Abstract
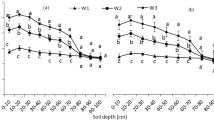
Root growth markedly influences crop yield and resource use efficiency. The present study investigated the effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation (AWD) and the mixed application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer (CRNF) and common urea (CU) on the physiological and morphological characteristics of roots and their relationships with grain yield, crop water productivity (CWP), and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Three nitrogen (N) fertilization treatments (100% CU (N1), 60% CRNF + 40% CU (N2), and 100% CRNF (N3)) were applied to rice (N rate = 240 kg ha−1) under conventional flooded irrigation (CI) and AWD conditions. Compared to N1, N2, and N3 increased the length, number, dry weight, surface area, oxidation activity, and zeatin + zeatin riboside, and indole-3-acetic acid contents of the roots at the latter (heading and maturity) stages under both AWD and CI. In the same N compounding mode, AWD provided better root parameters. Although grain yield, CWP, and NUE were positively associated with these root traits at the latter stages of growth, they showed a negative correlation with the root traits at the early (tillering) stage. Additionally, the AWDN2 treatment enhanced the number of panicles per m2, spikelets per panicle, filled grain percentage, and 1000-grain weight, providing the greatest grain yield, CWP, and NUE. The combination of AWD and the mixed application of CRNF and CU can improve root growth and root activity, contributing to high grain yield, CWP, and NUE in rice. The results also provide scientific basis for CRNF management strategy mediates rice yield and resource use efficiency under AWD.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The obtained data will be available upon request.
References
Bollmark M, Kubat B, Eliasson L (1988) Variations in endogenous cytokinin content during adventitious root formation in pea cuttings. J Plant Physiol 132:262–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(88)80102-0
Bouman BAM, Peng SB, Castñeda AR, Visperas RM (2005) Yield and water use of irrigated tropical aerobic rice systems. Agric Water Manag 74:87–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2004.11.007
Cao XC, Zhang JH, Yu YJ, Ma QX, Kong YL, Pan WK, Wu LH, ** QY (2022) Alternate wetting–drying enhances soil nitrogen availability by altering organic nitrogen partitioning in rice-microbe system. Geoderma 424:115993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.115993
Chu G, Chen TT, Wang ZQ, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2014) Morphological and physiological traits of roots and their relationships with water productivity in water-saving and drought-resistant rice. Field Crops Res 162:108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.06.026
Chu G, Xu R, Chen S, Xu CM, Liu YH, Zhang XF, Wang DY (2021) Effects of improved crop management on growth characteristic of root and shoot, water and nitrogen use efficiency, and grain yield in rice (in Chinese). Chin J Rice Sci 35:586–594. https://doi.org/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.201213
Ding WC, Xu XP, He P, Ullah S, Zhang JJ, Cui ZL, Zhou W (2018) Improving yield and nitrogen use efficiency through alternative fertilization options for rice in China: a meta-analysis. Field Crop Res 227:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.08.001
Dong NM, Brandt KK, Sørensen J, Hung NN, Hach CV, Tan PS, Dalsgaard T (2012) Effects of alternating wetting and drying versus continuous flooding on fertilizer nitrogen fate in rice fields in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Soil Bio Biochem 47:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.12.028
Fertitta-Roberts C, Oikawa PY, Jenerette GD (2019) Evaluating the GHG mitigation potential of alternate wetting and drying in rice through life cycle assessment. Sci Total Environ 653:1343–1353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.327
Garnett T, Conn V, Kaiser BN (2009) Root based approaches to improving nitrogen use efficiency in plants. Plant Cell Environ 32:1272–1283. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02011.x
Geng JB, Sun YB, Zhang M, Li CL, Yang YC, Liu ZG, Li SL (2015) Long-term effects of controlled release urea application on crop yields and soil fertility under rice-oilseed rape rotation system. Field Crops Res 184:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.09.003
Guo JJ, Fan JL, Zhang FC, Yan SC, Zheng J, Wu Y, Li J, Wang YL, Sun X, Liu XQ, **ang YZ, Li ZJ (2021) Blending urea and slow release nitrogen fertilizer increases dryland maize yield and nitrogen use efficiency while mitigating ammonia volatilization. Sci Total Environ 790:148058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148058
