Abstract
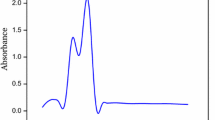
In this study, the synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Amberlite LA-2 functionalized with benzoyl thiourea as a cap** agent were investigated. Silver nanoparticles were prepared from silver nitrate using the chemical reduction method in the presence of sodium borohydride as a reducing agent and Amberlite LA-2 bearing benzoyl thiourea (ALA-BTU) as a cap** agent. The reaction conditions, such as reactant concentrations, reaction time, pH, and temperature, are optimized to achieve the desired nanoparticle size and morphology. Silver nanoparticles were characterized by using different techniques, including UV‒visible spectroscopy (UV‒Vis), infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and dynamic light scattering (DLS). The surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles was obtained at 400 nm. The average diameter of the silver nanoparticles was in the range of 86.36 to 103.4 nm, as determined by DLS; however, the average diameter was 3 nm, as determined by TEM. The absorbance of the tested solutions was found to increase with increasing AgNO3 concentration and pH; however, the absorbance decreased with increasing temperature, time and ionic strength. The silver nanoparticles and ALA-BTU showed moderate antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus bacteria. However, they exhibited insignificant antimicrobial effects against Streptococcus, E. coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ridwan IP (2020) Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) skin extract. Jurnal Akta Kimia Indonesia (Indonesia Chimica Acta) 73–78
Jalab J, Kitaz A, Abdelwahed W, Al-Kayali R (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using some medicinal plants. Int Res J Pure Appl Chem 13–26
Patel N, Singh S (2020) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana and papaya leaves extracts and their applications
Siakavella IK et al (2020) Effect of plant extracts on the characteristics of silver nanoparticles for topical application. Pharmaceutics 12(12):1244
Islam A, Mandal C, Habib A (2021) Antibacterial potential of synthesized silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Moringa oleifera. J Adv Biotechnol Exp Ther 4:67
Kaabipour S, Hemmati S (2021) A review on the green and sustainable synthesis of silver nanoparticles and one-dimensional silver nanostructures. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 12(1):102–136
Singh R, Hano C, Nath G, Sharma BJB (2021) Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Carissa carandas L. and their antioxidant and antimicrobial activity against human pathogenic bacteria. Biomolecules 11(2):299
Tu NC, Sang HM, Anh LTL, Lam NH (2021) Eco-friendly synthesis and applicability to silver ink of silver nanoparticles prepared via stepwise-modified Tollens method. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 21(4):2568–2575
Quintero-Quiroz C et al (2019) Optimization of silver nanoparticle synthesis by chemical reduction and evaluation of its antimicrobial and toxic activity. Biomater Res 23(1):1–15
Saha C, Das A, Das P, Chakraborty A (2021) Effect of quercetin loaded silver nanoparticles on gram negative and gram positive bacteria. Indian J Exp Biol 59(02):132–140
Avitabile E et al (2020) The potential antimalarial efficacy of hemocompatible silver nanoparticles from Artemisia species against P. falciparum parasite. PLoS ONE 15(9):e0238532
Belkher N, Al-abbasi A, Zidan M (2019) Potentiometric studies on stability constant of the complexes of some essential transition metal ions with l-valine. J Pure Appl Sci 13(3):59–63
Iravani S, Korbekandi H, Mirmohammadi SV, Zolfaghari B (2014) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: chemical, physical and biological methods. Res Pharm Sci 9(6):385
Natsuki J, Natsuki T, Hashimoto Y (2015) A review of silver nanoparticles: synthesis methods, properties and applications. Int J Mater Sci Appl 4(5):325–332
Al-abbasi A, Tahir M, Kayed S, Kassim M (2022) Synthesis, characterisation and biological activities of mixed ligand oxovanadium(IV) complexes derived from N,N-diethyl-N′-para-substituted-benzoylthiourea and hydrotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate. Appl Organometal Chem 36(4):e6607. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.6607
Kumari RM, Thapa N, Gupta N, Kumar A, Nimesh S (2016) Antibacterial and photocatalytic degradation efficacy of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using Cordia dichotoma leaf extract. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 7(4):045009
