Abstract
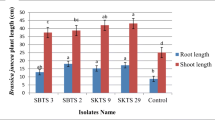
The present study was conducted to investigate the possibility of using iron waste along with Thiobacillus bacteria to supply soybean iron requirement in a calcareous soil. In vitro, two strains of Thiobacillus thiooxidans (T. thiooxidans) and Thiobacillus ferrooxidans (T. ferrooxidans) have been investigated for their bioleaching potential from mill scale and pyrite in in the presence and absence of sulfur. In a greenhouse experiment, the effect of iron sources (control, ferrous sulfate, mill scale, and pyrite) and bacterial inoculation (T. thiooxidans, T. ferrooxidans, and simultaneous application of two bacteria) on iron uptake by soybeans was investigated. In laboratory experiment, the effect of T. ferrooxidans on iron bioleaching from the studied iron waste was greater than T. thiooxidans. T. ferrooxidans was more effective to enhance the iron dissolution from pyrite than mill scale. The application of sulfur increased the bioleaching efficiency. In the greenhouse experiment, inoculation with T. thiooxidans caused a significant increase in shoot iron concentration of soybean compared to control only in the application of pyrite, while T. ferrooxidans significantly increased iron uptake by soybean in the application of all iron sources as well as control treatment. The highest shoot iron concentration of soybean was obtained in simultaneous application of two bacteria species. While the addition of the mineral and waste iron components did not impact on iron uptake by soybeans, soil inoculation with T. ferrooxidans and simultaneous application of T. ferrooxidans and T. thiooxidans had a significant effect on iron biofortification in soybean.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour A, Kalbasi M, Shariatmadari H (2005) Effect of steel converter sludge as iron fertilizer and soil amendment in some calcareous soils. J Plant Nutr 27:377–394. https://doi.org/10.1081/PLN-120027661
Aciksoz S, Yazici A, Ozturk L, Cakmak I (2011) Biofortification of wheat with iron through soil and foliar application of nitrogen and iron fertilizers. Plant Soil 349:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0863-2
Adu MO, Asare PA, Yawson DO, Nyarko MA, Osei-Agyeman K (2018) Agronomic biofortification of selected underutilized Solanaceae vegetables for improved dietary intake of potassium (K) in Ghana. Heliyon 4:1–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00750
Akhtar MS, Babel S, Yadav BK, Yadav RS, Panwar J (2012) Potentiality of Thiobacillus in agricultural system. Adv Sci Eng Med 4:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1166/asem.2012.1123
Anandham R, Sridar R, Nalayini P, Poonguzhali S, Madhaiyan M, Tongmin S (2007) Potential for plant growth promotion in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cv. ALR-2 by co-inoculation of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and Rhizobium. Microbiol Res 162:139–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2006.02.005
Argaw A, Mekonnen E, Muleta D (2015) Agronomic efficiency of N of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in some representative soils of Eastern Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric 1:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311932.2015.1074790
Askary M, Amirjani MR, Saberi T (2017) Comparison of the effects of nano-iron fertilizer with iron-chelate on growth parameters and some biochemical properties of Catharanthus roseus. J Plant Nutr 40:974–982. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2016.1262399
NM Awad AA Abd El-Kader M Attia AK Alva 2011 Effects of nitrogen fertilization and soil inoculation of sulfur-oxidizing or nitrogen-fixing bacteria on onion plant growth and yield Int J Agron 1–6 https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/316856
Aziz MZ, Yaseen M, Abbas T, Naveed M, Mustafa A, Hamid Y, Saeed Q, Ming-gang XU (2019) Foliar application of micronutrients enhances crop stand, yield and the biofortification essential for human health of different wheat cultivars. J Integr Agric 18:1369–1378. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(18)62095-7
O Bayat Z Kaya (1998) The use of pyrite from a zinc processing plant as a fertilizer in calcareous soils. 1998 2nd International Symposium on Mine Environmental Engineering 29–31 July Brunel University England https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2014.957392
Besharati H (2017) Effects of sulfur application and Thiobacillus inoculation on soil nutrient availability, wheat yield and plant nutrient concentration in calcareous soils with different calcium carbonate content. J Plant Nutr 40:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2016.1245326
