Abstract
Background
Shoulder strength evaluation is a recommended procedure in musculoskeletal rehabilitation.
Aim
To examine hand-held sphygmomanometer (HHS) and hand-held dynamometer (HHD) intra- and inter-rater reliability during isometric shoulder external and internal rotation strength testing in prone rotation position in asymptomatic participants, and to compare these two testing modalities.
Design
Reliability study.
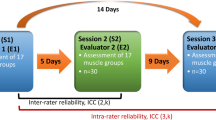
Methods
A total of 20 asymptomatic participants (27.7 ± 7.4 years; 77.1 ± 10.1 kg) attended a strength assessment consisting of HHS and HHD tests. Reliability was assessed using the intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), coefficient of variation (CV) with 95%CI, and standard error of measurement (SEM). Pearson correlation and linear regression analysis were used to compare HHS and HHD testing modalities.
Results
“Good” to “excellent” intra (ICC range = 0.896 to 0.979) and inter-rater reliability scores (ICC range = 0.850 to 0.978) were displayed during both HHS and HHD tests during internal and external rotation strength assessments. Linear relationships between HHS and HHD measures were found, with coefficients of determination (R2) ranging between 0.60 and 0.79.
Conclusion
HHS and HHD resulted to be reliable strength assessment modalities for clinical practice. These assessment modes can be equally valid in assessing intra and inter-limb asymmetries in isometric shoulder rotation strength. The affordability and availability of HHS in ordinary clinical settings can facilitate its implementation in musculoskeletal practice.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Suchomel TJ, Nimphius S, Bellon CR, Stone MH. The importance of muscular strength: training considerations. Sports Med. 2018;48(4):765–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-018-0862-z.
Maestroni L, Read P, Bishop C, Papadopoulos K, Suchomel TJ, Comfort P, Turner A. The benefits of strength training on musculoskeletal system health: practical applications for interdisciplinary care. Sports Med. 2020;50(8):1431–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-020-01309-5.
Bettariga F, Turner A, Maloney S, Maestroni L, Jarvis P, Bishop C. The effects of training interventions on interlimb asymmetries: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Strength Cond J. 2022;44(5):69–86.
Byram IR, Bushnell BD, Dugger K, Charron K, Harrell Jr FE, Noonan TJ. Preseason shoulder strength measurements in professional baseball pitchers: identifying players at risk for injury. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(7):1375–82.
Kwan C-K, Ko M-C, Fu S-C, Leong H-T, Ling SK, Oh J-H, Yung PS. Are muscle weakness and stiffness risk factors of the development of rotator cuff tendinopathy in overhead athletes: a systematic review. Therapeutic Adv Chronic Disease. 2021;12:20406223211026178.
Edouard P, Degache F, Oullion R, Plessis J-Y, Gleizes-Cervera S, Calmels P. Shoulder strength imbalances as injury risk in handball. Int J Sports Med. 2013;34(7):654–60.
Maestroni L, Marelli M, Gritti M, Civera F, Rabey M. External rotator strength deficits in non-athletic people with rotator cuff related shoulder pain are not associated with pain intensity or disability levels. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020;48:102156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msksp.2020.102156.
Vigolvino LP, Barros BRS, Medeiros CEB, Pinheiro SM, Sousa CO. Analysis of the presence and influence of Glenohumeral Internal Rotation Deficit on posterior stiffness and isometric shoulder rotators strength ratio in recreational and amateur handball players. Phys Ther Sport. 2020;42:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ptsp.2019.12.004.
Miller JE, Higgins LD, Dong Y, Collins JE, Bean JF, Seitz AL, Katz JN, Jain NB. Association of Strength Measurement with Rotator Cuff tear in patients with Shoulder Pain: the Rotator Cuff Outcomes Workgroup Study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;95(1):47–56. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0000000000000329.
McLaine SJ, Ginn KA, Fell JW, Bird M-L. Isometric shoulder strength in young swimmers. J Sci Med Sport. 2018;21(1):35–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2017.05.003.
Lee SM, Seo YG, Park WH, Yoo JC. Preoperative Rotator muscle strength ratio predicts shoulder function in patients after Rotator Cuff Repair. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020;8(2):2325967119899346–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967119899346.
McLaine SJ, Bird M-L, Ginn KA, Hartley T, Fell JW. Shoulder extension strength: a potential risk factor for shoulder pain in young swimmers? J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(5):516–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2018.11.008.
Hams AH, Evans K, Adams R, Waddington G, Witchalls J. Shoulder internal and external rotation strength and prediction of subsequent injury in water-polo players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2019;29(9):1414–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13459.
Hopman K, Krahe L, Lukersmith S, McColl AR, Vine K. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of rotator cuff syndrome in the workplce. The University of New South Wales. 2013. http://rcs.med.unsw.edu.au/rotatorcuffsyndromeguidelines.
Cools AM, Vanderstukken F, Vereecken F, Duprez M, Heyman K, Goethals N, Johansson F. Eccentric and isometric shoulder rotator cuff strength testing using a hand-held dynamometer: reference values for overhead athletes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(12):3838–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3755-9.
