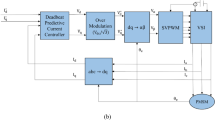
Abstract
For improving the speed fluctuation of permanent magnet synchronous motor under parameter variation and load disturbance, the control method based on double extended state observer (ESO) is introduced in the paper. Firstly, the defects of the traditional speed and current controller are analyzed, based on the speed mathematical model. The influence of the disturbance on the speed is also analyzed, where produces in the speed loop and current loop. And the improved motor robust control system is established. Secondly, the proportional ESO (PESO) of the dq-axes current loop is established. It accurately compensate the dq-axes output voltage error caused by the parameter changes. And the system stability is also proved. Thirdly, the anti-windup controller is introduced to improve the response lag of speed PI regulator. The time-varying parameter ESO of speed loop is established to reduce the influence on current output, which caused by parameter variation and load disturbance. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method are verified by simulation and experiment results.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joshi AVA, Mehta H, Walambe R (2020) Disturbance observer based sensorless control of PMSM using integral state feedback controller. IEEE Trans Power Electron 35(6):6082–6090
Türker T, Buyukkeles U, Bakan AF (2016) A robust predictive current controller for PMSM drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(6):3906–3914
Tarczewski T, Grzesiak LM (2016) Constrained state feedback speed control of PMSM based on model predictive approach. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(6):3867–3875
Errouissi R, Ouhrouche M, Chen W-H, Trzynadlowski A (2012) Robust cascaded nonlinear predictive control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor with antiwindup compensator. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(8):3078–3088
Liang D, Li J, Qu R, Kong W (2018) Adaptive second-order sliding-mode observer for PMSM sensorless control considering VSI nonlinearity. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(10):8994–9004
Xu W, Jiang Y, Mu C, Blaabjerg F (2019) Improved nonlinear flux observer-based second-order SOIFO for PMSM sensorless control. IEEE Trans Power Electron 34(1):565–579
Liu M, Chan KW, Hu J, Xu W, Rodriguez J (2019) Model predictive direct speed control with torque oscillation reduction for PMSM drives. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 15(9):4944–4956
Kim S (2018) Proportional-type performance recovery current tracking control algorithm for PMSM. IET Electr Power Appl 12(3):332–338
Yang J, Chen W, Li S, Guo L, Yan Y (2017) Disturbance/uncertainty estimation and attenuation techniques in PMSM drives—a survey. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(4):3273–3285. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2016.2583412
Chen W, Yang J, Guo L, Li S (2016) Disturbance-observer-based control and related methods—an overview. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(2):1083–1095. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2015.2478397
Zhu Q, Yin Z, Zhang Y, Niu J, Li Y, Zhong Y (2016) Research on two-degree-of-freedom internal model control strategy for induction motor based on immune algorithm. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(3):1981–1992. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2015.2512222
Li S, Gu H (2012) Fuzzy adaptive internal model control schemes for PMSM speed-regulation system. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 8(4):767–779. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2012.2205581
Masoudi S, Mehrjerdi H, Ghorbani A (2020) Adaptive control strategy for velocity control of a linear switched reluctance motor. IET Electr Power Appl 14(8):1496–1503. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-epa.2019.0888
Na J, Chen Q, Ren X, Guo Y (2014) Adaptive prescribed performance motion control of servo mechanisms with friction compensation. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(1):486–494
Junejo AK, Xu W, Mu C, Ismail MM, Liu Y (2020) Adaptive speed control of PMSM drive system based a new sliding-mode reaching law. IEEE Trans Power Electron 35(11):12110–12121
Wang Y, Feng Y, Zhang X, Liang J (2020) A new reaching law for antidisturbance sliding-mode control of PMSM speed regulation system. IEEE Trans Power Electron 35(4):4117–4126
Zhang X, Sun L, Zhao K, Sun L (2013) Nonlinear speed control for PMSM system using sliding-mode control and disturbance compensation techniques. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(3):1358–1365
Li J, Ren H, Zhong Y (2015) Robust speed control of induction motor drives using first-order auto-disturbance rejection controllers. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 51(1):712–720
Du B, Wu S, Han S, Cui S (2016) Application of linear active disturbance rejection controller for sensorless control of internal permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(5):3019–3027
Bekiroglu E, Esmer S (2023) Design and double-stage optimization of synchronous reluctance motor for electric vehicles. Electr Power Compon and Syst 51(20):1–16
Chandran P, Mylsamy K, Umapathy PS (2023) Analytical evaluation of single-input dual-output based integrated luo-buck converter for BLDC motor. IET Power Electronics 16(6):937–947. https://doi.org/10.1049/pel2.12441
Vanchinathan K, Valluvan KR, Gnanavel C, Gokul C, Renold RA (2021) An improved incipient whale optimization algorithm based robust fault detection and diagnosis for sensorless brushless DC motor drive under external disturbances. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/2050-7038.13251
Vanchinathan K, Valluvan KR, Gnanavel C et al (2021) Design methodology and experimental verification of intelligent speed controllers for sensorless permanent magnet Brushless DC motor. Int Trans Electric Energy Syst 31(9):e12991
Vanchinathan K, Valluvan KR, Gnanavel C, Gokul C (2022) Numerical simulation and experimental verification of fractional-order piλ controller for solar PV fed sensorless brushless DC motor using whale optimization algorithm. Electric Power Compon and Syst 50(1–2):64–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325008.2022.2135644
Lascu C, Andreescu G (2020) PLL position and speed observer with integrated current observer for sensorless PMSM drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(7):5990–5999
Liu X, Yu H, Yu J, Zhao L (2018) Combined speed and current terminal sliding mode control with nonlinear disturbance observer for PMSM drive. IEEE Access 6:29594–29601
Liu H, Li S (2012) Speed control for PMSM servo system using predictive functional control and extended state observer. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(2):1171–1183
Shi T, Wang Z, **a C (2015) Speed measurement error suppression for PMSM control system using self-adaption Kalman observer. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(5):2753–2763
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2108085ME179), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51607002), Key project of National Natural Science funds (51637001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
**e, F., Ni, S. & Wang, H. Speed Fluctuation Suppression of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Double Extended State Observer. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 19, 3079–3088 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-023-01760-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-023-01760-0