Abstract
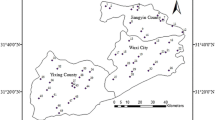
The study aimed to investigate the suitability of moss Thuidium cymbifolium, as a bio-monitor for assessing atmospheric metal deposition in various locations across the Champawat district of Uttarakhand, India. Moss bags containing T. cymbifolium were transplanted at nearly equal heights covering different sites, varying in direction and seasonal placement, to analyze the accumulation of heavy metals in the moss. The recorded values of metal deposition and contamination factors (CF) from all study sites were systematically analysed. Remarkably, the results consistently fell within the second category (1 < CF ≤ 2) of the contamination factor, indicating minimal metal deposition. This suggests that the levels of heavy metal contamination across all monitoring locations were relatively low. Crucially, no instances of severe contamination were observed for any element at any of the monitoring sites. Overall, analysis of transplant moss suggests that none of the studied locations are currently experiencing alarming levels of metal dispersion in the Champawat.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi K, Tainosho Y (2004) Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ Inter 30(8):1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.04.004
Adamiec E, Jarosz-Krzemińska E, Wieszała R (2016) Heavy metals from non-exhaust vehicle emissions in urban and motorway road dusts. Environ Monit Assess 188:369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5377-1
Aksu A (2015) Sources of metal pollution in the urban atmosphere (a case study: Tuzla, Istanbul). J Environ Health Sci Eng 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-015-0224-9
Alengebawy A, Abdelkhalek ST, Qureshi SR, Wang MQ (2021) Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 9(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9030042
Ares A, Aboa JR, Carballeira A, Giordano S, Adamo P, Fernández JA (2012) Moss bag biomonitoring: a methodological review. Sci Total Environ 432:143–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.087
Aslam J, Khan SA, Khan SH (2013) Heavy metals contamination in roadside soil near different traffic signals in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. J Saudi Chem Soc 17(3):315–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2011.04.015
Asthana DK, Asthana M (2005) Environment: problems and solutions. S. Chand and Company Ltd., New Delhi
Chandra S, Kulshrestha MJ, Singh R (2014) Temporal variation and concentration weighted trajectory analysis of lead in PM10 aerosols at a site in Central Delhi, India. Int J Atm Sci 2014:323040. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/323040
Cherednichenko VS, Cherednichenko AV, Cherednichenko AV et al (2021) Heavy metal deposition through precipitation in Kazakhstan. Heliyon 7(1):05844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05844
Das R (2022) Sources of lead (Pb) in atmosphere over Indian cities and health impacts. In: Asian Atmospheric Pollution. Elsevier pp 435–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816693-2.00014-7
De Oliveira RC, do, Nascimento Queiroz SC, da Luz CFP et al (2016) Bee pollen as a bioindicator of environmental pesticide contamination. Chemosphere 163:525–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.022
District Administration Champawat https://www.champawat.nic.in
Dollery R, Bowie MH, Dickinson NM (2022) The ecological importance of moss ground cover in dry shrubland restoration within an irrigated agricultural landscape matrix. Ecol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.8843
Eisler R (1998) Copper hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review (No. 33). US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey, pp 7–14
Gao G, Zeng H, Zhou Q (2022) Biomonitoring atmospheric pollution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using mosses. Atmosphere 14(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010026
Grodzińska K, Szarek-Łukaszewska G (2001). Response of mosses to the heavy metal deposition in Poland: an overview. Environ Poll 114:443–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00227-X
Grodzińska K, Szarek-Łukaszewska G (2001) Response of mosses to the heavy metal deposition in Poland—an overview. Environ Pollut 114(3):443–451
Harmens H, Norris DA, Sharps K et al (2015) Heavy metal and nitrogen concentrations in mosses are declining across Europe whilst some hotspots remain in 2010. Environ Poll 200:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.036
Iodice P, Adamo P, Capozzi F, Di Palma A et al (2016) Air pollution monitoring using emission inventories combined with the moss bag approach. Sci Total Environ 541:1410–1419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.034
Kapusta P, Stanek M, Szarek-Lukaszewska G et al (2019) Long-term moss monitoring of atmospheric deposition near a large steelworks reveals the growing importance of local non-industrial sources of pollution. Chemosphere 230:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.058.
