Abstract
To develop a green, rapid and energy-efficient route for the toxic waste immobilization, chromium was captured from aqueous system and subsequently solidified using calcium hydroxyapatite (HA) powder. The effect of sintering temperatures on the inter-conversion of Cr(III/VI) species in the HA matrix was investigated by synchrotron X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The results of X-ray absorption near edge structure showed the gradual transformation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) oxides from ~ 0 to ~ 100% at sintering temperatures of 100–1150 °C. The extended X-ray absorption fine structure results revealed a typical Cr(III) oxide as the dominant structure at a temperature lower than 500 °C and Cr(VI) oxide structure at higher temperatures. Thus, the oxidation behavior of Cr(III) is strongly dependent on sintering temperatures. Therefore, this study will help to design a waste management route for toxic wastes including Cr(VI) to reduce its leaching from the waste matrix. Rapid oxidation of Cr(III) inside HA matrix may be avoided by adopting low-temperature sintering techniques.
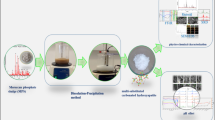
Graphical abstract

Article Highlights
-
Nanoceramic hydroxyapatite was used to capture and solidify chromium simultaneously for rapid waste management.
-
The effect of sintering temperatures on the inter-conversion of Cr(III/VI) species was investigated.
-
The chemical behavior of Cr metal in the HA matrix is strongly dependant on sintering temperatures.
-
XAFS study showed Cr(III) transformation to Cr(VI) from 0 to 100 % by increasing sintering temperature from 100 to 1150 °C.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas Z, Steenari B-M, Lindqvist O (2001) A study of Cr(VI) in ashes from fluidized bed combustion of municipal solid waste: leaching, secondary reactions and the applicability of some speciation methods. Waste Manag 21:725–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(01)00005-8
Abdel Rahman RO, Ibrahium HA, Hung YT (2011) Liquid radioactive wastes treatment: a review. Water 3:551–565. https://doi.org/10.3390/w3020551
Bolaños-Benítez V, Hullebusch ED, Lens PNL et al (2018) (Bio) leaching behavior of chromite tailings. Minerals 8:1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8060261
Chen B, Hu X, Wang J et al (2022) Novel catalytic self-cleaning membrane with peroxymonosulfate activation for dual-function wastewater purification: performance and mechanism. J Clean Prod 355:131858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131858
Comley GCW (1985) The significance of corrosion products in water reactor coolant circuits. Prog Nucl Energy 16:41–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/0149-1970(85)90005-8
Coulon A, Laurencin D, Granjean A et al (2016) Key parameters for spark plasma sintering of wet-precipated iodate-substituted hydroxyapatite. J Eur Ceram Soc 36:2009–2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.02.041
Donald IW (2015) Waste immobilisation in glass and ceramic based hosts. A John Wiley & Sons Ltd, UK
Dybowska A, Manning DAC, Collins MJ et al (2009) An evaluation of the reactivity of synthetic and natural apatites in the presence of aqueous metals. Sci Total Environ 407:2953–2965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.12.053
Elliott JC (1994) Structure and chemistry of the apatite and other calcium orthophosphate. Elsevier B.V., Amsterdam, The Netherland
Fihri A, Len C, Varma RS, Solhy A (2017) Hydroxyapatite: a review of syntheses, structure and applications in heterogeneous catalysis. Coord Chem Rev 347:48–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CCR.2017.06.009
Guerrero A, Goni S (2002) Efficiency of a blast furnace slag cement for immobilizing simulated borate radioactive liquid waste. Waste Manag 22:831–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00054-5
Hassan M, Iqbal S, Yun J-I, Ryu HJ (2019) Immobilization of radioactive corrosion products by cold sintering of pure hydroxyapatite. J Hazard Mater 374:228–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.038
Ikoma T, Yamazaki A, Nakamura S, Akao M (1999) Preparation and structure refinement of monoclinic hydroxyapatite. J Solid State Chem 144:272–276. https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.1998.8120
Iqbal S, Hassan M, Ryu HJ, Yun J-I (2018) Environmentally benign and novel management route for radioactive corrosion products by hydroxyapatite. J Nucl Mater 507:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2018.05.016
Lee KP, Ulrich CEGR (1989) Inhalation toxicity of chromium dioxide dust to rats after two years’ exposure. Sci Total Environ 86:83–108
Liu Y, Shen L, Huang Z et al (2022) A novel in-situ micro-aeration functional membrane with excellent decoloration efficiency and antifouling performance. J Memb Sci 641:119925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119925
Luginina M, Angioni D, Montinaro S et al (2020) Hydroxyapatite / bioactive glass functionally graded materials ( FGM ) for bone tissue engineering. J Eur Ceram Soc 40:4623–4634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.05.061
Ma G, Liu XY (2009) Hydroxyapatite: hexagonal or monoclinic? Cryst Growth Des 9:2991–2994. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg900156w
Morgan H, Wilson RM, Elliott JC et al (2000) Preparation and characterisation of monoclinic hydroxyapatite and its precipitated carbonate apatite intermediate. Biomaterials 21:617–627
Murray AP (1986) A chemical decontamination process for decontaminating and decommissioning nuclear reactors. Nucl Technol 74:324–332