Landage S, Wasif A, Dhuppe P (2014) Synthesis of nanosilver using chemical reduction methods. Int J Adv Res Eng Appl Sci 3(5):14–22
Almutaleb A, Alabbasi A (2023) Synthesis, characterization and computational studies for (2′S*,3R*,3′S*,8a′R*)-2′,3′-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)-2-oxo-2′,3′-dihydro-8a′H-spiro[indoline-3,1′-indolizine]-6′-carboxylic acid and some derivatives. J Phys Org Chem 36(2):e4452. https://doi.org/10.1002/poc.4452
Al-Abbasi A et al (2023) BaO as a heterogeneous nanoparticle catalyst in oil transesterification for the production of FAME fuel. Inorg Chem Commun 158:111620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111620
Khalifa S, Al-Abbasi A, Suliman M (2018) Adsorption and corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic media by expired pharmaceutical drug. J Pure Appl Sci 17:1–6
Salim SM, Izriq R, Almaky MM, Al-Abbasi AA (2022) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles for the production of biodiesel by transesterification: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Fuel 321:124135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124135
Douglass IB, Dains FB (1934) Some derivatives of benzoyl and furoyl isothiocyanates and their use in synthesizing heterocyclic compounds1. J Am Chem Soc 56(3):719–721. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01318a057
Beyer L, Hoyer E, Hennig H, Kirmse R, Hartmann H, Liebscher J (1975) Synthese und Charakterisierung neuartiger Übergangsmetallchelate von 1,1-Dialkyl-3-benzoyl-thioharnstoffen. J Prakt Chem 317(5):829–839. https://doi.org/10.1002/prac.19753170518
Sanchooli N, Saeidi S, Barani HK, Sanchooli E (2018) In vitro antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Verbena officinalis leaf extract on Yersinia ruckeri, Vibrio cholera and Listeria monocytogenes (in eng). Iran J Microbiol 10(6):400–408
Hudzicki J (2009) Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test protocol. Am Soc Microbiol 15:55–63
Sacht CI, Datt MS, Otto S, Roodt A (2000) Chiral and achiral platinum(n) complexes for potential use as chemotherapeutic agents: crystal and molecular structures of cis-[Pt(V)2] and [PtflL^CKMPSO] [HL1 = JV,yV-diethyWV-benzoylthiourea]. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans (5):727–733. [Online]. Available: http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-11144278339&partnerID=40&md5=38adf954605f5adf654453a77a615e3f
Hernandez W et al (2005) Synthesis, characterization and antitumor activity of copper(II) complexes, [CuL2] [HL1-3 = N, N-diethyl-N’-(R-benzoyl)thiourea (R = H, o-Cl and p-NO2)]. Bioinorg Chem Appl 3(3–4):299–316. https://doi.org/10.1155/bca.2005.299
Hernandez W et al (2003) Synthesis, characterization and antitumor activity of cis-bis(acylthioureato) platinum(II) complexes, cis-[PtL(2)] [HL=N,N-diphenyl-N'-benzoylthiourea or HL=N,N-diphenyl-N'-(p-nitrobenzoyl)thiourea]. Bioinorg Chem Appl 271–84
Otazo-Sánchez E et al (2002) Aroylthioureas: new organic ionophores for heavy metal ion selective electrodes. A nuclear magnetic resonance study. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 58(10):2281–2290. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-1425(01)00724-7
Al-abbasi A, Kassim M (2011) 1-Ethyl-1-methyl-3-(2-nitrobenzoyl)thiourea. Acta Crystallogr Sect E 67(7):o1840. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536811024652
Al-abbasi A, Tan S, Kassim M (2010) 1-Benzoyl-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)thiourea. Acta Crystallogr Sect E 66(12):o3181. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536810045988
Al-abbasi AA, MohamedTahir MI, Kassim MB (2012) N-(Pyrrolidin-1-ylcarbothioyl)benzamide. Acta Crystallogr Sect E 68(1):o201. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536811053694
Al-Abbasi AA, Kayed SF, Kassim MB (2023) Spectral, theoretical, physicochemical and corrosion inhibition studies of ortho-, meta- and para-hydroxyphenyl-benzoylthiourea ligands. Inorg Chem Commun 156:111155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111155
Alabbasi A, Essa E, Emrayed H (2022) Removal of cadmium from its aqueous solution by benzoyl thiourea compounds as an extractant. Arab J Chem Environ Res 9(2):184–196. [Online]. Available: http://www.mocedes.org/ajcer/volume9/AJCER-11-Alabbasi-2022.pdf
