasonable request.
References
Abel, J. R., & Deitz, R. (2014). Do the benefits of college still outweigh the costs? Current Issues in Economics and Finance, 20(3), 1–11.
Akın, A. (2008). Self-compassion and achievement goals: A structural equation modeling approach. Egitim Arastirmalari-Eurasian Journal of Educational Research, 31, 1–15.
Alpert, R., & Haber, R. N. (1960). Anxiety in academic achievement situations. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 61(2), 207–215.
Ames, C. (1992). Classrooms: Goals, structures, and student motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 84, 261–271. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.84.3.261
Anderman, E. M., Griesinger, T., & Westerfield, G. (1998). Motivation and cheating during early adolescence. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(1), 84–93. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.90.1.84
Anderson, R. C., Beach, P. T., Jacovidis, M. J. N., and Chadwick, K. L. (2020). Academic buoyancy and resilience for diverse students around the world. Retrieved May 23, 2022, from https://ibo.org/globalassets/publications/ib-research/policy/academic-resilience-research-brief-en.pdf
Avery, C., & Turner, S. (2012). Student loans: Do college students borrow too much or not enough? Journal of Economic Perspectives, 26, 165–192. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.26.1.165
Axelson, R. D., & Flick, A. (2010). Defining student engagement. Change: The magazine of higher learning, 43(1),38-43. https://doi.org/10.1080/00091383.2011.533096
Aydın, G., & Michou, A. (2020). Self-determined motivation and academic buoyancy as predictors of achievement in normative settings. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(4), 964–980. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12338
Bardach, L., Oczlon, S., Pietschnig, J., & Lüftenegger, M. (2020). Has achievement goal theory been right? A meta-analysis of the relation between goal structures and personal achievement goals. Journal of Educational Psychology, 112(6), 1197–1220. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000419
Bicaker, E., Lane, S. P., Sadikaj, G., & Racine, S. E. (2022). The roles of negative emotion intensity, negative emotion differentiation, and self-compassion in loss of control eating. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 55(7), 966–976. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.23723
Bieg, S., Reindl, M., & Dresel, M. (2017). The relation between mastery goals and intrinsic motivation among university students: A longitudinal study. Educational Psychology, 37(6), 666–679. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2016.1202403
Bland, H. W., Melton, B. F., Welle, P., & Bigham, L. (2012). Stress tolerance: New challenges for millennial college students. College Student Journal, 46(2), 362–376.
Briggs, A. R., Clark, J., & Hall, I. (2012). Building bridges: Understanding student transition to university. Quality in Higher Education, 18(1), 3–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/13538322.2011.614468
Chapin, K. (2015). The effect of emotional intelligence on student success. Journal of Adult Education, 44(1), 25–31.
Chatterjee, S., & Price, B. (1991). Regression analysis by example (2nd ed.). Wiley.
Ciarrochi, J., Dean, F. P., & Anderson, S. (2002). Emotional intelligence moderates the relationship between stress and mental health. Personality and Individual Differences, 32, 197–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(01)00012-5
Collie, R. J., Martin, A. J., Malberg, L., Hall, J., & Ginns, P. (2015). Academic buoyancy, student’s achievement, and the linking role of control: A cross-lagged analysis of high school students. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 85, 113–130. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12066
Datu, J. A. D., & Yuen, M. (2018). Predictors and consequences of academic buoyancy: A review of literature with implications for educational psychological research and practice. Contemporary School Psychology, 22(3), 207–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40688-018-0185-y
Davies, K. A., Lane, A. M., Devonport, T. J., & Scott, J. A. (2010). Validity and reliability of a brief emotional intelligence scale (BEIS-10). Journal of Individual Differences, 31, 198–208. https://doi.org/10.1027/1614-0001/a000028
Davis, S. K., & Nichols, R. (2016). Does emotional intelligence have a “dark” side? A review of the literature. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 1316.
Deemer, E. D., & Smith, J. L. (2018). Motivational climates: Assessing and testing how science classroom environments contribute to undergraduates’ self-determined and achievement-based science goals. Learning Environments Research, 21(2), 245–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-017-9252-y
Di Fabio, A., & Saklofske, D. H. (2021). The relationship of compassion and self-compassion with personality and emotional intelligence. Personality and Individual Differences, 169, 110109.
Egan, H., O’Hara, M., Cook, A., & Mantzios, M. (2021). Mindfulness, self-compassion, resiliency and wellbeing in higher education: A recipe to increase academic performance. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 46(3), 301–311.
