Abstract
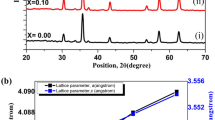
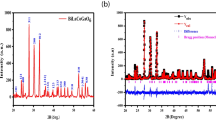
The spinel ferrites (SFs) are renowned for their distinctive magnetic and electrical characteristics. Sol-gel route was used for the fabrication of Sr0.6 Zn0.4 Gdx Fe2-x O4 (0.00, 0.025, 0.050, 0.075, 0.100) ferrites. The structural, magnetic, microwave, and DC (direct current) properties of prepared Nps were found using of number characterization techniques. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of Sr0.6 Zn0.4 Gdx Fe2-x O4 SFs showed a single cubic phase. The magnetic behavior was determined by applying a field of 2 kOe. The various magnetic features, including those determined based on the M-H loop, and prepared spinel ferrites showed the soft nature of magnetic materials. When amount of gadolinium (Gd) is increased, then saturation magnetization, coercivity, remanence magnetization is decreased. The Ms values decreased from 69.36 to 32.18 emu/g, coercivity reduced from 220 to 14 emu/g, and remanence magnetization is decreased from 32 to 3 emu/g. The electrical parameters revealed that direct current resistivity and activation energy (Ea) increased (from 0.16 eV to 0.28eV) with the inclusion of the Gd. The activation energy was increased from 0.16 to 0.28 eV. The dielectric constant and loss of permittivity and permeability were determined by applying the frequency 5.5–9.5 GHz. From the above enhanced parameters, it can be concluded that fabricated SFs may be suitable for high-frequency devices.






Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Subramanian, A.P., Jaganathan, S.K., Manikandan, A., Pandiaraj, K.N., Gomathi, N., Supriyanto, E.: Recent trends in nano-based drug delivery systems for efficient delivery of phytochemicals in chemotherapy. RSC Adv. 6, 48294–48314 (2016)
Abraham, A.G., Manikandan, A., Manikandan, E., Vadivel, S., Jaganathan, S.K., Baykal, A., SriRenganathan, iP.: Enhanced magneto-optical and photo-catalytic properties of transition metal cobalt (Co2+ions) doped spinel MgFe2O4 ferrite nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 452, 380–388 (2018)
Stergiou, C.: Magnetic, dielectric and microwave absorption properties of rare earth doped Ni–Co and Ni–Co–Zn spinel ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 629–635 (2017)
Sattar, A.A., Wafik, A.H., El-shokrofy, K.M.: Magnetic properties of Cu ± Zn ferrites doped with rare earth oxides. Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 171, 563–570 (1999)
Zipare, K.V., Bandgar, S.S., Shahane, G.S.: Effect of Dy-substitution on structural and magnetic properties of MnZn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Rare Earths 36, 86–94 (2018)
Abdellatif, M.H., Abdellatif, M.H., El-Komy, G.M., Azab, A.A.: Magnetic characterization of rare earth doped spinel ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 442, 445–452 (2017)
Azim-Araghi, M.E., et al.: Synthesis and magnetic properties of SrZn1−xNixFe16O27 (x ≤ 0.25) hexagonal ferrites prepared by solution combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 464, 225–231 (2018)
Kim, J.H., et al.: Effect of Ni substitution on structural and magnetic properties of SrZn0.5Fe11.5O19 hexagonal ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 766, 228–233 (2018)
Kuhire, M.S., et al.: Structural and magnetic properties of Sr-Zn nanoferrites synthesized by a modified co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 458, 313–320 (2018)
Al-Wahaibi, T., et al.: Magnetic and structural properties of Sr-Zn nanoferrite synthesized by microwave-assisted combustion method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29(3), 2554–2560 (2018)
Wang, H., et al.: Synthesis and magnetic properties of Sr1−xZnxFe12−2xTi2xO19 ferrite nanoparticles for high-frequency applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 460, 189–195 (2018)