Kaur S, Rao A, Kumar SS (2010) Studies on the effect of heavy metals on the growth of some bryophytes-I (mosses). Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 5:102–107
Kayee P, Songphim W, Parkpein A (2015) Using Thai native moss as bio-adsorbent for contaminated heavy metal in air. Procedia-Social Behav Sci 197:1037–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.07.312
Korzeniowska J, Panek E (2012) The content of Trace metals (cd, cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) in selected plant species (Moss Pleurozium Schreberi, Dandelion Taraxacum Officianale, Spruce Picea Abies) along the Road Cracow–Zakopane. Geomatics Environ Eng 6(1):43–50
Kosior G, Pribylova P, Vankova L et al (2017) Bioindication of PBDEs and PCBs by native and transplanted moss Pleurozium schreberi. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 143:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.05.025
Lamichhane JR, Osdaghi E, Behlau F et al (2018) Thirteen decades of antimicrobial copper compounds applied in agriculture. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 38:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-018-0503-9
Luo XS, Xue Y, Wang YL et al (2015) Source identification and apportionment of heavy metals in urban soil profiles. Chemosphere 127:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.048
Makholm MM, Mladenoff DJ (2005) Efficacy of a biomonitoring (moss bag) technique for determining element deposition trends on a mid-range (375 km) scale. Environ Monit Assess 104:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-6398-3
Mao F, Zhao X, Chang Y, Jia J (2022) Controllable construction of IrCo nanoclusters and the performance for Water Electrolysis. Catalysts 12(8):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080914
Mikhailenko AV, Ruban DA, Ermolaev VA, Van Loon AJ (2020) Cadmium pollution in the tourism environment: a literature review. Geosciences 10(6):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060242
Nawrot N, Wojciechowska E, Rezania S et al (2020) The effects of urban vehicle traffic on heavy metal contamination in road swee** waste and bottom sediments of retention tanks. Sci Tot Environ 749:141511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141511
Nicholson SE, Some B, McCollum J et al (2003) Validation of TRMM and other rainfall estimates with a high-density gauge dataset for West Africa. Part II: validation of TRMM rainfall products. J Appl Meteorol 42(10):1355–1368. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(2003)042<1355:VOTAOR>2.0.CO;2
Oishi Y (2018) Comparison of moss and pine needles as bioindicators of transboundary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution in Central Japan. Environ Pollut 234:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.035
Otvos E, Pazmandi T, Tuba Z (2003) First national survey of atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Hungary by the analysis of mosses. Sci Tot Environ 309(1–3):151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00681-2
Proctor MC, Oliver MJ, Wood AJ et al (2007) Desiccation-tolerance in bryophytes: a review. Bryologist 110(4):595–621
Heindel RC, Putman AL, Murphy SF et al (2020) Atmospheric dust deposition varies by season and elevation in the Colorado front range, USA. J Geophys Research: Earth Surf 125(5):e2019JF005436. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JF005436.