Elliot, A. J. (2005). A conceptual history of the achievement goal construct. In A. J. Elliot & C. S. Dweck (Eds.), Handbook of Competence and Motivation (1st ed., pp. 52–72). The Guilford Press.
Elliot, A. J., & Church, M. A. (1997). A hierarchical model of approach and avoidance achievement motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 72(1), 218–232.
Elliot, A. J., & Hulleman, C. S. (2018). Achievement goals. In A. J. Elliot, C. S. Dweck, & D. S. Yeager (Eds.), Handbook of Competence and Motivation (2nd ed., pp. 43–60). The Guilford Press.
Elliot, A. J., & McGregor, H. A. (2001). A 2 x 2 achievement goal framework. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 8, 501–519. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.80.3.501
Elliot, A. J., Murayama, K., & Pekrun, R. (2011). A 3 x 2 achievement goal model. Journal of Educational Psychology, 103, 632–648. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0023952
Fenollar, P., Román, S., & Cuestas, P. J. (2007). University students’ academic performance: An integrative conceptual framework and empirical analysis. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 77, 873–891. https://doi.org/10.1348/000709907X189118
Ferguson, L. J., Kowalski, K. C., Mack, D. E., & Sabiston, C. M. (2014). Exploring self-compassion and eudaimonic well-being in young women athletes. Journal of sport and exercise psychology, 36(2), 203–216. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsep.2013-0096
Fong, C. J., & Kim, Y. W. (2021). A clash of constructs? Re-examining grit in light of academic buoyancy and future time perspective. Current Psychology, 40, 1824–1837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-018-0120-4
Hayes, A. F. (2018). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach (2nd ed.). The Guilford Press.
Heffernan, M., Quinn Griffin, M. T., McNulty, S. R., & Fitzpatrick, J. J. (2010). Self-compassion and emotional intelligence in nurses. International Journal of Nursing Practice, 16(4), 366–373.
Heublein, U., & Wolter, A. (2011). Studienabbruch in Deutschland. Def-inition, Häufigkeit, Ursachen, Maßnahmen [University dropout in Ger-many. Definition, frequency, reasons, provisions]. Zeitschrift fur Pada-gogik, 57, 214–236.
Huang, C. (2011). Achievement goals and achievement emotions: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 23(3), 359–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-011-9155-x
Hyde, J., Grieve, R., Norris, K., & Kemp, N. (2020). The dark side of emotional intelligence: The role of gender and the Dark Triad in emotional manipulation at work. Australian Journal of Psychology, 72(4), 307–317.
İskender, M. (2011). The influence of self-compassion on academic procrastination and dysfunctional attitudes. Educational Research and Reviews, 6(2), 230–234.
Jackson, L. M., Pancer, S. M., Pratt, M. W., & Hunsberger, B. E. (2000). Great expectations: The relation between expectancies and adjustment during the transition to university. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 30(10), 2100–2125. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2000.tb02427.x
Joseph, D. L., & Newman, D. A. (2010). Emotional intelligence: An integrative meta-analysis and cascading model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95, 54–78. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017286
Keeley, J., Smith, D., & Buskist, W. (2006). The teacher behaviors checklist: Factor analysis of its utility for evaluating teaching. Teaching of Psychology, 33(2), 84–91. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328023top3302_1
Kilduff, M., Chiaburu, D. S., & Menges, J. I. (2010). Strategic use of emotional intelligence in organizational settings: Exploring the dark side. Research in Organizational Behavior, 30, 129–152.
Kock, F., Berbekova, A., & Assaf, A. G. (2021). Understanding and managing the threat of common method bias: Detection, prevention and control. Tourism Management, 86, 104330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2021.104330
Kotera, Y., Taylor, E., Fido, D., Williams, D., & Tsuda-McCaie, F. (2021). Motivation of UK graduate students in education: Self-compassion moderates pathway from extrinsic motivation to intrinsic motivation. Current Psychology, 42(12), 10163–10176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02301-6
Lathren, C., Bluth, K., & Park, J. (2019). Adolescent self-compassion moderates the relationship between perceived stress and internalizing symptoms. Personality and Individualdifferences, 143, 36–41.
Liao, K. Y. H., Stead, G. B., & Liao, C. Y. (2021). A meta-analysis of the relation between self-compassion and self-efficacy. Mindfulness, 12(8), 1878–1891.