Roy, P.K., Bera, J.: Electromagnetic properties of samarium-substituted NiCuZn ferrite prepared by auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 247–251 (2009)
Chen, L., Shen, Y., Bai, J.: Large-scale synthesis of uniform spinel ferrite nanoparticles from hydrothermal decomposition of trinuclear heterometallic oxo-centered acetate clusters. Mater. Lett. 63, 1099–1101 (2009)
Sangeeta, T., Katyal, S.C., Singh, M.: Structural and magnetic properties of nano nickel–zinc ferrite synthesized by reverse micelle technique. J. Magnet. Magnet. Mater. 321, 1–7 (2009)
Gadkari, A.B., Shinde, T.J., Vasambekar, P.N.: Structural analysis of Y3þ doped Mg–Cd ferrites prepared by oxalate co-precipitation method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 505–510 (2009)
Hung, M., Rao, M.V.M., Tsai, D.: Microstructures and electrical properties of calcium substituted LaFeO3 as SOFC cathode. Mater. Chem. Phys. 101, 297–302 (2007)
Wang, W., Lin, B., Zhang, H., Sun, Y., Zhang, X., Yang, H.: Synthesis, morphology and electrochemical performances of perovskite type oxide LaxSr1−xFeO3 nanofbers prepared by electrospinning. J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 124, 144–150 (2019)
Islam, M., Khan, M. K. R., Kumar, A., Rahman, M. M., Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M., Rashid, R., ... & Sarker, M. S. I.: Sol–gel route for the synthesis of CoFe2–x Er x O4 nanocrystalline ferrites and the investigation of structural and magnetic properties for magnetic device applications. Acs Omega 7(24), 20731–20740 (2022)
Kumar, P., Chand, J., Verma, S., Singh, M.: Micro-structural studies of gadolinium doped cobalt ferrites. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Sci 3(2), 10–12 (2011)
Manzoor, A., Khan, M.A., Shahid, M., Warsi, M.F.: Investigation of structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Ho substituted nanostructured lithium ferrites synthesized via auto-citric combustion route. J. Alloy. Compd. 710, 547–556 (2017)
Ramzan, R., Tariq, M., Ashiq, M. N., Albalawi, H., Ahmad, I., Alhossainy, M. H., ... & AlObaid, A. A.: Effect of yttrium ion on electrical and magnetic properties of barium based spinel ferrites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 12, 1104–1112 (2021)
Nairan, A., Khan, U., Naz, S., Saeed, M., Dang, W., Gao, J.: Effect of Barium do** on structural and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite. Solid State Sci. 131, 106965 (2022)
Zubair, A., Ahmad, Z., Mahmood, A., Cheong, W.-C., Ali, I.: Muhammad Azhar Khan, Adeel Hussain Chughtai, Muhammad Naeem Ashiq, Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Eu-doped CoFe2O4 nano-ferrites. Results Phys. 7, 3203–3208 (2017)
Ahmad, S.I., Ansari, S.A., Kumar, D.R.: Structural, morphological, magnetic properties and cation distribution of Ce and Sm co-substituted nano crystalline cobalt ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 208, 248–257 (2018)
Rahman, M.T., Vargas, M., Ramana, C.V.: Structural characteristics, electrical conduction and dielectric properties of gadolinium substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 617, 547–562 (2014)
Mozafari, M., Amighian, J., Darsheshdar, E.: Magnetic and structural studies of nickel-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles, synthesized by the sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 350, 19–22 (2014)
Demirezen, S., et al.: Frequency and voltage dependent profle of dielectric properties, electric modulus and ac electrical conductivity in the PrBaCoO nanofiber capacitors. Results Phys. 6, 180–185 (2016)
Shannon, R.D.: Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A: Cryst. Phys., Diffr., Theor. Gen. Crystallogr. 32(5), 751–767 (1976)
Haralkar, S.J., Kadam, R.H., More, S.S., Shirsath, S.E., Mane, M.L., Patil, S., Mane, D.R.: Substitutional effect of Cr3? ions on the properties of Mg–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Physica B 407, 4338–4346 (2012)
