Abstract
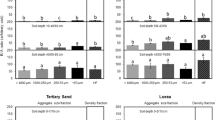
Studying the patterns of change in soil aggregate stability and ecological stoichiometry in different forest types is of significant importance to the research on the distribution, limitations, balance, and cycling of soil organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus (C–N–P). However, the impacts of pure Eucalyptus forests and mixed artificial forests on the stability of aggregates and the stoichiometric characteristics of organic carbon (OC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP) remain unclear. Samples were collected from the 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm soil layers of a Eucalyptus–Mytilaria laosensis mixed forest, a Eucalyptus–Erythrophleum fordii mixed forest, and a pure Eucalyptus forest. Soil samples were dry sieved into four types of aggregates according to particle size (> 2 mm, 1–2 mm, 0.25–1 mm, and < 0.25 mm). The OC, TN, and TP contents and composition were measured to evaluate the soil structure stability; soil OC, TN, and TP stock potential; and ecological stoichiometric characteristics. Our results showed that the structural stability of the soil and the contents and stocks of OC, TN, and TP were significantly higher in mixed forests than in the pure Eucalyptus forest: the 0.25- to 1-mm-sized aggregates had the highest soil OC, TN, and TP contents, and the aggregates > 2 mm in size had the greatest contribution to the soil OC, TN, and TP stocks in bulk soil. The aggregates > 2 mm in size generally had the lowest C/N, C/P, and N/P ratios (0–20 cm). The mean weight diameter (MWD) was the main factor affecting the stoichiometric characteristics of the 0–20 cm soil layer. The Eucalyptus–M. laosensis mixed forest promoted soil-aggregate stability and improved soil fertility. Increasing the proportion of soil aggregates with large sizes (> 2 mm) is key to improving soil ecological environments. Thus, selecting suitable tree species mixed with Eucalyptus can play a vital role in alleviating the reduction of soil aggregate stability, thereby causing the accumulation of soil C, N, and P contents and protecting soil productivity, quality, and health in subtropical China.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting the results presented in this paper can be provided by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
An H, Li G (2015) Effects of grazing on carbon and nitrogen in plants and soils in a semiarid desert grassland, China. J Arid Land 7:341–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-014-0049-x
Bai Y, Chen S, Shi S et al (2020) Effects of different management approaches on the stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N, and P in a mature Chinese fir plantation. Sci Total Environ 723:137868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137868
Bai T, Wang P, Ye C et al (2021) Form of nitrogen input dominates N effects on root growth and soil aggregation: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 157:108251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108251
Buchkowski RW, Schmitz OJ, Bradford MA (2015) Microbial stoichiometry overrides biomass as a regulator of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling. Ecology 96:1139–1149. https://doi.org/10.1890/14-1327.1
Chen F, Feng X, Liang C (2012) Endogenous versus exogenous nutrient affects C, N, and P dynamics in decomposing litters in mid-subtropical forests of China. Ecol Res 27:923–932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-012-0970-4
Cleveland CC, Liptzin D (2007) C: N: P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 85:235–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-007-9132-0
Deng H, Mo X, Mei J et al (2020) Growth and soil nutrient of Eucalyptus mixed plantations. Cent South Univ For Technol 48:95–102. https://doi.org/10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2020.01.012
Forrester D, Bauhus J, Cowie A et al (2006) Mixed-species plantations of Eucalyptus with nitrogen-fixing trees: a review. Forest Ecol Manag 233(2–3):211–230
Garcia L, Damour G, Gary C et al (2019) Trait-based approach for agroecology: contribution of service crop root traits to explain soil aggregate stability in vineyards. Plant Soil 435:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3874-4
Giumbelli LD, Loss A, Ventura BS et al (2020) Aggregation index, carbon, nitrogen, and natural abundance of 13C and 15N in soil aggregates and bulk soil cultivated with onion under crop successions and rotations. Soil Res 58:622–635. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR19346
Gonzalez-Rosado M, Parras-Alcantara L, Aguilera-Huertas J et al (2020) Effects of land management change on soil aggregates and organic carbon in Mediterranean olive groves. Catena 195:104840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104840
He X, Huang Y, Zhang Q et al (2021) Distribution of organic carbon fractions in soil aggregates in Chinese fir plantations with different stand ages. Ecol Process 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-021-00321-5
