Abstract
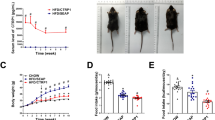
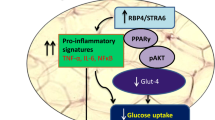
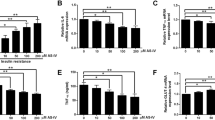
To investigate the impact of Sitagliptin against obesity and the underlying mechanism. Obese immature mice were treated with 10, 30, and 90 mg/kg Sitagliptin, respectively. The body weights were recorded and the level of serum biochemical indexes were detected. The visceral fat ratio of each mouse was determined. The pathological change in adipose tissues was determined by HE staining, while F4/80 and CD206 levels in adipose tissues were determined by the immunohistochemical analysis. Lipid formation was evaluated by Oil red O staining assay. RAW264.7 cells were stimulated using oxLDL, followed by being incubated with different concentrations of Sitagliptin. The release of ADPN, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and the activity of SOD, was measured by ELISA assay. Western blotting was applied to determine adipsin, Nrf2, Keap1, and HO-1 protein levels. ROS level was checked using the DCFH-DA assay. RT-PCR assay was utilized to detect the mRNA levels of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, Nrf2, Keap1, and HO-1. The body weight gain, infiltration of multinucleated cells, enlarged size of adipocytes, increased lipid accumulation, elevated visceral fat ratio, declined ADPN level, upregulated adipsin, and disordered serum biochemical indexes in obese immature mice were statistically significantly reversed by Sitagliptin. Excessive release of inflammatory factors and upregulated F4/80 and CD206 were observed in obese immature mice, which were statistically significantly repressed by Sitagliptin. Furthermore, the elevated MDA level, increased SOD activity, and inhibited Nrf2 pathway in obese immature mice were significantly reversed by Sitagliptin. In oxLDL stimulated RAW264.7 cells, increased release of inflammatory factors, ROS, and MDA, elevated SOD activity, and inactivated Nrf2 pathway were observed, which were statistically significantly abolished by the treatment of Sitagliptin. Sitagliptin alleviated obesity in immature mice by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Yoshida Y, Simoes EJ. Sugar-Sweetened Beverage, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents: Policies, Taxation, and Programs. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18:31.
Reinehr T, Wabitsch M. Childhood obesity. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011;22:21–5.
Hassapidou M, Tzotzas T, Makri E, Pagkalos I, Kaklamanos I, Kapantais E, et al. Prevalence and geographic variation of abdominal obesity in 7- and 9-year-old children in Greece; World Health Organization Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative 2010. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:126.
Chen S, Binns CW, Zhang Y. The importance of definition in diagnosing obesity: a review of studies of children in China. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2012;24:248–62.
Kinlen D, Cody D, O’Shea D. Complications of obesity. QJM. 2018;111:437–43.
Sies H. Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015;4:180–3.
Keaney JF Jr, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Wilson PW, Lipinska I, Corey D, et al. Obesity and systemic oxidative stress: clinical correlates of oxidative stress in the Framingham Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:434–9.
Strauss RS. Comparison of serum concentrations of alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene in a cross-sectional sample of obese and nonobese children (NHANES III). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Pediatr. 1999;134:160–5.
Pérez-Torres I, Castrejón-Tellez V, Soto ME, Rubio-Ruiz ME, Manzano-Pech L, Guarner-Lans V. Oxidative stress, plant natural antioxidants, and obesity. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1786.
Scott LJ. Sitagliptin: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes. Drugs. 2017;77:209–24.
Barnett A. DPP-4 inhibitors and their potential role in the management of type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract. 2006;60:1454–70.
Ji Y, Nyamagoud SB, SreeHarsha N, Mishra A, Gubbiyappa SK, Singh Y. Sitagliptin protects liver against aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity through upregulating Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 pathway. BioFactors. 2020;46:76–82.
Chan J, Telang R, Kociszewska D, Thorne PR, Vlajkovic SM. A high-fat diet induces low-grade cochlear inflammation in CD-1 mice. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23(9):5179.
Brestoff JR, Artis D. Immune regulation of metabolic homeostasis in health and disease. Cell. 2015;161:146–60.
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993;259:87–91.
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:1821–30.
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:1796–808.
Engin A. The Pathogenesis of Obesity-Associated Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:221–45.
Wang Y, Tang B, Long L, Luo P, **ang W, Li X, et al. Improvement of obesity-associated disorders by a small-molecule drug targeting mitochondria of adipose tissue macrophages. Nat Commun. 2021;12:102.
Kania DS, Gonzalvo JD, Weber ZA. Saxagliptin: a clinical review in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther. 2011;33:1005–22.
Shan B, Wang X, Wu Y, Xu C, **a Z, Dai J, et al. The metabolic ER stress sensor IRE1alpha suppresses alternative activation of macrophages and impairs energy expenditure in obesity. Nat Immunol. 2017;18:519–29.
Kawanishi N, Yano H, Yokogawa Y, Suzuki K. Exercise training inhibits inflammation in adipose tissue via both suppression of macrophage infiltration and acceleration of phenotypic switching from M1 to M2 macrophages in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2010;16:105–18.
Shin S, Wakabayashi J, Yates MS, Wakabayashi N, Dolan PM, Aja S, et al. Role of Nrf2 in prevention of high-fat diet-induced obesity by synthetic triterpenoid CDDO-imidazolide. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009;620:138–44.
Yu Z, Shao W, Chiang Y, Foltz W, Zhang Z, Ling W, et al. Oltipraz upregulates the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 [corrected](NRF2) antioxidant system and prevents insulin resistance and obesity induced by a high-fat diet in C57BL/6J mice. Diabetologia. 2011;54:922–34.
Nagata N, Xu L, Kohno S, Ushida Y, Aoki Y, Umeda R, et al. Glucoraphanin Ameliorates Obesity and Insulin Resistance Through Adipose Tissue Browning and Reduction of Metabolic Endotoxemia in Mice. Diabetes. 2017;66:1222–36.
Tarantini S, Valcarcel-Ares MN, Yabluchanskiy A, Tucsek Z, Hertelendy P, Kiss T, et al. Nrf2 Deficiency Exacerbates Obesity-Induced Oxidative Stress, Neurovascular Dysfunction, Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption, Neuroinflammation, Amyloidogenic Gene Expression, and Cognitive Decline in Mice, Mimicking the Aging Phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2018;73:853–63.
A JIR, Uddandrao VVS, G S, G S, P C, S S, et al. Biochanin A attenuates obesity cardiomyopathy in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation through the Nrf-2 pathway. Arch Physiol Biochem 2021;129(3):788–798. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2021.1874017.
Funding
NA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chaochun Zou designed the research and wrote the original draft. **aoying Wang performed experiments. Wenbo Weng performed the analysis. Yifei Cui confirms the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethic Statements
All animal experiments involved in this manuscript were authorized by the animal experimentation ethical committee of Zhejiang Yingyang Pharmaceutical Research and Development Co., LTD (Certificate No. ZJEY-20211118–02).
Patient consent for publication
NA.
Competing interests
The authors declare there is no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Weng, W., Cui, Y. et al. Sitagliptin Alleviates Obesity in Immature Mice by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Reprod. Sci. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-024-01623-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-024-01623-7