Hooper P, Zhou Y, Coventry DR, McDonald GK (2014) Use of nitrogen fertilizer in a targeted way to improve grain yield, quality, and nitrogen use efficiency. Agron J 107:903–915. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj14.0363
Ishfaq M, Farooq M, Zulfiqar U, Hussain S, Akbar N, Nawaz A, Anjum SA (2020) Alternate wetting and drying: a water-saving and ecofriendly rice production system. Agric Water Manag 241:106363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106363
Ju CX, Buresh RJ, Wang ZQ, Zhang H, Liu LJ, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2015) Root and shoot traits for rice varieties with higher grain yield and higher nitrogen use efficiency at lower nitrogen rates application. Field Crops Res 175:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.02.007
Ju XT, **ng GX, Chen XP, Zhang S, Zhang L, Liu X, Cui ZL, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu Z, Zhang FS (2009) Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. PANS 106:3041–3046. 10. 1073/pnas.08134 17106
Ke J, Chen TT, Xu CH, Zhu TZ, Wu H, He HB, You CC, Zhu DQ, Wu LQ (2021) Effects of different application methods of controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on grain yield and nitrogen utilization of indica-japonica hybrid rice in pot-seedling mechanically transplanted (in Chinese). Acta Agron Sin 47(7):1372–1382. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.02055
Kiran JK, Khanif YM, Amminuddin H, Anuar AR (2010) Effects of controlled release urea on the yield and nitrogen nutrition of flooded rice. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 41:811–819. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103621003592333
Kukal SS, Aggarwal GC (2003) Pudding depth and intensity effects in rice-wheat system on a sandy loam soil: II water use and crop performance. Soil Tillage Res 74:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(03)00124-7
Lampayan RM, Rejesus RM, Singleton GR, Bouman BA (2015) Adoption and economics of alternate wetting and drying water management for irrigated lowland rice. Field Crops Res 170:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.10.013
Leon A, Izumi T (2022) Impacts of alternate wetting and drying on rice farmers’ profits and life cycle greenhouse gas emissions in An Giang Province in Vietnam. J Clean Prod 354:131621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131621
Li QQ, Dong BD, Qiao YZ, Liu MY, Zhang J (2010) Root growth, available soil water, and water-use efficiency of winter wheat under different irrigation regimes applied at different growth stages in North China. Agric Water Manage 97:1676–1682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2010.05.025
Li JL, Li YE, Wan YF, Wang B, Waqas MA, Cai WW, Guo C, Zhou SH, Su RS, Qin XB, Gao QZ, Wilkes A (2018) Combination of modified nitrogen fertilizers and water saving irrigation can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase rice yield. Geoderma 315:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.11.033
Li GH, Fu PX, Cheng GG, Lu WP, Lu DL (2022) Delaying application time of slow-release fertilizer increases soil rhizosphere nitrogen content, root activity, and grain yield of spring maize. Crop J 10:1798–1806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2022.04.014
Liang KM, Zhong XH, Fu YQ, Hu XY, Li MJ, Pan JF, Liu YZ, Hu R, Ye QH (2023) Mitigation of environmental N pollution and greenhouse gas emission from double rice crop** system with a new alternate wetting and drying irrigation regime coupled with optimized N fertilization in South China. Agric Water Manag 282:108282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2023.108282
Liu LJ, Chen TT, Wang ZQ, Zhang H, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2013) Combination of site-specific nitrogen management and alternate wetting and drying irrigation increases grain yield and nitrogen and water use efficiency in super rice. Field Crops Res 154:226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.08.016
Liu K, Chen Y, Li SY, Wang WL, Zhang WY, Zhang H, Gu JF, Yang JC, Liu LJ (2023) Differing responses of root morphology and physiology to nitrogen application rates and their relationships with grain yield in rice. Crop J 11:618–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2022.07.019
Luo L (2010) Breeding for water-saving and drought-resistance rice (WDR) in China. J Exp Bot 61:3509–3517. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq185
National Bureau of Statistics (2022) China statistical yearbook. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/