Bevilaqua D, Leite ALLC, Garcia O, Tuovinen OH (2002) Oxidation of chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in shake flasks. Process Biochem 38:587–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00169-3
Bouranis DL, Chorianopoulou SN, Margetis M, Saridis GI, Sigalas PP (2018) Effect of elemental sulfur as fertilizer ingredient on the mobilization of iron from the iron pools of a calcareous soil cultivated with Durum wheat and the crop’s iron and sulfur nutrition. Agriculture 8:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture8020020
Cakmak I (2008) Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: agronomic or genetic biofortification? Plant Soil 302:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9466-3
MA Castelo-Branco A Oliveira F Pereira Pires S Dias LM Fernandes VE Silva JM, Santos J, Magalhaes I, Ramalho Ribeiro J, Moreira O, Gama J, 1999 Potential use of pyrite as an amendment for calcareous soil J Geochem Explor 66 363 367 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(99)00026-6
Chandra AP, Gerson AR (2010) The mechanisms of pyrite oxidation and leaching: a fundamental perspective. Surf Sci Rep 65:293–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfrep.2010.08.003
Chen X, Wei X, Hao M, Zhao J (2019) Changes in soil iron fractions and availability in the loess belt of northern China after 28 years of continuous cultivation and fertilization. Pedosphere 29:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60331-X
Colombo C, Palumbo G, He JZ, Pinton R, Cesco S (2014) Review on iron availability in soil: interaction of Fe minerals, plants, and microbes. J Soils Sediments 14:538–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0814-z
Devasia P, Natarajan K, Sathyanarayana D, Rao GR (1993) Surface chemistry of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans relevant to adhesion on mineral surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:4051–4055. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.59.12.4051-4055.1993
Dubey SK, Mondal RC (1994) Effect of amendments and saline irrigation water on soil properties and yields of rice and wheat in a highly sodic soil. J Agric Sci 122:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859600067277
Espejo RT, Escobar B, Jedlicki E, Badilla-Ohlbaum UP, R, (1988) Oxidation of ferrous iron and elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1694–1699. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.54.7.1694-1699.1988
Fowler TA, Holmes PR, Crundwell FK (1999) Mechanism of pyrite dissolution in the presence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2987–2993. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.65.7.2987-2993.1999
García-Bañuelos ML, Sida-Arreola JP, Sánchez E (2014) Biofortification-promising approach to increasing the content of iron and zinc in staple food crops. J Elem 19:865–888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-020-00100-w
Garg M, Sharma N, Sharma S, Kapoor P, Kumar A, Chundari V, Arora P (2018) Breeding crops generated by breeding, agronomy, and transgenic approaches are improving lives of millions of people around the world. Front Nutr 5:1–33. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2018.00012
Gehrke T, Telegdi J, Thierry D, Sand W (1998) Importance of extracellular polymeric substances from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for bioleaching. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2743–2747. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.64.7.2743-2747.1998
Granja F, Covarrubias JI (2018) Evaluation of acidifying nitrogen fertilizers in avocado trees with iron deficiency symptoms. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 18:157–172. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162018005000702
Heitholt JJ, Sloan JJ, MacKown CT, Cabrera RI (2003) Soybean growth on calcareous soil as affected by three iron sources. J Plant Nutr 26:935–948. https://doi.org/10.1081/PLN-120018575
Hosseini T, Kolahdoozan M, Tabatabaei Y, Oliazadeh M, Noaparast M, Eslami A, Manafi Z, Alfantazi A (2005) Bioflotation of Sarcheshmeh copper ore using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans bacteria. Miner Eng 18:371–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2004.06.005
Jiang L, Zhou HY, Peng XT (2007) Bio-oxidation of pyrite, chalcopyrite and pyrrhotite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Chin Sci Bull 52:2702–2714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0352-4
Joseph AR, Kavimandan SK, Tilak KV, Nain L (2014) Response of canola and wheat to amendment of pyrite and sulphur-oxidizing bacteria in soil. Arch Agron Soil Sci 60: 367–375. /https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2013.799275