Ohata M, Matsubayashi N (2014) Determination of hexavalent chromium in plastic certified reference materials by X-ray absorption fine structure analysis. Spectrochim Acta - Part B 93:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2013.12.005
Onchoke KK, Sasu SA (2016) Determination of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) concentrations via ion chromatography and UV-Vis spectrophotometry in samples collected from Nacogdoches wastewater treatment plant, East Texas (USA). Adv Environ Chem 2016:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3468635
Orlovskii VP, Komlev VS, Barinov SM (2002) Hydroxyapatite and hydroxyapatite-based ceramics. Inorg Mater 38:973–984. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020585800572
Osaka A, Miura Y, Takeuchi K et al (1991) Calcium apatite prepared from calcium hydroxide and orthophosphoric acid. J Mater Sci Mater Med 2:51–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00701687
Pan Z, Zeng B, Lin H et al (2022) Fundamental thermodynamic mechanisms of membrane fouling caused by transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in water treatment. Sci Total Environ 820:153252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153252
Paoletti F (2002) Behavior of oxyanions forming heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration. Karlsruhe, Germany
Peterson ML, Brown GE, Parks GA (1997) Quantitative determination of chromium valence in environmental samples using XAFS spectroscopy. In: Material research society proceedings, pp 75–80
Rahman ROA, Rakhimov RZ, Rakhimova NR, Ojovan MI (2015) Cementitious materials for nuclear waste immobilization. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, UK
Rao L, You X, Chen B et al (2022) A novel composite membrane for simultaneous separation and catalytic degradation of oil/water emulsion with high performance. Chemosphere 288:132490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132490
Raouf MWA, Nowier HG (2004) Assessment of fossil fuel fly ash formulations in the immobilization of hazardous wastes. J Environ Eng 130:499–507. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2004)130:5(499)
Ravel B, Newville M (2005) ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J Synchrotron Radiat 12:537–541. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0909049505012719
Rehr JJ, Albers RC (2000) Theoretical approaches to x-ray absorption fine structure. Rev Mod Phys 72:621–654. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.72.621
Ressler T (1998) WinXAS: a program for X-ray absorption spectroscopy data analysis under MS-Windows. J Synchrotron Radiat 5:118–122. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0909049597019298
Richard FC, Bourg ACM (1991) Aqueous geochemistry of chromium: a review. Water Res 25:807–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(91)90160-R
Sidney AK, Salem H (1993) The toxicology of chromium with respect to its chemical speciation: a review. J Appl Toxicol 3:217–224
Singh SP, Ma LQ, Harris WG (2001) Heavy metal interactions with phosphatic clay: sorption and desorption behavior. J Environ Qual 30:1961–1968. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2001.1961
Smičiklas I, Dimović S, Plećaš I, Mitrić M (2006) Removal of Co2+ from aqueous solutions by hydroxyapatite. Water Res 40:2267–2274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.031
Stam AF, Meij R, Te WH et al (2011) Chromium speciation in coal and biomass co-combustion products. Environ Sci Technol 45:2450–2456. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103361g
Verbinnen B, Billen P, Van Coninckxloo M, Vandecasteele C (2013) Heating temperature dependence of Cr(III) oxidation in the presence of alkali and alkaline earth salts and subsequent Cr(VI) leaching behavior. Environ Sci Technol 47:5858–5863. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4001455
Wu L, Forsling W, Schindler PW (1991) Surface complexation of calcium minerals in aqueous solution: 1. Surface protonation at fluorapatite—water interfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 147:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(91)90145-X
Wu Y, Song S, Garbers-Craig AM, Xue Z (2018) Formation and leachability of hexavalent chromium in the Al2O3-CaO-MgO-Cr2O3 system. J Eur Ceram Soc 38:2649–2661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.01.012
Xu HB, Zhang Y, Li ZH et al (2006) Development of a new cleaner production process for producing chromic oxide from chromite ore. J Clean Prod 14:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.09.001
Zhang R, Xu Y, Shen L et al (2022) Preparation of nickel@polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) conductive membranes to couple a novel electrocoagulation-membrane separation system for efficient oil-water separation. J Memb Sci 653:120541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2022.120541
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Pakistan Institute of Nuclear Science and Technology (PINSTECH), Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2016R1A5A1013919), Richard Lounsbery Foundation and the SESAME, Allan Jordan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no competing financial or personal interests to influence the work reported in this paper.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iqbal, S., Faiz, Y., Harfouche, M. et al. Temperature-Dependent Speciation Analysis of Chromium Immobilized in Calcium Hydroxyapatite Matrix. Int J Environ Res 16, 40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-022-00421-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-022-00421-w