Riemann BL, Davies GJ, Ludwig L, Gardenhour H. Hand-held dynamometer testing of the internal and external rotator musculature based on selected positions to establish normative data and unilateral ratios. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(8):1175–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2010.05.021. 2010/09/21.
Nagatomi T, Mae T, Nagafuchi T, Yamada S-I, Nagai K, Yoneda M. Shoulder manual muscle resistance test cannot fully detect muscle weakness. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(7):2081–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4380-y.
Ashworth B, Hogben P, Singh N, Tulloch L, Cohen DD. The Athletic Shoulder (ASH) test: reliability of a novel upper body isometric strength test in elite rugby players. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2018;4(1): e000365. https://doi/org/10.1136/bmjsem-2018-000365.
Stark T, Walker B, Phillips JK, Fejer R, Beck R. Hand-held dynamometry correlation with the gold standard isokinetic dynamometry: a systematic review. PM R. 2011;3(5):472–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2010.10.025.
Dollings H, Sandford F, O’ Conaire E, Lewis JS. Shoulder strength testing: the intra- and inter-tester reliability of routine clinical tests, using the PowerTrack™ II Commander. Shoulder Elbow. 2017;4(2):131–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1758-5740.2011.00162.x.
Roy JS, MacDermid JC, Orton B, Tran T, Faber KJ, Drosdowech D, Athwal GS. The concurrent validity of a hand-held versus a stationary dynamometer in testing isometric shoulder strength. J Hand Ther. 2009;22(4):320–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2009.04.008.
Holt KL, Raper DP, Boettcher CE, Waddington GS, Drew MK. Hand-held dynamometry strength measures for internal and external rotation demonstrate superior reliability, lower minimal detectable change and higher correlation to isokinetic dynamometry than externally-fixed dynamometry of the shoulder. Phys Ther Sport. 2016;21:75–81.
Perossa DR, Dziak M, Vernon HT, Hayashita K. The intra-examiner reliability of manual muscle testing of the hip and shoulder with a modified sphygmomanometer: a preliminary study of normal subjects. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 1998;42(2):73–82.
Toohey L, De Noronha M, Nunes G. The use of a sphygmomanometer to measure shoulder isometric strength: a validity and reliability study. O uso do esfigmomanômetro para mensurar força isométrica do ombro: um estudo de validade e confiabilidade. Fisioterapia e Movimento. 2017;30(3):585–91. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5918.030.003.AO17.
Barbosa A, Intelangelo L, Bordachar D, Fernandes I, Cardoso D, Fernandes I, Porfirio W, Felicio D. Validity and reliability of shoulder strength assessment during scaption, internal rotation and external rotation using an anchored, non-modified sphygmomanometer. Human Movement. 2018;19(2):90–8. https://doi.org/10.5114/hm.2018.74064.
McLaine SJ, Ginn KA, Kitic CM, Fell JW, Bird M-L. The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a Handheld Dynamometer. J Sport Rehabil. 2016;25(2):2015-0034. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsr.2015-0034.
Boettcher CE, Ginn KA, Cathers I. Which is the optimal exercise to strengthen supraspinatus? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41(11):1979–83. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181a740a7.
Souza LAC, Martins JC, Moura JB, Teixeira-Salmela LF, De Paula FVR, Faria CDCM. Assessment of muscular strength with the modified sphygmomanometer test: what is the best method and source of outcome values? Braz J Phys Ther. 2014;18(2):191–200. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-35552012005000149.
Koo TK, Li MY. A Guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med. 2016;15(2):155–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012.
Weir JP. Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and the SEM. J Strength Cond Res. 2005;19(1):231–40.
Turner A, Brazier J, Bishop C, Chavda S, Cree J, Read P. Data analysis for strength and conditioning coaches: using excel to analyze reliability, differences, and relationships. Strength Cond J. 2015; 37(1):76–83.
Borg DN, Bach AJ, O’Brien JL, Sainani KL. Calculating sample size for reliability studies. PM R. 2022;14(8):1018–25.
Bhinderwala S, Bedekar N. Reliability of modified sphygmomanometer for measurement of maximum isometric shoulder muscle strength. Physiotherapy. 2019;13(1):9–13. https://doi.org/10.4103/pjiap.Pjiap_15_18.
Funding
No sources of funding were used to assist in the preparation of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FB and LM: concept, design, testing and writing the first version of the manuscript. FB and FC: ethics. LM, NFL, SL and FB: statistical analysis. NFL, LiM, FC, SL: writing and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Francesco Bettariga, Nicola Francesco Lopomo, Fabio Civera, Stefano Lazzarini, Lisa Mantovani, Luca Maestroni declare that they have no conflict of interest relevant to the content of this review.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bettariga, F., Lopomo, N.F., Civera, F. et al. Reliability and Validity of Hand-Held Dynamometer and Hand-Held Sphygmomanometer for Testing Shoulder Isometric External and Internal Rotator Muscles Strength. J. of SCI. IN SPORT AND EXERCISE (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42978-023-00232-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42978-023-00232-1