Karimian N, Kalbasi M, Hajrasuliha S (2012) Effect of converter sludge, and its mixtures with organic matter, elemental sulfur and sulfuric acid on availability of iron, phosphorus and manganese of 3 calcareous soils from central Iran. Afr J Agric Res 7:568–576. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR11.1484
Khan A, Singh J, Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Shah S (2019) Microbial biofortification: a green technology through plant growth promoting microorganisms. In: Shah S, Venkatramanan V, Prasad R. (eds.) Sustain Green Technol Environ Manage Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2772-8_13
Klikocka H, Marks M (2018) Sulfur and nitrogen fertilization as a potential means of agronomic biofortification to improve the content and uptake of microelements in spring wheat grain DM. J Chem 2018:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9326820
Ko MS, Park HS, Kim KW, Lee JU (2013) The role of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in arsenic bioleaching from soil. Environ Geochem Health 35:727–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9530-2
Lara RH, Mallet M, Monroy MG, Dossot M, Gonzalez MA, Cruz R (2015) An experimental study of iron sulfides weathering under simulated calcareous soil conditions. Environ Earth Sci 73:1849–1869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3540-y
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200030009x
Liu H, Gu G, Xu Y (2011) Surface properties of pyrite in the course of bioleaching by pure culture of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and a mixed culture of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 108:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2011.03.010
Lucena JJ (2006) Synthetic iron chelates to correct iron deficiency in plants. In: Barton L L, Abadia J. (eds.) Iron nutrition in plants and rhizospheric microorganisms. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4743-6_5
Marsolek MD, Hagstrom GR (1982) Acidified mining residue for correction of iron chlorosis on calcareous soils. J Plant Nutr 5:941–948. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904168209363024
McFarland J (1907) Nephelometer: an instrument for media used for estimating the number of bacteria in suspensions used for calculating the opsonic index and for vaccines. J Am Med Assoc 14: 1176–1178. Cited in: Dalynn Biologicals (2012) McFarland standard-for in vitro use only- Catalogue No. TM50-TM60. www.dalynn.com/dyn/ck_assets/files/tech/TM53.pdf
MitSunobu S, Zhu M, Takeichi Y, Ohigashi T, Suga H, Makita H, Sakata M, Ono K, Mase K, Takahashi Y (2016) Direct detection of Fe (II) in extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) at the mineral-microbe interface in bacterial pyrite leaching. Microbes Environ 31:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME15137
Mohammadi Torkashvand A (2011) Effect of steel converter slag as iron fertilizer in some calcareous soils. Acta Agric Scand B 61:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710903410031
S Ndlovu GS Simate E Matinde 2017 Waste production and utilization in the metal extraction industry Taylor and Francis, CRC Press https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315153896
Nesheim L, Gautneb H, Myhr K (1997) Plant uptake of sulphur and trace elements from pyrite applied on grassland. Acta Agric Scand B 47:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064719709362453
Nguyen VK, Lee MH, Park HJ, Lee JU (2015) Bioleaching of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings by pure and mixed cultures of Acidithiobacillus spp. J Ind Eng Chem 21:451–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.03.004
Niyigaba E, Twizerimana A, Mugenzi I, Ngnadong WA, Ye YP, Wu BM, Hai JB (2019) Winter wheat grain quality, zinc and iron concentration affected by a combined foliar spray of zinc and iron fertilizers. Agronomy 9:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9050250
Ortas I, Kaya Z, Ercan S (2015) Effect of pyrite application on wheat-maize growth and nutrient uptake under diverse soil conditions. J Plant Nutr 38:295–309. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2014.957392
Prasanna R, Nain L, Rana A, Shivay YS (2016) Biofortification with microorganisms: present status and future challenges. In: Singh U, Praharaj C, Singh S, Singh N. (eds.) Biofortification of food crops. Springer, New Delhi. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2716-8