Liem, A. D., Lau, S., & Nie, Y. (2008). The role of self-efficacy, task value, and achievement goals in predicting learning strategies, task disengagement, peer relationship, and achievement outcome. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 33(4), 486–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2007.08.001
Liem, G. A. D., Ginns, P., Martin, A. J., Stone, B., & Herrett, M. (2012). Personal best goals and academic and social functioning: A longitudinal perspective. Learning and Instruction, 22(3), 222–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2011.11.003
Liu, G., Isbell, L. M., & Leidner, B. (2021). Quiet ego and subjective well-being: The role of emotional intelligence and mindfulness. Journal of Happiness Studies: An Interdisciplinary Forum on Subjective Well-Being, 22(6), 2599–2619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-020-00331-8
Lowe, P. A., & Lee, S. W. (2008). Factor structure of the Test Anxiety Inventory for Children and Adolescents (TAICA) scores across gender among students in elementary and secondary school settings. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 26(3), 231–246.
MacCann, C., Erbas, Y., Dejonckheere, E., Minbashian, A., Kuppens, P., & Fayn, K. (2020). Emotional intelligence relates to emotions, emotion dynamics, and emotion complexity: A meta-analysis and experience sampling study. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 36(3), 460–470. https://doi.org/10.1027/1015-5759/a000588
MacCann, C., Fogarty, G. J., Zeidner, M., & Roberts, R. D. (2011). Co** mediates the relationship between emotional intelligence (EI) and academic achievement. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 36, 60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2010.11.002
Maguire, R., Egan, A., Hyland, P., & Maguire, P. (2017). Engaging students emotionally: The role of emotional intelligence in predicting cognitive and affective engagement in higher education. Higher Education Research & Development, 36(2), 343–357. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2016.1185396
Martin, A. J., & Marsh, H. W. (2006). Academic resilience and its psychological and educational correlates: A construct validity approach. Psychology in the Schools, 43(3), 267–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.20149
Martin, A. J., & Marsh, H. W. (2008). Academic buoyancy: Towards an understanding of students’ everyday academic resilience. Journal of School Psychology, 46(1), 53–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2007.01.002
Martin, A. J., Yu, K., Ginns, P., & Papworth, B. (2017). Young people’s academic buoyancy and adaptability: A cross-cultural comparison of China with North America and the United Kingdom. Educational Psychology, 37(8), 930–946. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2016.1202904
Martins, A., Ramalho, N., & Morin, E. (2010). A comprehensive meta-analysis of the relationship between emotional intelligence and health. Personality and Individual Differences, 49(6), 554–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2010.05.029
Matthews, G., Zeidner, M., & Roberts, R. D. (2006). Models of personality and affect for education: A review and synthesis. In P. Alexander & P. H. Winne (Eds.), Handbook of Educational Psychology (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Mayer, J. D., & Salovey, P. (1993). The intelligence of emotional intelligence. Intelligence, 17(4), 433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/0160-2896(93)90010-3
Mayer, J. D., & Salovey, P. (1997). What is emotional intelligence? In D. J. Sluyter (Ed.), Emotional development and emotional intelligence: Educational implications (pp. 3–34). Basic Books.
Mayer, J. D., Roberts, R. D., & Barsade, S. G. (2008). Human abilities: Emotional intelligence. Annual Review of Psychology, 59, 507–536. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.59.103006.093646
Mayer, J. D., Caruso, D. R., & Salovey, P. (2016). The ability model of emotional intelligence: Principles and updates. Emotion Review, 8(4), 290–300. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073916639667
Meece, J. L., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Hoyle, R. H. (1988). Students’ goal orientations and cognitive engagement in classroom activities. Journal of Educational Psychology, 80(4), 514.
Meece, J. L., Anderman, E. M., & Anderman, L. H. (2006). Classroom goal structures, student motivation, and academic achievement. Annual Review of Psychology, 57, 487–503. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.56.091103.070258
Mikolajczak, M. (2009). Going beyond the ability-trait debate: The three-level model of emotional intelligence. E-Journal of Applied Psychology, 5(2), 25–31.
Mishra, P., Pandey, C. M., Singh, U., Gupta, A., Sahu, C., & Keshri, A. (2019). Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia, 22(1), 67–72. https://doi.org/10.4103/aca.ACA_157_18
Miyagawa, Y., Taniguchi, J., & Niiya, Y. (2018). Can self-compassion help people regulate unattained goals and emotional reactions toward setbacks? Personality and Individual Differences, 134, 239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2018.06.029
Mortimer, J. T. (2016). Changing experiences of work. In A. Furlong (Ed.), Handbook of Youth and Young Adulthood (2nd ed., pp. 149–156). Routledge.
