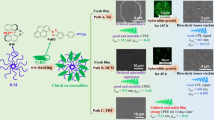
Abstract
Circularly polarized luminescence materials have attracted plenty of interest by virtue of their fascinating characteristics as well as prospective applications in information encryption, optoelectronic devices, and so on. However, the spatiotemporal modulation of circularly polarized luminescence materials by using light irradiation is still challenging. Herein, we have constructed a kind of hybrid supramolecular nanofibers with tunable circularly polarized luminescence based on photoresponsive chiral cinnamic acid gelator and achiral spiropyran through photoisomerization. The chiral cinnamic acid gelator could self-assemble into nanofiber structures by hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interaction and π-π stacking, displaying intense right-handed circularly polarized luminescence at 400 nm. However, UV irradiation causes the trans–cis isomerization of the cinnamic acid moiety, resulting in the transformation of nanofibers into rod-like structures and the loss of circularly polarized luminescence signal. In view of this problem, we discovered that the photoisomerized spiropyran can help with the photostability of the nanofibers as well as tuning of their CPL emission, as spiropyran molecule could be transformed into its merocyanine state by ring-opening reaction under 254 nm UV irradiation following with the formation of chiral merocyanine aggregates on the surfaces of the nanofibers. The as-obtained hybrid nanofibers emit both right-handed circularly polarized luminescence at 400 nm and left-handed circularly polarized luminescence at 700 nm with a high luminescence dissymmetry factor. The present study provides a new hybrid strategy to control the photostability as well as regulate the circularly polarized luminescence performance of soft materials.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information files.
References
Liu YP, **ng PY (2023) Circularly polarized light responsive materials: Design strategies and applications. Adv Mater 35:e2300968. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202300968
Gong Z-L, Zhu XF, Zhou ZH, Zhang S-W, Yang D, Zhao B, Zhang Y-P, Deng JP, Cheng YX, Zheng Y-X, Zang S-Q, Kuang H, Duan PF, Yuan MJ, Chen C-F, Zhao YS, Zhong Y-W, Tang BZ, Liu MH (2021) Frontiers in circularly polarized luminescence: Molecular design, self-assembly, nanomaterials, and applications. Sci China Chem 64(12):2060–2104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-021-1146-6
Yang XF, Gao XQ, Zheng Y-X, Kuang H, Chen C-F, Liu MH, Duan PF, Tang ZY (2023) Recent progress of circularly polarized luminescence materials from chinese perspectives. CCS Chem 5(12):2760–2789. https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.023.202303346
Di Nuzzo D, Kulkarni C, Zhao B, Smolinsky E, Tassinari F, Meskers SCJ, Naaman R, Meijer EW, Friend RH (2017) High circular polarization of electroluminescence achieved via self-assembly of a light-emitting chiral conjugated polymer into multidomain cholesteric films. ACS Nano 11(12):12713–12722. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b07390
Geng ZX, Zhang YX, Zhang Y, Li Y, Quan YW, Cheng YX (2021) Circularly polarized electroluminescence from an achiral fluorophore induced by co-assembly with chiral polymers. J Mater Chem C 9(36):12141–12147. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1tc01948a
Imai Y, Nakano Y, Kawai T, Yuasa J (2018) A smart sensing method for object identification using circularly polarized luminescence from coordination-driven self-assembly. Angew Chem Int Ed 57(29):8973–8978. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201803833
Song FY, Xu Z, Zhang QS, Zhao Z, Zhang HK, Zhao WJ, Qiu ZJ, Qi CX, Zhang H, Sung HHY, Williams ID, Lam JWY, Zhao ZJ, Qin AJ, Ma DG, Tang BZ (2018) Highly efficient circularly polarized electroluminescence from aggregation-induced emission luminogens with amplified chirality and delayed fluorescence. Adv Funct Mater 28(17):1800051. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201800051
Zhan XQ, Xu FF, Zhou ZH, Yan YL, Yao JN, Zhao YS (2021) 3D laser displays based on circularly polarized lasing from cholesteric liquid crystal arrays. Adv Mater 33(37):2104418. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202104418
Zheng HZ, Li WR, Li W, Wang XJ, Tang ZY, Zhang SXA, Xu Y (2018) Uncovering the circular polarization potential of chiral photonic cellulose films for photonic applications. Adv Mater 30(13):1705948. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201705948
Zheng HZ, Ju B, Wang XJ, Wang WH, Li MJ, Tang ZY, Zhang SXA, Xu Y (2018) Circularly polarized luminescent carbon dot nanomaterials of helical superstructures for circularly polarized light detection. Adv Opt Mater 6(23):1801246. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201801246
Chen SB, Jiang SJ, Qiu JB, Guo HY, Yang FF (2020) Dual-responding circularly polarized luminescence based on mechanically and thermally induced assemblies of cyano-distyrylbenzene hydrogen bonding liquid crystals. Chem Commun 56(56):7745–7748. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc09826g
