Abstract
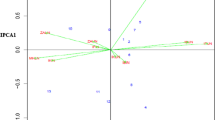
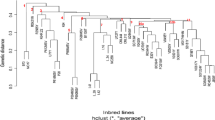
Genetic dissection of high kernel row numbers (KRNs) trait and cob length has been undertaken by several researchers resulting in identification of loci controlling the traits. Further fine map** of QTLs controlling KRN and cob length and TILLING strategies identified the underlying genes. All these studies are used temperate maize genotypes which are of limited use to researcher in sub-tropical region and the sub-tropical maize production systems. Present investigation explores the availability of genetic regions responsible for KRN in sub-tropical maize germplasm. A total of 280 sub-tropical maize germplasm were analyzed for their KRN variation and selected 45 stable lines were subjected to molecular characterization using genes linked to KRN in maize. Diversity analysis was also performed to understand the possible association of character with the KRN gene in deciding its variation in the given population. It was revealed that four genes showed highest probability of influencing KRN traits in these tropical maize inbred lines. The remaining genes not establishing specific pattern of association with high and low KRN genotypes may need further study on its allelic variation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bomblies K, Doebley JF (2006) Pleiotropic effects of the duplicate maize FLORICAULA/LEAFY genes zfl1 and zfl2 on traits under selection during maize domestication. Genetics 172:519–531 (PMID: 16204211)
Bomblies K, Wang RL, Ambrose BA, Schmidt RJ, Meeley RB, Doebley J (2003) Duplicate FLORICA/LEAFY homologs zfl1 and zfl2 control inflorescence architecture and flower pattern in maize. Development 130:2385–2395
Bommert P, Lunde C, Nardmann J, Vollbrecht E, Running M, Jackson D, Hake S, Werr W (2005) thick tassel dwarf1 encodes a putative maize ortholog of the Aspringdopsis CLAVATA1 leucine-rich repeat receptor like kinase. Development 132:1235–1245 (PMID: 15716347)
Bommert P, Je BI, Goldshmidt A, Jackson D (2013a) The maize Gα gene COMPACT PLANT2 functions in CLAVATA signalling to control shoot meristem size. Nature 502:555–558. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12583. (PMID: 24025774)
Bommert P, Nagasawa NS, Jackson D (2013b) Quantitative variation in maize kernel row number is controlled by the FASCIATED EAR2 locus. Nat Genet 45(3):334–337. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2534. (PMID: 23377180)
Bortiri E, Chuck G, Vollbrecht E, Rocheford T, Martienssen R, Hake S (2006) ramosa2 encodes a lateral organ boundary domain protein that determines the fate of stem cells in branch meristems of maize. Plant Cell 18:574–585
Brown PJ, Upadyayula N, Mahone GS, Tian F, Bradbury PJ et al (2011) Distinct genetic architectures for male and female inflorescence traits of maize. PLoS Genet 7(11):e1002383
Calderón CI, Yandell BS, Doebley JF (2016) Fine map** of a QTL associated with kernel row number on chromosome 1 of maize. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0150276
Chuck G, Meeley RB, Hake S (1998) The control of maize spikelet meristem fate by the APETALA2-like gene indeterminate spikelet1. Genes Dev 12:1145–1154
Chuck G, Cigan AM, Saeteurn K, Hake S (2007) The heterochronic maize mutant Corngrass1 results from overexpression of a tandem microRNA. Nat Genet 39(4):544–549 (PMID: 17369828)
Chuck G, Whipple C, Jackson D, Hake S (2010) The maize SBP-box transcription factor encoded by tasselsheath4 regulates bract development and the establishment of meristem boundaries. Development 137:1243–1250. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.048348. (PMID: 20223762)
Chuck GS, Brown PJ, Meeley R, Hake S (2014) Maize SBP-box transcription factors unbranched2 and unbranched3 affect yield traits by regulating the rate of lateral primordia initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(52):18775–18780. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1407401112. (PMID: 25512525)
Dass S, Kaul J, Manivannan A, Singode A, Chikkappa GK (2009) Single cross hybrid maize—A viable solution in the changing climate Scenario. Indian J Genet 69(4):331–334
Gallavotti A, Long JA, Stanfield S, Yang X, Jackson D, Vollbrecht E, Schmidt RJ (2010) The control of axillary meristem fate in the maize ramosa pathway. Stem Cells Dev 2856:2849–2856
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (1989) Applied Logistic Regression. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Je BI, Gruel J, Lee YK, Bommert P, Arevalo ED, Eveland AL, Wu Q, Goldshmidt A, Meeley R, Bartlett M, Komatsu M, Sakai H, Jönsson H, Jackson D (2016) Signaling from maize organ primordia via FASCIATED EAR3 regulates stem cell proliferation and yield traits. Nature Genet 48(7):785–791
Li M, Zhong W, Yang F, Zhang Z (2018) Genetic and molecular mechanisms of quantitative trait loci controlling maize inflorescence architecture. Plant Cell Physiol 59(3):448–457