Ogawa A, Kawashima C, Yamauchi A (2005) Sugar accumulation along the seminar root axis as affected by osmotic stress in maize: a possible physiological basis for plastic lateral root development. Plant Prod Sci 8:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1626/pps.8.173
Pan C, Yang Y, Qi DL (2023) The combined effect of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on dry matter and yield of rice (in Chinese). J Irri Drain 42:73–78. https://doi.org/10.13522/j.cnki.ggps.2022242
Peng YF, Li XX, Li CJ (2012) Temporal and spatial profiling of root growth revealed novel response of maize roots under various nitrogen supplies in the field. PLoS ONE 7:e3326. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037726
Peng Y, Sun YJ, Jiang MJ, Xu H, Qin J, Yang ZY, Ma J (2014) Effects of water management and slow/controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on biomass and nitrogen accumulation, translocation, and distribution in rice (in Chinese). Acta Agron Sin 40:859–870. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.00859
Qi DL, Wu QX, Zhu JQ (2020) Nitrogen and phosphorus losses from paddy fields and the yield of rice with different water and nitrogen management practices. Sci Rep 10:9734. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66757-5
Qi DL, Zhu JQ, Wang XG (2023) Nitrogen loss via runoff and leaching from paddy fields with the proportion of controlled-release urea and conventional urea rates under alternate wetting and drying irrigation. Enviro Sci Poll Res 30:61741–61752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26480-w
Qi DL, Hu TT (2022) Effects of nitrogen application rates and irrigation regimes on root growth and nitrogen‑use efficiency of maize under alternate partial root‑zone irrigation. J Soil Sci Plant Nutri 22:2793–2804. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63205-1
Ramasamy S, ten Berge HFM, Purushothaman S (1997) Yield formation in rice in response to drainage and nitrogen application. Field Crops Res 51:65–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(96)01039-8
Shaviv A (2001) Advances in controlled-release fertilizers. Adv Agron 71:1–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(01)71011-5
Song C, Guan Y, Wang D, Zewudie D, Li FM (2014) Palygorskite-coated fertilizers with a timely release of nutrients increase potato productivity in a rain-fed cropland. Field Crops Res 166:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.06.015
Spiertz JHJ (2010) Nitrogen, sustainable agriculture and food security: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2666-839
Sun YJ, Ma J, Sun YY, Xu H, Yang ZY, Liu SJ, Jia XW, Zheng HZ (2012) The effects of different water and nitrogen managements on yield and nitrogen use efficiency in hybrid rice of China. Field Crops Res 127:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2011.11.015
Sun Y, Mi WH, Su LJ, Shan YY, Wu LH (2019) Controlled-release fertilizer enhances rice grain yield and N recovery efficiency in continuous non-flooding plastic film mulching cultivation system. Field Crops Res 231:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.11.013
Tian ZW, Liu XX, Yu JH, Gu SL, Zhang L, Jiang D, Cao WX, Dai TB (2019) Early nitrogen deficiency favors high nitrogen recovery efficiency by improving deeper soil root growth and reducing nitrogen loss in wheat. Arch Agronomy Soil Sci 66:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1671972
Wang CY, Liu W, Li QX, Ma DY, Lu HF, Feng W, **e YX, Zhu YJ, Guo TC (2014) Effects of different irrigation and nitrogen regimes on root growth and its correlation with above-ground plant parts in high-yielding wheat under field conditions. Field Crops Res 165:138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.04.011
Wang ZQ, Zhang WY, Beebout SS, Zhang H, Liu LJ, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2016) Grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice as influenced by irrigation regimes and their interaction with nitrogen rates. Field Crops Res 193:54–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.03.006
Wang L, Xue C, Pan X, Chen F, Liu Y (2018) Application of controlled-release urea enhances grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Front Plant Sci 9:999. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00999
Wei J, Cui YL, Zhou SH, Luo YF (2022) Regional water-saving potential calculation method for paddy rice based on remote sensing. Agric Water Manag 267:107610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107610
Wu P, Liu F, Wang JY, Liu YH, Gao Y, Zhang XQ, Chen GZ, Huang FY, Ahmad S, Zhang P, Cai T, Jia ZK (2022) Suitable fertilization depth can improve the water productivity and maize yield by regulating development of the root system. Agric Water Manag 271:107784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107784