Jia P, Shen R, Chen Y et al (2021) Allelopathic effects of aqueous leaf leachates of Eucalyptus urophylla × E. grandis on eight native tree species. Cent South Univ For Technol 41:27–34. https://doi.org/10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2021.11.004
Koutika LS (2019) Afforesting savannas with Acacia mangium and eucalyptus improves P availability in Arenosols of the Congolese coastal plains. Geoderma Reg 16:e00207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2019.e00207
Kurmi B, Nath AJ, Lal R et al (2020) Water stable aggregates and the associated active and recalcitrant carbon in soil under rubber plantation. Sci Total Environ 703:135498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135498
Li J, Yuan X, Ge L et al (2020) Rhizosphere effects promote soil aggregate stability and associated organic carbon sequestration in rocky areas of desertification. Agr Ecosyst Environ 304:107126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107126
Liu M, Han G, Zhang Q (2019) Effects of soil aggregate stability on soil organic carbon and nitrogen under land use change in an erodible region in Southwest China. Int J Env Res Pub He 16:3809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203809
Liu H, Wang X, Liang C et al (2020a) Glomalin-related soil protein affects soil aggregation and recovery of soil nutrient following natural revegetation on the Loess Plateau. Geoderma 357:113921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.113921
Liu J, Zhou Z, Su X (2020b) Review of the mechanism of root system on the formation of soil aggregates. J Soil Water Conserv 34:267–273. https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2020.03.040
Lu R (2000) Soil agrochemical analysis. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Bei**g
Mao L, Ye S, Wang S (2022) Dynamics of soil aggregate-related stoichiometric characteristics with tea-planting age and soil depth in the southern Guangxi of China. Soil Discussions 2022:1–44. https://doi.org/10.5194/soil-2021-147
McKiernan AB, Hovenden MJ, Brodribb TJ et al (2014) Effect of limited water availability on foliar plant secondary metabolites of two Eucalyptus species. Environ Exp Bot 105:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2014.04.008
Menon M, Mawodza T, Rabbani A et al (2020) Pore system characteristics of soil aggregates and their relevance to aggregate stability. Geoderma 366:114259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114259
Ming A, Liu S, Nong Y et al (2015) Comparison of carbon stocks in juvenile monoculture and mixed plantation stands of three common broadleaved tree species in subtropical China. Acta Ecol Sin 35:180–188. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201408181638
Mustafa A, Minggang X, Shah SAA et al (2020) Soil aggregation and soil aggregate stability regulate organic carbon and nitrogen storage in a red soil of southern China. J Environ Manage 270:110894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110894
Okolo CC, Gebresamuel G, Zenebe A et al (2020) Accumulation of organic carbon in various soil aggregate sizes under different land use systems in a semi-arid environment. Agr Ecosyst Environ 297:106924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.106924
Pathan SI, Arfaioli P, Ceccherini MT et al (2021) Physical protection of extracellular and intracellular DNA in soil aggregates against simulated natural oxidative processes. Appl Soil Ecol 165:104002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104002
Qi J, Han S, Lin B et al (2021) Improved soil structural stability under no-tillage is related to increased soil carbon in rice paddies: evidence from literature review and field experiment. Environ Technol Inno 2021:102248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102248
Qi D, Feng F, Lu C et al (2022) C: N: P stoichiometry of different soil components after the transition of temperate primary coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forests to secondary forests. Soil Till Res 216:105260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.105260
Rachid CTCC, Balieiro FC, Peixoto RS et al (2013) Mixed plantations can promote microbial integration and soil nitrate increases with changes in the N cycling genes. Soil Biol Biochem 66:146–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.07.005
Santos FM, Chaer GM, Diniz AR et al (2017) Nutrient cycling over five years of mixed-species plantations of Eucalyptus and Acacia on a sandy tropical soil. Forest Ecol Manag 384:110–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.10.041
Sarker JR, Singh BP, Cowie AL et al (2018) Agricultural management practices impacted carbon and nutrient concentrations in soil aggregates, with minimal influence on aggregate stability and total carbon and nutrient stocks in contrasting soils. Soil Till Res 178:209–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2017.12.019