Han DX, Li CX, ** X, Zhou J, Xu YL, Jiao TF, Duan PF (2021) Tunable circularly polarized luminescence of excited-state-proton-transfer-based chiral guanidine. Adv Photonics Res 3(3):2100287. https://doi.org/10.1002/adpr.202100287
Wang Y-J, Shi X-Y, **ng PY, Zang S-Q (2023) Metallophilic interactions drive supramolecular chirality evolution and amplify circularly polarized luminescence. JACS Au 3(2):565–574. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacsau.2c00653
Xu L, Wang C, Li YX, Xu XH, Zhou L, Liu N, Wu ZQ (2020) Crystallization-driven asymmetric helical assembly of conjugated block copolymers and the aggregation induced white-light emission and circularly polarized luminescence. Angew Chem Int Ed 59(38):16675–16682. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202006561
Du C, Li ZJ, Zhu XF, Ouyang GH, Liu MH (2022) Hierarchically self-assembled homochiral helical microtoroids. Nat Nanotechnol 17(12):1294–1302. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-022-01234-w
Kang SG, Kim KY, Cho Y, Jeong DY, Lee JH, Nishimura T, Lee SS, Kwak SK, You Y, Jung JH (2022) Circularly polarized luminescence active supramolecular nanotubes based on ptiicomplexes that undergo dynamic morphological transformation and helicity inversion. Angew Chem Int Ed 61(38):e202207310. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202207310
Li PP, Gao XB, Zhao B, Pan K, Deng JP (2022) Multi-color tunable and white circularly polarized luminescent composite nanofibers electrospun from chiral helical polymer. Adv Fiber Mater 4(6):1632–1644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00196-x
Guo Q, Zhang MJ, Tong Z, Zhao SS, Zhou YJ, Wang YX, ** S, Zhang J, Yao H-B, Zhu MZ, Zhuang TT (2023) Multimodal-responsive circularly polarized luminescence security materials. J Am Chem Soc 145(7):4246–4253. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c13108
Dai L, Js Lu, Kong FG, Liu KF, Wei HG, Si CL (2019) Reversible photo-controlled release of bovine serum albumin by azobenzene-containing cellulose nanofibrils-based hydrogel. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 2(3):462–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-019-00112-9
Hashimoto Y, Nakashima T, Kuno J, Yamada M, Kawai T (2018) Dynamic modulation of circularly polarized luminescence in photoresponsive assemblies. ChemNanoMat 4(8):815–820. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.201800124
** X, Yang D, Jiang YQ, Duan PF, Liu MH (2018) Light-triggered self-assembly of a cyanostilbene-conjugated glutamide from nanobelts to nanotoroids and inversion of circularly polarized luminescence. Chem Commun 54(36):4513–4516. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CC00893K
Shi YH, Han JL, ** X, Miao WG, Zhang Y, Duan PF (2022) Chiral luminescent liquid crystal with multi-state-reversibility: Breakthrough in advanced anti-counterfeiting materials. Adv Sci 9(20):e2201565. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202201565
Han DX, Jiao TF (2022) Reversible chiral optical switching based on co-assembled spiropyran gels. Langmuir 38(45):13668–13673. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c01473
Miao W, Wang S, Liu MH (2017) Reversible quadruple switching with optical, chiroptical, helicity, and macropattern in self-assembled spiropyran gels. Adv Funct Mater 27(29):1701368. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201701368
Liu GF, Sheng JH, Teo WL, Yang GB, Wu HW, Li YX, Zhao YL (2018) Control on dimensions and supramolecular chirality of self-assemblies through light and metal ions. J Am Chem Soc 140(47):16275–16283. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b10024
Yao LF, Fu K, Liu GF (2023) Solvent-directed hierarchical self-assembly of tetraphenylpyrazine-cholesterol with amplified circularly polarized luminescence. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 15(34):40817–40827. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c10358
Basak S, Nandi N, Baral A, Banerjee A (2015) Tailor-made design of J-or H-aggregated naphthalenediimide-based gels and remarkable fluorescence turn on/off behaviour depending on solvents. Chem Commun 51(4):780–783. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc06680d
**ng PY, Tham HP, Li PZ, Chen HZ, **ang HJ, Zhao YL (2018) Environment-adaptive coassembly/self-sorting and stimulus-responsiveness transfer based on cholesterol building blocks. Adv Sci 5(1):1700552. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201700552
Jiang HJ, Jiang YQ, Han JL, Zhang L, Liu MH (2019) Helical nanostructures: Chirality transfer and a photodriven transformation from superhelix to nanokebab. Angew Chem Int Ed 58(3):785–790. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201811060
Harada N, Chen S-ML, Nakanishi K (1975) Quantitative definition of exciton chirality and the distant effect in the exciton chirality method. J Am Chem Soc 97(19):5345–5352. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00852a005