Purakayastha TJ, Singh CS, Chhonkar PK (1998) Growth and iron nutrition of broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. var. italic Plenck), grown in a Typic Ustochrept, as influenced by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the presence of pyrite and farmyard manure. Biol Fertil Soil 27:35–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050396
Rengel Z (2015) Availability of Mn, Zn and Fe in the rhizosphere. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 15:397–409. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162015005000036
Rodríguez Y, Ballester A, Blázquez M, González F, Muñoz J (2003) New information on the pyrite bioleaching mechanism at low and high temperature. Hydrometallurgy 71:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(03)00172-5
Rohwerder T, Gehrke T, Kinzler K, Sand W (2003) Bioleaching review part A: Progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1448-7
Rui M, Ma C, Hao Y, Guo J, Rui Y, Tang X, Zhao Q, Fan X, Zhang Z, Hou T, Zhu S (2016) Iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential iron fertilizer for peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Front Plant Sci 7:815. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00815
Sand W, Gehrke T (2006) Extracellular polymeric substances mediate bioleaching/biocorrosion via interfacial processes involving iron (III) ions and acidophilic bacteria. Res Microbiol 157:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2005.07.012
Sharma P, Das A, Rao KH, Forssberg K (2003) Surface characterization of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cells grown under different conditions. Hydrometallurgy 71:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(03)00167-1
Shenker M, Chen Y (2005) Increasing iron availability to crops: fertilizers, organo-fertilizers, and biological approaches. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 51:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2005.tb00001.x
Singh BR, Timsina YN, Lind OC, Cagno S, Janssens K (2018) Zinc and iron concentration as affected by nitrogen fertilization and their localization in wheat grain. Front Plant Sci 9:307. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00307
Soil Survey Staff (2010) Keys to soil taxonomy, 11th edn. Lincoln, USDA. National Resources Conservation Service. National Soil Survey Center
Sugio T, Domatsu C, Munakata O, Tano T, Imai K (1985) Role of a ferric ion-reducing system in sulfur oxidation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1401–1406. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.49.6.1401-1406.1985
Tiwari KN, Pathak AN, Upadhyay GP (1982) Effect of sedimentary pyrites and Zn application on yield, Zn and ca nutrition of rice and wheat crops and on amelioration of saline sodic soil. J Agric Sci 99:411–416. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859600030203
Tozsin G, Arol AI (2015) Pyritic tailings as a source of plant micronutrients in calcareous soils. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal 46: 1473–1481. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2015.1043446
Wallace A, Wallace GA (1992) Factors influencing oxidation of iron pyrite in soil. J Plant Nutr 15:1579–1587. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169209364423
Wang J, Bai J, Xu J, Liang B (2009) Bioleaching of metals from printed wire boards by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and their mixture. J Hazard Mater 172:1100–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.102
Wang X, Cai QS (2006) Steel slag as an iron fertilizer for corn growth and soil improvement in a pot experiment. Pedosphere 16:519–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(06)60083-0
Wu L, Yang B, Wang X, Wu B, He W, Gan M, Qiu G, Wang J (2019) Effects of single and mixed energy sources on intracellular nanoparticles synthesized by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Minerals 9:163. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9030163
Yang X, Alidoust D, Wang C (2020) Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles on the mineral composition and growth of soybean (Glycine max L.) plants. Acta Physiol Plant 42: 128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03104-1
Funding
This study was funded by Ferdowsi University of Mashhad with grant number 3/38839.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daliran, T., Halajnia, A. & Lakzian, A. Thiobacillus Bacteria-Enhanced Iron Biofortification of Soybean in a Calcareous Soil Enriched with Ferrous Sulfate, Mill Scale, and Pyrite. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22, 2221–2234 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00804-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00804-0