Abstract
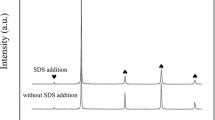
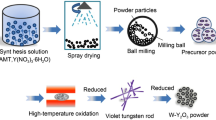
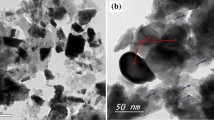
Y2O3-doped tungsten (W–Y2O3) composite powders prepared by a traditional chemical co-precipitation method possess obvious bimodal distribution in size, which would deteriorate their sintering properties. The bimodal distribution can be effectively eliminated by an improved chemical co-precipitation method, in which the cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) was innovatively employed. The reduced powders with excellent uniformity have an average grain size of only ~ 31.5 nm. It is noteworthy that Y2O3 particles would fuse and grow with the growth of W grains during subsequent spark plasma sintering (SPS) process, which was rarely reported in relevant literature before. On top of that, phase interfaces of sintered W–Y2O3 alloys were systematically analyzed. Compared to the intracrystalline oxygen content, the oxygen content at W/Y2O3 phase boundaries is relatively higher. It can be found that the (110) crystal planes of W form coherent, semi-coherent, and non-coherent interfaces with different crystal planes of Y2O3. The weak interfacial bonding strength between W and Y2O3 phases results from relatively more oxygen impurities as well as more semi-coherent/non-coherent interfaces at phase boundaries compared with the inner W grains.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 August 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-021-00115-4
References
Zhao M, Zhou Z, Ding Q, Zhong M, Arshad K. Effect of rare earth elements on the consolidation behavior and microstructure of tungsten alloys. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2015;48:19.
Stewart DA, Shipway PH, McCartney DG. Abrasive wear behaviour of conventional and nanocomposite HVOF-sprayed WC-Co coatings. Wear. 1999;225–229(Part 2):789.
Moitra A, Kim S, Kim SG, Park SJ, German RM, Horstemeyer MF. Investigation on sintering mechanism of nanoscale tungsten powder based on atomistic simulation. Acta Mater. 2010;58(11):3939.
Smid I, Akiba M, Vieider G, Plöchl L. Development of tungsten armor and bonding to copper for plasma-interactive components. J Nucl Mater. 1998;258–263(Part 1):160.
Zhang S, Wen Y, Zhang H. Low temperature preparation of tungsten nanoparticles from molten salt. Powder Technol. 2014;253:464.
Kurishita H, Kobayashi S, Nakai K, Ogawa T, Hasegawa A, Abe K, Arakawa H, Matsuo S, Takida T, Takebe K, Kawai M, Yoshida N. Development of ultra-fine grained W–(0.25–0.8)wt%TiC and its superior resistance to neutron and 3 MeV He-ion irradiations. J Nucl Mater. 2008;377(1):34.
Tokar MZ, Coenen JW, Philipps V, Ueda Y, the TEXTOR Team. Tokamak plasma response to droplet spraying from melted plasma-facing components. Nucl Fusion. 2012;52(1):13013.
Norajitra P, Boccaccini LV, Diegele E, Filatov V, Gervash A, Giniyatulin R, Gordeev S, Heinzel V, Janeschitz G, Konys J, Krauss W, Kruessmann R, Malang S, Mazul I, Moeslang A, Petersen C, Reimann G, Rieth M, Rizzi G, Rumyantsev M, Ruprecht R, Slobodtchouk V. Development of a helium-cooled divertor concept: design-related requirements on materials and fabrication technology. J Nucl Mater. 2004;329–333(Part B):1594.
Liu R, **e ZM, Zhang T, Fang QF, Wang XP, Hao T, Liu CS, Dai Y. Mechanical properties and microstructures of W-1%Y2O3 microalloyed with Zr. Mater Sci Eng A. 2016;660:19.
Ryu T, Hwang KS, Choi YJ, Sohn HY. The sintering behavior of nanosized tungsten powder prepared by a plasma process. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2009;27(4):701.
Yar MA, Wahlberg S, Bergqvist H, Salem HG, Johnsson M, Muhammed M. Chemically produced nanostructured ODS–lanthanum oxide–tungsten composites sintered by spark plasma. J Nucl Mater. 2011;408(2):129.
Veleva L, Oksiuta Z, Vogt U, Baluc N. Sintering and characterization of W–Y and W–Y2O3 materials. Fusion Eng Des. 2009;84(7–11):1920.
Liu N, Dong Z, Ma Z, Yu L, Li C, Liu C, Guo Q, Liu Y. Eliminating bimodal structures of W–Y2O3 composite nanopowders synthesized by wet chemical method via controlling reaction conditions. J Alloys Compd. 2019;774:122.
Kim Y, Lee KH, Kim EP, Cheong DI, Hong SH. Fabrication of high temperature oxides dispersion strengthened tungsten composites by spark plasma sintering process. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2009;27(5):842.
Lv Y, Fan J, Han Y, Liu T, Li P, Yan H. The influence of modification route on the properties of W-0.3 wt%Y2O3 powder and alloy prepared by nano-in situ composite method. J Alloys Compd. 2019;774:1140.
Liu R, **e ZM, Fang QF, Zhang T, Wang XP, Hao T, Liu CS, Dai Y. Nanostructured yttria dispersion-strengthened tungsten synthesized by sol–gel method. J Alloys Compd. 2016;657:73.
Liu R, Wang XP, Hao T, Liu CS, Fang QF. Characterization of ODS-tungsten microwave-sintered from sol–gel prepared nano-powders. J Nucl Mater. 2014;450:69.
**e ZM, Liu R, Miao S, Yang XD, Zhang T, Wang XP, Fang QF, Liu CS, Luo GN, Lian YY, Liu X. Extraordinary high ductility/strength of the interface designed bulk W-ZrC alloy plate at relatively low temperature. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16014.