Xu GW, Lu DK, Wang HZ, Li YJ (2018) Morphological and physiological traits of rice roots and their relationships to yield and nitrogen utilization as influenced by irrigation regime and nitrogen rate. Agric Water Manag 203:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.02.033
Xu YQ, Su BL, Wang HQ, He JY, Yang YX (2020) Analysis of the water balance and the nitrogen and phosphorus runoff pollution of a paddy field in situ in the Taihu Lake basin. Paddy Water Environ 18:385–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-020-00789-5
Yan J, Wu QX, Qi DL, Zhu JQ (2022) Rice yield, water productivity, and nitrogen use efficiency responses to nitrogen management strategies under supplementary irrigation for rain-fed rice cultivation. Agric Water Manag 263:107486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107486
Yang JC, Zhang JH, Wang ZQ, Xu GW, Zhu QS (2004) Activities of key enzymes in sucrose-to-starch conversion in wheat grains subjected to water deficit during grain filling. Plant Physiol 135:1621–1629. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.041038
Yang LX, Wang YL, Kobayashi K, Zhu JG, Huang JY, Yang HJ, Wang YX, Dong GC, Liu G, Han Y, Shan YH, Hu J, Zhou J (2008) Seasonal changes in the effects of ree-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) on growth, morphology and physiology of rice root at three levels of nitrogen fertilization. Global Change Bio 14:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01624.x
Yang JC, Zhang H, Zhang JH (2012) Root morphology and physiology in relation to the yield formation of rice. J Integ Agric 11:920–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(12)60082-3
Yang ZY, Li N, Ma P, Li Y, Zhang RP, Song Q, Guo X, Sun YJ, Xu H, Ma J (2022) Improving nitrogen and water use efficiencies of hybrid rice through methodical nitrogen–water distribution management. Field Crops Res 246:107698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.107698
Ye YS, Liang XQ, Chen YX, Liu J, Gu JT, Guo R, Li L (2013) Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer in late-season rice. Effects on dry matter accumulation, yield, water and nitrogen use. Field Crops Res 144:212–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2012.12.003
Zhang H, Li HW, Yuan LN, Wang ZQ, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2011) Post-anthesis alternate wetting and moderate soil drying enhances activities of key enzymes in sucrose-to-starch conversion in inferior spikelets of rice. J Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err263
Zhang WY, Xu YJ, Wang ZQ, Liu LJ, Zhang H, Gu JF, Zhang JH, Yang JC (2021) Alternate wetting and drying irrigation combined with the proportion of polymer-coated urea and conventional urea rates increases grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies in rice. Field Crops Res 268:108165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108165
Zheng WK, Zhang M, Liu ZG, Zhou HY, Lu H, Zhang WT, Yang YC, Li CL, Chen BC (2016) Combining controlled-release urea and normal urea to improve the nitrogen use efficiency and yield under wheat-maize double crop** system. Field Crops Res 197:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.08.004
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the reviewers who participated in the review, as well as MJEditor (www. mjedi tor. com) for providing English editing services during the preparation of this manuscript. The authors are also thankful to Ms. Chen Pan and Mr. Yu Yang for providing the assistance in field investigation and nitrogen content measurements.
Funding
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Fund of China (U21A2039) and State Key Laboratory of Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering Science, Wuhan University, China (2020NSG05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D. L. Q. was involved in the acquisition and analysis of data and wrote this paper. X. G. W. and J. Q. Z. revised it critically for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All the authors agreed to participate.
Consent for Publication
All the authors agreed to publish the following manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, D., Zhu, J. & Wang, X. Root Growth in Rice (Liangyou 152) Under Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation and Mixed Application of Polymer-coated and Common Urea. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 6838–6850 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01546-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01546-3