Yang D, Duan PF, Zhang L, Liu MH (2017) Chirality and energy transfer amplified circularly polarized luminescence in composite nanohelix. Nat Commun 8(1):15727. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15727
Yao LF, Fu K, Wang XJ, He ML, Zhang WN, Liu PY, He YP, Liu GF (2023) Metallophilic interaction-mediated hierarchical assembly and temporal-controlled dynamic chirality inversion of metal-organic supramolecular polymers. ACS Nano 17(3):2159–2169. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c08315
Hu Y, Huang ZZ, Willner I, Ma X (2024) Multicolor circularly polarized luminescence of a single-component system revealing multiple information encryption. Chinese Chem Soc Chem 6(2):518–527. https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.023.202302904
Yang L, Wang F, D-iY A, Feng CL (2019) Achiral isomers controlled circularly polarized luminescence in supramolecular hydrogels. Nanoscale 11(30):14210–14215. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr05033g
Zeng JQ, Qi PF, Wang Y, Liu YH, Sui KY (2021) Electrostatic assembly construction of polysaccharide functionalized hybrid membrane for enhanced antimony removal. J Hazard Mater 410:124633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124633
Feng Y, Li YC, Almalki ASA, Meng XN, Alhadhrami A, Ye XM, Ibrahim MM, Guo X, Algadi H, Huang MN, Winchester W, Wang Z (2022) Synthesis and characterization of poly(butanediol sebacate-butanediol) terephthalate (PBSeT) reinforced by hydrogen bond containing amide group, with good mechanical properties and improved water vapor barrier. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(3):2051–2065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00542-y
Jiang HJ, Jiang YQ, Zhang L, Guo ZX, Liu MH (2018) Symmetry breaking and amplification in a self-assembled helix from achiral trans-3-nitrocinnamic acid. J Phys Chem C 122(23):12559–12565. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b03412
Kuang G-C, Ji Y, Jia X-R, Li Y, Chen E-Q, Zhang Z-X, Wei Y (2009) Photoresponsive organogels: An amino acid-based dendron functionalized with p-nitrocinnamate. Tetrahedron 65(17):3496–3501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2009.02.038
Gong ZL, Li ZQ, Zhong YW (2022) Circularly polarized luminescence of coordination aggregates. Aggregate 3(5):e177. https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.177
Wang L, Xue YX, Cui MH, Huang YM, Xu HY, Qin CC, Yang JE, Dai HT, Yuan MJ (2020) A chiral reduced-dimension perovskite for an efficient flexible circularly polarized light photodetector. Angew Chem Int Ed 59(16):6442–6450. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201915912
Zhang LY, ** YS, Wang YK, Li WJ, Guo ZL, Zhang JY, Yuan L, Zheng C, Zheng YX, Chen RF (2023) High-quality circularly polarized organic afterglow from nonconjugated amorphous chiral copolymers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 15(42):49623–49632. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c10605
Bao YL, Zhang G, Wang NW, Pan MH, Zhang W (2023) Circularly polarized luminescent organogels based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer in an achiral polymer system. J Mater Chem C 11(7):2475–2479. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2tc05101j
Dai YK, Zhang ZW, Wang D, Li TL, Ren YZ, Chen JQ, Feng LY (2023) Machine-learning-driven G-quartet-based circularly polarized luminescence materials. Adv Mater 36(4):2310455. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202310455
Yuan W, Chen LT, Yuan CT, Zhang ZD, Chen XK, Zhang XD, Guo JJ, Qian C, Zhao ZJ, Zhao YL (2023) Cooperative supramolecular polymerization of styrylpyrenes for color-dependent circularly polarized luminescence and photocycloaddition. Nat Commun 14(1):8022–8032. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43830-x
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.22202113), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (Nos.ZR2021QB006, Nos.2022HWYQ-083, Nos.ZR2023ME019), the Taishan Scholar Program of Shandong Province (Nos.tsqnz20221136), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos.2021M701809, Nos.2023T160347), the State Key Laboratory of Bio-Fibers and Eco-Textiles (Qingdao University) (Nos.GZRC202012), and the Qingdao Applied Research Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiuya Yang, Xueli Liu, and Zhaocun Shen designed the experiments. Qiuya Yang, Zhichao Xu, and **nnuo Wu conducted experiments and drafted the manuscript. Min Lin, Zhaocun Shen, and Kunyan Sui supervised the project. Qiuya Yang, Xueli Liu, Zhichao Xu, **nnuo Wu, Gemeng Liang, Min Lin, Zhaocun Shen, and Kunyan Sui discussed the experiments and results. All authors have given approval for the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Liu, X., Xu, Z. et al. Tunable circularly polarized luminescence of hybrid supramolecular nanofibers based on a cinnamic acid gelator and spiropyran by photoisomerization. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 7, 121 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-024-00931-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-024-00931-5