Abstract
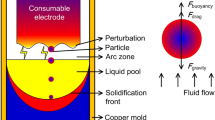
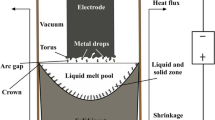
The feeding parameters in the final stage of vacuum arc remelting process obviously affect the solute segregation and shrinkage pore depth. Coupled with the electromagnetic field, fluid flow, and solute transport, a numerical model was built to investigate the effect of feeding parameters on the ingot solidification phenomena. The Nb segregation and shrinkage pore depth in the solidified ingot were measured. The results show that the liquid moves along the solidification front and the vertex flow is formed in the liquid pool, which promotes solute transport. In the solidified ingot, the Nb segregation in the lower part is negative, while that in the upper part is positive. With the differential electrode applied, the positive segregation is slightly reduced but the segregation distribution remains unchanged. As the feeding current decreases, the positive segregation zone moves toward the ingot top surface, due to the final solidification position moving upward. With the feeding time extended, the positive segregation moves to the top surface and the shrinkage pore depth is reduced. As the feeding time is set at 12 min, the shrinkage pore depth can be reduced to 21 mm.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Valdés, P. King, X. Liu, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41 (2010) 2408–2416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-010-0331-2.
X. Wang, R.M. Ward, M.H. Jacobs, M.D. Barratt, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 39 (2008) 2981–2989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9638-7.
L. Nastac, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45 (2014) 44–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-012-9715-6.
P.O. Delzant, B. Baque, P. Chapelle, A. Jardy, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 958–968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1194-y.
F.J. Zanner, L.A. Bertram, C. Adasczik, T. O’Brien, Metall. Trans. B 15 (1984) 117–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02661069.
C.R. Woodside, P.E. King, C. Nordlund, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44 (2013) 154–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-012-9760-1.
H.E. Mir, A. Jardy, J.P. Bellot, P. Chapelle, D. Lasalmonie, J. Senevat, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 210 (2010) 564–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2009.11.008.
R. Bhar, A. Jardy, P. Chapelle, V. Descotes, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 51 (2020) 2492–2503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01966-x.
E. Karimi-Sibaki, A. Kharicha, M. Wu, A. Ludwig, J. Bohacek, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 51 (2020) 222–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01719-5.
E.N. Kondrashov, M.I. Musatov, A.Y. Maksimov, A.E. Goncharov, L.V. Konovalov, J. Eng. Thermophys. 16 (2007) 19–25. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232807010031.
A. Jardy, D. Ablitzer, Mater. Sci. Technol. 25 (2009) 163–169. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328408X355406.
W. Zhang, P.D. Lee, M. McLean, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 33 (2002) 443–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0105-6.
D. Zagrebelnyy, M.J.M. Krane, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 40 (2009) 281–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9163-5.
A. Kermanpur, D.G. Evans, R.J. Siddall, P.D. Lee, M. McLean, J. Mater. Sci. 39 (2004) 7175–7182. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000048729.68319.f0
H. Kou, Y. Zhang, P. Li, H. Zhong, R. Hu, J. Li, L. Zhou, Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 43 (2014) 1537–1542. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5372(14)60120-X
D. Jiang, L. Zhang, JOM 74 (2022) 1601–1609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-05093-z.
W.D. Bennon, F.P. Incropera, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 30 (1987) 2161–2170. https://doi.org/10.1016/0017-9310(87)90094-9.
B.G. Thomas, L. Zhang, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 1181–1193. https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.41.1181.
D. Jiang, M. Zhu, Steel Res. Int. 86 (2015) 993–1003. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201400281.
F.Z. Yang, J. Zhang, L.F. Zhang, Y. Zhou, D.B. Jiang, Y. Ren, J. Iron Steel Res. 34 (2022) 916–924. https://doi.org/10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20210206.
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful for the support from Science and Technology Program of Hebei (Nos. 20311004D and 20591001D), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51904024), the High Steel Center (HSC) at North China University of Technology, Yanshan University, and University of Science and Technology Bei**g.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Db., Yang, Fz., Zhang, J. et al. Effect of feeding parameters on ingot segregation and shrinkage pore in vacuum arc remelting. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30, 1268–1278 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00862-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00862-9