Lian Y, Liu X, Feng F, Song J, Yan B, Wang Y, Wang J, Chen J. Mechanical properties and thermal shock performance of W–Y2O3 composite prepared by high-energy-rate forging. Phys Scr. 2017;T170:014044.
Ren C, Fang ZZ, Koopman M, Butler B, Paramore J, Middlemas S. Methods for improving ductility of tungsten—a review. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2018;75:170.
Lin JS, Luo LM, Huang K, Zan X, Xu Q, Liu JQ, Zhu XY, Cheng JG, Wu YC. Preparation and properties of fine-grained and ultrafine-grained W–TiC–Y2O3 composite. Fusion Eng Des. 2018;126:147.
Lin JS, Hao YC, Luo LM, Zhao ML, Xu Q, Zan X, Zhu XY, Wu YC. Microstructure and performances of W–TiC–Y2O3 composites prepared by mechano-chemical and wet-chemical methods. J Alloys Compd. 2018;732:871.
Li J, Cheng J, Wei B, Zhang M, Luo L, Wu Y. Microstructure and properties of La2O3 doped W composites prepared by a wet chemical process. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2017;66:226.
Li C, Liu S, **ong L, Wang W. Preparation and sintering of nanometer W-2 wt%Y2O3 composite powders. J Rare Earths. 2015;33(7):752.
Zhou Z, Tan J, Qu D, Pintsuk G, Rödig M, Linke J. Basic characterization of oxide dispersion strengthened fine-grained tungsten based materials fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. J Nucl Mater. 2012;431(1–3):202.
Veleva L, Schaeublin R, Battabyal M, Plociski T, Baluc N. Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of W-Y and W–Y2O3 materials fabricated by powder metallurgy method. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2015;50:210.
Battabyal M, Schäublin R, Spätig P, Baluc N. W–2 wt%Y2O3 composite: microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;538:53.
Zhao ML, Luo LM, Lin JS, Zan X, Zhu XY, Luo GN, Wu YC. Thermal shock behavior of W-0.5 wt% Y2O3 alloy prepared via a novel chemical method. J Nucl Mater. 2016;479:616.
Yao G, Tan XY, Luo LM, Zan X, Liu JQ, Xu Q, Zhu XY, Wu YC. Repair behavior of He+-irradiated W–Y2O3 composites after different temperature-isochronal annealing experiments. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B. 2018;415:82.
Wahlberg S, Yar MA, Abuelnaga MO, Salem HG, Johnsson M, Muhammed M. Fabrication of nanostructured W–Y2O3 materials by chemical methods. J Mater Chem. 2012;22:12622.
Dong Z, Liu N, Ma Z, Liu C, Guo Q, Alothman ZA, Yamauchi Y, Shahriar AHM, Liu Y. Microstructure refinement in W–Y2O3 alloy fabricated by wet chemical method with surfactant addition and subsequent spark plasma sintering. Sci Rep. 2017;7:6051.
Dong Z, Liu N, Ma Z, Liu C, Guo Q, Yamauchi Y, Alamri HR, Alothman ZA, Shahriar A, Hossain M, Liu Y. Synthesis of nanosized composite powders via a wet chemical process for sintering high performance W–Y2O3 alloy. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2017;69:266.
Li X, Wen X, Zhao H, Ma Z, Yu L, Li C, Liu C, Guo Q, Liu Y. The formation and evolution mechanism of amorphous layer surrounding Nb nano-grains in Nb-Al system during mechanical alloying process. J Alloys Compd. 2019;779:175.
Wang S, Luo LM, Shi J, Zan X, Zhu XY, Luo GN, Wu YC. Effect of mechanical alloying on the microstructure and properties of W–Ti alloys fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Powder Technol. 2016;302:1.
Yar MA, Wahlberg S, Bergqvist H, Salem HG, Johnsson M, Muhammed M. Spark plasma sintering of tungsten–yttrium oxide composites from chemically synthesized nanopowders and microstructural characterization. J Nucl Mater. 2011;412(2):227.
Meligrana G, Gerbaldi C, Tuel A, Bodoardo S, Penazzi N. Hydrothermal synthesis of high surface LiFePO4 powders as cathode for Li-ion cells. J Power Sour. 2006;160(1):516.
Fernández IE, Rodríguez- Páez JE. Wet-chemical preparation of TiO2-nanostructures using different solvents: effect of CTAB concentration and tentative mechanism of particle formation. J Alloys Compd. 2019;780:756.
Fan J, Han Y, Li P, Sun Z, Zhou Q. Micro/nano composited tungsten material and its high thermal loading behavior. J Nucl Mater. 2014;455(1–3):717.
Dong Z, Liu N, Ma Z, Liu C, Guo Q, Liu Y. Preparation of ultra-fine grain W–Y2O3 alloy by an improved wet chemical method and two-step spark plasma sintering. J Alloys Compd. 2017;695:2969.
**e Z, Liu R, Fang Q, Zhang T, Jiang Y, Wang X, Liu C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of nano-size zirconium carbide dispersion strengthened tungsten alloys fabricated by spark plasma sintering method. Plasma Sci Technol. 2015;17(12):1066.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51822404 and 51574178) and the Science and Technology Program of Tian** (Grant No. 18YFZCGX00070), the Natural Science Foundation of Tian** (Grant No. 18JCYBJC17900) and the Seed Foundation of Tian** University (Grant Nos. 2018XRX-0005 and 2019XYF-0066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W., Ma, Q., Ma, Z. et al. Ultra-fine W–Y2O3 composite powders prepared by an improved chemical co-precipitation method and its interface structure after spark plasma sintering. Tungsten 1, 220–228 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-019-00021-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-019-00021-w