Six J, Bossuyt H, Degryze S et al (2004) A history of research on the link between (micro) aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res 79:7–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2004.03.008
Tamura M, Suseela V, Simpson M et al (2017) Plant litter chemistry alters the content and composition of organic carbon associated with soil mineral and aggregate fractions in invaded ecosystems. Global Change Biol 23:4002–4018. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13751
Tang L, Wang S (2022) Dynamics of soil aggregate-related C-N-P stoichiometric characteristics with stand age and soil deepness in Chinese fir plantations. Land Degrad Dev 33:1290–1306. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.4217
Tian H, Chen G, Zhang C et al (2010) Pattern and variation of C: N: P in China’s soils: a synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 98:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-009-9382-0
Tian S, Zhu B, Yin R et al (2022) Organic fertilization promotes crop productivity through changes in soil aggregation. Soil Biol Biochem 165:108533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108533
Wang E, Cruse RM, Chen X et al (2012) Effects of moisture condition and freeze/thaw cycles on surface soil aggregate size distribution and stability. Can J Soil Sci 92:529–536. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjss2010-044
Wang S, Yao X, Ye S (2020a) Soil aggregate-related organic carbon and relevant enzyme activities as affected by tea (Camellia sinensis L.) planting age in hilly region of southern Guangxi, China. Appl Soil Ecol 150:103444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.103444
Wang S, Zhang Z, Ye S (2020b) Response of soil fertility characteristics in water-stable aggregates to tea cultivation age in hilly region of southern Guangxi, China. Catena 191:104578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104578
Wang S, Huang Y, Ye S (2021) Distribution of organic carbon and nutrients in soil aggregates under different stand types of Cunninghamia lanceolata in southern Guangxi of China. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 67:427–438. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2021.1932585
Wang Y, Zheng Y, Liu Y, Huang J, Mamtimin A (2022) Spatial prediction models for soil stoichiometry in complex terrains: a case study of Schrenk’s spruce forest in the Tianshan mountains. Forests 13:1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13091407
**ao S, Zhang W, Ye Y et al (2017) Soil aggregate mediates the impacts of land uses on organic carbon, total nitrogen, and microbial activity in a Karst ecosystem. Sci Rep-Uk 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41402
Xu C, Pu L, Li J et al (2019) Effect of reclamation on C, N, and P stoichiometry in soil and soil aggregates of a coastal wetland in eastern China[J]. J Soil Sediment 19:1215–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2131-z
Zhang J, An M, Wu H et al (2012) Chemical composition of essential oils of four Eucalyptus species and their phytotoxicity on silverleaf nightshade (Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav.) in Australia. Plant Growth Regul 68:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-012-9711-5
Zhang J, Zhao N, Liu C et al (2018) C: N: P stoichiometry in China’s forests: from organs to ecosystems. Funct Ecol 32:50–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12979
Zhang Y, Li P, Liu X et al (2019) Effects of farmland conversion on the stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil aggregates on the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 351:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.05.037
Zhang J, Liu Y, Zheng T et al (2021) Nutrient and stoichiometric characteristics of aggregates in a slo** farmland area under different tillage practices. Sustainability-Basel 13:890. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020890
Zhao F, Sun J, Ren C et al (2015) Land use change influences soil C, N and P stoichiometry under ‘Grain-to-Green Program’ in China. Sci Rep-Uk 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10195
Zhou L, Sun Y, Saeed S et al (2020) The difference of soil properties between pure and mixed Chinese fir (Cunning-hamia lanceolata) plantations depends on tree species. Glob Ecol Conserv 22: e01009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e01009
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on the manuscript and American Journal Experts (www.aje.cn) for assistance with language editing during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 31460196 and 32260382).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Wang, S., Cui, Y. et al. Soil C–N–P Stoichiometric Characteristics at the Aggregate Scales in Eucalyptus Plantations with Different Stand Types in Subtropical China. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 6527–6541 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01508-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01508-9