Tholkappiyan, R., Vishista, K.: Influence of lanthanum on the optomagnetic properties of zinc ferrite prepared by combustion method. Physica B 448, 177 (2014)
Almessiere, M.A., Slimani, Y., Güner, S., Nawaz, M., Baykal, A., Aldakheel, F., et al.: Magnetic and structural characterization of Nb3+ -substituted CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 45, 8222 (2019)
Gao, Y., Wang, Z., Pei, J., Zhang, H.: Structural, elastic, thermal and soft magnetic properties of Ni-Zn-Li ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 774, 1233 (2019)
Kakade, S., Kambale, R., Ramanna, C., Kolekar, Y.: Crystal strain, chemical bonding, magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of erbium (Er3+) ion substituted cobalt-rich ferrite (Co1.1Fe1.9−xErxO4). RSC Adv. 6(40), 33308 (2016)
Venturini, J., Zampiva, R.Y.S., Piva, D.H., et al.: Conductivity dynamics of metallic-to-insulator transition near room temperature in normal spinel CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C. 6, 4720–4726 (2018)
Verwey, E.J.W., De Boer, J.H.: Cation arrangement in a few oxides with crystal structures of the spinel type. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 55, 531–540 (1936)
Chand, J., Kumar, G., Pawan Kumar, S.K., Sharma, M., Knobel, M.S.: Effect of Gd3+ do** on magnetic, electric and dielectric properties of MgGdxFe2−xO4 ferrites processed by solid state reaction technique. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 9638–9644 (2011)
Lakshman, A., SubbaRao, P.S.V., Rao, B.P., Rao, K.H.: Electrical properties of In3+ and Cr3+ substituted magnesium–manganese ferrites. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 38, 673–678 (2005)
Dar, M.A., Batoo, K.M., Verma, V., Siddiqui, W.A., Kotnala, R.K.: Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized pure and Al-doped lithium ferrite having high value of dielectric constant. J. Alloys Compd. 493, 553–560 (2010)
Yousaf, S., Ahmad, I., Kanwal, M., et al.: Structural and electrical properties of Ba-substituted spinel ferrites. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 122, 105488 (2021)
Kambale, R.C., Shaikh, P.A., Kambale, S.S., Kolekar, Y.D.: J. Alloy. Compd. 478, 599 (2009)
Almessiere, M.A., Slimani, Y., Baykal, A.: Impact of Nd-Zn co-substitution on microstructure and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 nanohexaferrite. Ceram. Int. 45, 963–969 (2019)
Thakur, P., Sharma, R., Sharma, V., Barman, P.B., Kumar, M., Barman, D., Katyal, S.C., Sharma, P.: Gd3+ doped Mn-Zn soft ferrite nanoparticles: superparamagnetism and its correlation with other physical properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 432, 208–217 (2017)
Ji, B., Tian, C., Zhang, Q., Ji, D., Yang, J., ** Mn-Zn ferrites obtained by sol-gel auto-combustion method. J RARE EARTH. 34, 1017–1023 (2016)
Almessiere, M.A., Slimani, Y., Güner, S., Nawaz, M., Baykal, A., Aldakheel, F., Akhtar, S., Ercan, I., Belenli, İ, Ozçelik, B.: Magnetic and structural characterization of Nb3+-substituted CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 45, 8222–8232 (2019)
Funding
The researchers would like to acknowledge Deanship of Scientific Research, Taif University, for funding this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All have done equal contribution.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Yes, this article complies with ethical standards of the journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alhadhrami, A., Zeshan, M. & Farid, H.M.T. Microwave absorption behavior of Gd-doped spinel ferrites at high frequencies. J Aust Ceram Soc 60, 609–618 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-023-00982-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-023-00982-9