Neff, K. D. (2003). The development and validation of a scale to measure self-compassion. Self and Identity, 2, 223–250. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298860309027
Neff, K. D. (2009). Self-compassion. In M. R. Leary & R. H. Hoyle (Eds.), Handbook of individual differences in social behavior (pp. 561–573). Guilford Press.
Neff, K. D. (2023). Self-compassion: Theory, method, research, and intervention. Annual Review of Psychology, 74, 193–218. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-032420-031047
Neff, K. D., & McGehee, P. (2010). Self-compassion and psychological resilience among adolescents and young adults. Self and identity, 9(3), 225–240.
Neff, K. D., Hsieh, Y. P., & Dejitterat, K. (2005). Self-compassion, achievement goals, and co** with academic failure. Self and identity, 4(3), 263–287. Chicago.
Neff, K. D., Kirkpatrick, K. L., & Rude, S. S. (2007). Self-compassion and adaptive psychological functioning. Journal of Research in Personality, 41, 139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2006.03.004
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). (2010). Education at a glance 2010: OECD indicators. OECD.
Peifer, C., Schulz, A., Schächinger, H., Baumann, N., & Antoni, C. H. (2014). The relation of flow-experience and physiological arousal under stress—Can u shape it? Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 53, 62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2014.01.009
Pekrun, R. (1992). The impact of emotions on learning and achievement: Towards a theory of cognitive/motivational mediators. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 41(4), 359–376. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-0597.1992.tb00712.x
Pekrun, R. (2006). The control-value theory of achievement emotions: Assumptions, corollaries, and implications for educational research and practice. Educational Psychology Review, 18, 315–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-006-9029-9
Pekrun, R., Goetz, T., Titz, W., & Perry, R. P. (2002). Academic emotions in students’ self-regulated learning and achievement: A program of qualitative and quantitative research. Educational Psychologist, 37(2), 91–105. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15326985EP3702_4
Pekrun, R., Frenzel, A. C., Goetz, T., & Perry, R. P. (2007). The control - value theory of achievement emotions: An integrative approach to emotions in education. In P. A. Schutz & R. Pekrun (Eds.), Emotion in Education (pp. 13–36). Amsterdam.
Pekrun, R., Marsh, H. W., Elliot, A. J., Stockinger, K., Perry, R. P., Vogl, E., Goetz, T., van Tilburg, W. A. P., Lüdtke, O., & Vispoel, W. P. (2023). A three-dimensional taxonomy of achievement emotions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 124(1), 145–178. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspp0000448
Petrides, K. V., Mikolajczak, M., Mavroveli, S., Sanchez-Ruiz, M.-J., Furnham, A., & Pérez-González, J.-C. (2016). Developments in trait emotional intelligence research. Emotion Review, 8(4), 335–341. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073916650493
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J.-Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879–903. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Putwain, D. W., Gallard, D., & Beaumont, J. (2020). Academic buoyancy protects achievement against minor academic adversities. Learning and Individual Differences, Advance Online Publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2020.101936
Putwain, D. W., & Symes, W. (2012). Achievement goals as mediators of the relationship between competence beliefs and test anxiety. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 82(2), 207–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8279.2011.02021.x
Raes, F., Pommier, E., Neff, K. D., & Van Gucht, D. (2011). Construction and factorial validation of a short form of the self-compassion scale. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 18(3), 250–255. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.702
Rodríguez-Gómez, D., Feixas, M., Gairín, J., & Muñoz, J. L. (2015). Understanding Catalan university dropout from a cross-national approach. Studies in Higher Education, 40(4), 690–703. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2013.842966
Sanchez-Ruiz, M.-J., Mavroveli, S., & Poullis, J. (2013). Trait emotional intelligence and its links to university performance: An examination. Personality and Individual Differences, 54(5), 658–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2012.11.013
Şenyuva, E., Kaya, H., Işik, B., & Bodur, G. (2014). Relationship between self-compassion and emotional intelligence in nursing students. International Journal of Nursing Practice, 20(6), 588–596.
Shapiro, D., Dundar, A., Huie, F., Wakhungu, P. K., Bhimdiwala, A., & Wilson, S. E. (2019). Completing college: A state-level view of student completion rates (Signature Report No. 16a). National Student Clearinghouse Research Center.