Liu L, Du Y, Shen X, Li M, Sun W, Huang J, Liu Z, Tao Y, Zheng Y, Yan J, Zhang Z (2015) KRN4 controls quantitative variation in maize kernel row number. PLoS Genet 11(11):e1005670. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005670
Lu M, ** of quantitative trait loci for kernel row number in maize across seven environments. Mol Breed 28:143–152
McSteen P (2006) Branching out: the ramosa pathway and the evolution of grass inflorescence morphology. Plant Cell 18(3):518–522 (PMID: 16513602)
Messmer R, Fracheboud Y, Bänziger M, Vargas M, Stamp P, Ribaut JM (2009) Drought stress and tropical maize: QTL-by-environment interactions and stability of QTLs across environments for yield components and secondary traits. Theor Appl Genet 119(5):913–930
Mukri G, Kumar R, Rajendran A, Kumar B, Hooda KS, Karjagi CG, Singh V, Jat SL, Das AK, Sekhar JC, Singh SB (2018) Strategic selection of white maize inbred lines for tropical adaptation and their utilization in develo** stable, medium to long duration maize hybrids. Maydica 63:1–8
Pautler M, Eveland AL, LaRue T, Yang F, Weeks R, Lunde C et al (2015) FASCIATED EAR4 encodes a bZIP transcription factor that regulates shoot meristem size in maize. Plant Cell 27:104–120. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.132506
Peng B, Li Y, Wang Y, Liu C, Liu Z, Tan W, Li Y (2011) QTL analysis for yield components and kernel-related traits in maize across multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 122(7):1305–1320
Rakshit S, Ganapathy KN, Gomashe SS, Rathore A, Ghorade RB, Nagesh Kumar MV, Ganesmurthy K, Jain SK, Kamtar MY, Sachan JS, Ambekar SS, Ranwa BR, Kanawade DG, Balusamy M, Kadam D, Sarkar A, Tonapi VA, Patil JV (2012) GGE biplot analysis to evaluate genotype, environment and their interactions in sorghum multi-location data. Euphytica 185:465–479
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNAsepacer-length polymorphism in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81:8014–8019
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Nagasawa N, Malcomber S, Sakai H, Jackson D (2006) A trehalose metabolic enzyme controls inflorescence architecture in maize. Nature 441:227–230
Shen X, Zhao R, Liu L, Zhu C, Li M, Du H, Zhang Z (2019) Identification of a candidate gene underlying qKRN5b for kernel row number in Zea mays L. Theor Appl Genet 132:3439–3448
Sigmon B, Vollbrecht E (2010) Evidence of selection at the ramosa1 locus during maize domestication. Mol Ecol 19:1296–1311
Stuber CW, Edwards MD, Wendel JF (1987) Molecular marker facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize. II. Factors influencing yield and its component traits. Crop Sci 27(4):639–648
Taguchi-Shiobara F, Yuan Z, Hake S, Jackson D (2001) The fascinated ear2 gene encodes a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein that regulates shoot meristem proliferation in maize. Genes Dev 15:2755–2766
Toledo FHRB, Ramalho MAP, Abreu GB, de Souza JC (2011) Inheritance of kernel row number, a multicategorical threshold trait of maize ears. Genet Mol Res 10(3):2133–2139
Upadyayula N, Silva HS, Bohn MO, Rocheford TR (2006) Genetic and QTL analysis of maize tassel and ear inflorescence architecture. Theor Appl Genet 112(4):592–606
Veldboom LR, Lee M (1994) Molecular-marker-facilitated studies of morphological traits in maize. II: determination of QTLs for grain-yield and yield components. Theor Appl Genet 89(4):451–458
Weil CF, Monde R-A (2007) Induced mutations in maize. Israel J Plant Sci 55(2):183–190
Wu X, Skirpan A, McSteen P (2009) Suppressor of sessile spikelets1 functions in the ramosa pathway controlling meristem determinacy in maize. Plant Physiol 149:205–219
**ao Y, Liu H, Wu L, Warburton M, Yan J (2017) Genome-wide association studies in maize: praise and stargaze. Mol Plant 10(3):359–374
Yi Q, Liu Y, Hou X, Zhang X, Li H, Zhang J, Liu H, Hu Y, Yu G, Li Y, Wang Y, Huang Y (2019) Genetic dissection of yield-related traits and mid-parent heterosis for those traits in maize (Zea mays L.). BMC Plant Biol 19(1):392. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2009-2
Acknowledgements
This study is the output of an external project funded by DST-SERB, New Delhi. Authors are thankful for the financial support by the DST, New Delhi
Funding
This study was funded by DST-SERB, New Delhi, India, with the Grant No. EEQ/2016/000447. This grant was received by author1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors are declaring that there is no conflict of interest exists.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Hence, it does not require any ethical approval.
Additional information
Communicated by Ahmad Mohammad Alqudah.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mukri, G., Gadag, R.N., Bhat, J.S. et al. Characterization of sub-tropical maize (Zea Mays L.) inbred lines for the variation in kernel row numbers (KRNs). CEREAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 52, 277–285 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-023-00386-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-023-00386-2