Qarri F, Lazo P, Allajbeu S et al (2019) The evaluation of Air Quality in Albania by Moss Biomonitoring and metals Atmospheric Deposition. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 76(4):554–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-019-00608-x
Rahimzadeh MR, Rahimzadeh MR, Kazemi S et al (2017) Cadmium toxicity and treatment: an update. Casp J Intern Med 8(3):135–145. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim.8.3.135
Sager M (2020) Urban soils and road dust—civilization effects and metal pollution—a review. Environments 7(11):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7110098
Salo H, Makinen J (2019) Comparison of traditional moss bags and synthetic fabric bags in magnetic monitoring of urban air pollution. Ecol Ind 104:559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.05.033
Saxena DK, Agarwal S, Saxena A, Kodesia S (2020) Monitoring of temporal trend of atmospheric metals by moss Hypnum cupressiforme Hedw. in Jammu (India). Int. J. of Thermal & Environmental Engineering, 17(2), pp.121–132. https://doi.org/10.5383/ijtee.17.02.006
Saxena DK, Kaur H (2005) Effect of cadmium and nickel toxicity on the peroxidase activity and carotenoid content in moss Thuidium cymbifolium. Indian J Plant Physiol 10(7):393–399
Saxena DK, Singh S, Srivastava K (2007) Moss bag technique for monitoring of metal precipitation. Environ Conserv J 8(1–2):85–92
Saxena DK, Singh S, Srivastava K (2008) Atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Garhwal Hill area (India): estimation based on native moss analysis. Aerosol Air Qual Res 8:94–111. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2007.07.0031
Schilling JS, Lehman ME (2002) Bioindication of atmospheric heavy metals deposition in the southeastern US using the moss thudium delicatulum. Atmos Environ 36:1611–1618
Singh S, Srivastava K, Gahtori D et al (2017) Bryomonitoring of atmospheric elements in Rhodobryum giganteum (Schwaegr.) Par., growing in Uttarakhand region of the Indian Himalayas. Aerosol Air Qual Res 17(3):810–820. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2015.06.0429
Srivastava RK, Pandey P, Rajpoot R et al (2014) Cadmium and lead interactive effects on oxidative stress and antioxidative responses in rice seedlings. Protoplasma 251(5):1047–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0614-3
Stefanut S, Ollerer K, Manole A et al (2019) National environmental quality assessment and monitoring of atmospheric heavy metal pollution-A moss bag approach. J Environ Manag 248:109224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.06.125.
Stone D (2012) National pesticide information centre annual report. http://npic.orst.edu/reports/NPIC12AR.pdf
Sucharova J, Suchara I (1998) Atmospheric deposition levels of chosen elements in the Czech Republic were determined in the framework of the International Bryomonitoring Program 1995. Sci Tot Environ 223(1):37–52
Sun Y, Zhang D, Li F et al (2020) The rainfall effect onto solidification and stabilization of heavy metal-polluted sediments. Royal Soc Open Sci 7(7):192234. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.192234
Ugoeze KC, Amogu EO, Oluigbo, Ke et al (2021) Environmental and public health impacts of plastic wastes due to healthcare and food products packages: a review. J Environ Sci Public Health 5:1–31. https://doi.org/10.26502/jesph.96120114
Van Laaten N, Merten D, von Tümpling W et al (2020) Comparison of spider web and moss bag biomonitoring to detect sources of airborne trace elements. Water Air Soil Pollut 231 231:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04881-8
WHO (2020) World health statistics 2020: monitoring health for the SDGs. https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/3897953?ln=en
Xu F, Liu Z, Cao Y et al (2017) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in urban river sediments in the Jiaozhou Bay catchment, Qingdao, China. CATENA 150:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.004
Yuan Y, Liu B, Liu H (2022) Spatial distribution and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments of East Dongting Lake, China. Sci Rep 12:7940. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-12148-x
Zafra-Mejia C, Gutierrez-Malaxechebarria A, Hernandez-Pena Y (2019) Correlation between vehicular traffic and heavy metal concentrations in road sediments of Bogotá, Colombia. Rev Facul Med 67(2):193–199. https://doi.org/10.15446/revfacmed.v67n2.68269
Zannoni D, Valotto G, Visin F, Rampazzo G (2016) Sources and distribution of tracer elements in road dust: the Venice mainland case of study. J Geochemical Explo 166:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.04.007
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the University for providing the necessary support. We sincerely thank the Department of Forest, Uttarakhand, and the principal, HNB Government PG College Khatima for providing permission and support for the present work. The authors are also thankful to Prof. Dinesh Kumar Saxena and Dr. Manish Belwal for their valuable suggestions provided from time to time.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DG: Conceptualized, drafted the original manuscript, and performed formal analysis, AV: supervised, provided resources, JS: co-supervise, read, and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not applicable in this study.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gahtori, D., Singh, J. & Vyas, A. Assessment of atmospheric metal deposition by moss Thuidium cymbifolium (Dozy & Molk.) Dozy & Molk. At Champawat Hills, India. Vegetos (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-024-00937-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-024-00937-w