Shrout, P. E. (2011). Commentary: Mediation analysis, causal process, and cross-sectional data. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 46(5), 852–860. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273171.2011.606718
Sideridis, G. D., & Kaplan, A. (2011). Achievement goals and persistence across tasks: The roles of failure and success. The Journal of Experimental Education, 79(4), 429–451. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2010.539634
Skinner, E. A., Graham, J. P., Brule, H., Rickert, N., & Kindermann, T. A. (2020). “I get knocked down but I get up again”: Integrative frameworks for studying the development of motivational resilience in school. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 44(4), 290–300. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025420924122
Sutherland, L. M., Kowalski, K. C., Ferguson, L. J., Sabiston, C. M., Sedgwick, W. A., & Crocker, P. R. (2014). Narratives of young women athletes’ experiences of emotional pain and self-compassion. Qualitative Research in Sport, Exercise and Health, 6(4), 499–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/2159676X.2014.888587
Tajoldini, S., Tohidi, A., & Mousavinasab, H. (2018). The effect of mindfulness-based-stress reduction (MBSR) training on academic buoyancy and academic self-regulation in high school students. Journal of Educational Psychology Studies, 15(31), 59–88. https://doi.org/10.22111/JEPS.2018.4267
Thomas, C. L. (2021). Predicting test anxiety using the 3x2 achievement goal model. International Journal of School and Educational Psychology, 10(2), 232–242. https://doi.org/10.1080/21683603.2020.1816237
Thomas, C. L., & Allen, K. (2021). Driving engagement: Investigating the influence of emotional intelligence and academic buoyancy on student engagement. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 45, 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/0309877X.2020.1741520
Thomas, C. L., Sung, W., Bretl, B. (2023). Emotional intelligence and anxiety in university students: Evidence of a curvilinear relationship. The Journal of Further and Higher Education. Advance Online Publication. https://doi.org/10.1080/0309877X.2023.2185773.
Udayar, S., Fiori, M., & Bausseron, E. (2020). Emotional intelligence and performance in a stressful task: The mediating role of self-efficacy. Personality and Individual Differences, 156, 109790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2019.109790
Vassiou, A., Mouratidis, A., Andreou, E., & Kafetsios, K. (2016). Students’ achievement goals, emotion perception ability and affect and performance in the classroom: A multilevel examination. Educational Psychology, 36(5), 879–897. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2014.950192
Vignoles, A. F., & Powdthavee, N. (2009). The socioeconomic gap in university dropouts. BE journal of economic analysis & policy, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.2202/1935-1682.2051
What Works Clearinghouse (2020). What works clearinghouse standards handbook, version 4.1. US Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences. National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance. https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/handbooks
Wintre, M. G., & Bowers, C. D. (2007). Predictors of persistence to graduation: Extending a model and data on the transition to university model. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science / Revue Canadienne Des Sciences Du Comportement, 39(3), 220–234. https://doi.org/10.1037/cjbs2007017
Wohl, M. J., Salmon, M. M., Hollingshead, S. J., Lidstone, S. K., & Tabri, N. (2017). The dark side of self-forgiveness: Forgiving the self can impede change for ongoing, harmful behavior. Handbook of the psychology of self-forgiveness (pp. 147–159). Springer, Cham.
Wolters, C. A. (2004). Advancing achievement goal theory: Using goal structures and goal orientations to predict students’ motivation, cognition, and achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 96(2), 236–250. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.96.2.236
Wrosch, C., Scheier, M. F., Miller, G. E., Schulz, R., & Carver, C. S. (2003). Adaptive self-regulation of unattainable goals: Goal disengagement, goal reengagement, and subjective well-being. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 29(12), 1494–1508. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167203256921
Wrosch, C., Scheier, M. F., & Miller, G. E. (2013). Goal adjustment capacities, subjective well-being, and physical health. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 7(12), 847–860.
Wunsch, G., Russo, F., & Mouchart, M. (2010). Do we necessarily need longitudinal data to infer causal relations? Bulletin of Sociological Methodology/bulletin De Méthodologie Sociologique, 106(1), 5–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/0759106309360114
Yu, K., & Martin, A. J. (2014). Personal best (PB) and ‘classic’ achievement goals in the Chinese context: Their role in predicting academic motivation, engagement and buoyancy. Educational Psychology, 34(5), 635–658. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2014.895297
Zessin, U., Dickhäuser, O., & Garbade, S. (2015). The relationship between self-compassion and well-being: A meta-analysis. Applied Psychology: Health and Well-Being, 7(3), 340–364.
Acknowledgements
ChatGPT (https://chat.openai.com) was used to proofread the manuscript and identify grammatical/stylistic errors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, C.L., Allen, K. & Sung, W. Emotional Intelligence and Academic Buoyancy in University Students: The Mediating Influence of Self-Compassion and Achievement Goals. Trends in Psychol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43076-024-00363-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43076-024-00363-6