Veeramani S, Ernest R, Ramadoss P, Joseph C, Shanmugam KJ (2018) Silver nanoparticles–green synthesis with aq. extract of stems Ipomoea pes-caprae, characterization, antimicrobial and ant-cancer potential. Int J Med Nano Res 5:024
Mani M et al (2021) Studies on the spectrometric analysis of metallic silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) using Basella alba leaf for the antibacterial activities. Environ Res 199:111274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111274
Aljabali AAA et al (2018) Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of Ziziphus zizyphus and their antimicrobial activity. Nanomaterials 8(3):174. [Online]. Available: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-4991/8/3/174
Ferreira AM, Vikulina A, Loughlin M, Volodkin D (2023) How similar is the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles coated with different cap** agents? RSC Adv 13(16):10542–10555. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3RA00917C
Almatroudi A (2020) Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, characterisation and biomedical applications (in eng). Open Life Sci 15(1):819–839. https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2020-0094
Iravani S, Korbekandi H, Mirmohammadi S, Zolfaghari B (2014) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: chemical, physical and biological methods. Res Pharm Sci 9:385–406
Restrepo CV, Villa CC (2021) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles, influence of cap** agents, and dependence on size and shape: a review. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 15:100428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100428
Maddinedi SB, Mandal BK, Maddili SK (2017) Biofabrication of size controllable silver nanoparticles—a green approach. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 167:236–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.01.003
Pattanayak S et al (2017) Butea monosperma bark extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: characterization and biomedical applications. J Saudi Chem Soc 21(6):673–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2015.11.004
Raja S, Ramesh V, Thivaharan V (2017) Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Calliandra haematocephala leaf extract, their antibacterial activity and hydrogen peroxide sensing capability. Arab J Chem 10(2):253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.06.023
Crisan CM, Mocan T, Manolea M, Lasca LI, Tăbăran F-A, Mocan L Review on silver nanoparticles as a novel class of antibacterial solutions. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031120
Franci G et al (2015) Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 20(5):8856–8874. [Online]. Available: https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/20/5/8856
Lara HH, Ayala-Núñez NV, IxtepanTurrent LDC, Rodríguez Padilla C (2010) Bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26(4):615–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0211-3
Li W-R, **e X-B, Shi Q-S, Duan S-S, Ouyang Y-S, Chen Y-B (2011) Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus. Biometals 24(1):135–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9381-6
McNeilly O, Mann R, Hamidian M, Gunawan C (2021) Emerging concern for silver nanoparticle resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and other bacteria (in English). Front Microbiol Rev. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.652863
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the assistance of the Chemistry Department at Sebha University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Abdulrahman Dnkm is a postgraduate student who was in charge of the experiments, methodology, and writing. Dr. Mohamed Erhayem was responsible for the supervision, conceptualization, methodology, software, writing, review and editing. is Dr A. Al-Abbasi, a Cosupervisor who was responsible for the preparation of the original manuscript and the validation, review.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors affirm that they have no known financial or interpersonal conflicts that would have appeared to have an impact on the research presented in this study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dnkm, A., Al-Abbassi, A. & Erhayem, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Amberlite LA-2 Functionalized with Benzoyl Thiourea as a Cap** Agent. Chemistry Africa 7, 2643–2659 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-024-00902-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-024-00902-9