Abstract
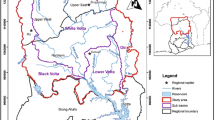
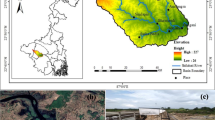
The present study has been carried out in the dry land Barind Tract, NW Bangladesh to delineate the potential zones for artificial recharge of groundwater and to assess scope for establishing sites for rainwater harvesting (RWH) and runoff water conservation to revert ever depleting groundwater resource through construction of check dam, managed aquifer recharge (MAR) model, percolation tanks, etc. using multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) approach in GIS environment to have a sustainable groundwater resource management plan. The Tract possesses dendritic drainage patterns which indicate scope for loss of major portion of runoff water with less infiltration to recharge the groundwater having its less potentiality for occurrence, but represents good category for surface water conservation. The semi-permeable or poor permeable surface soil lithology (Barind Clay) is less favorable for groundwater recharge, and here, lineament and slope are the most influencing factor for its recharge mechanisms. Here, about 65% of the area falls under ‘moderately suitable’, 1% area under ‘highly suitable’ and about 34% area has unsuitability for artificial recharge of groundwater. The artificial recharge structures like check dams have suggested only for the ‘moderately’ and ‘highly’ suitable zones, and that of artificial recharge through injection well by the MAR and percolation tanks are suggested as only option for the ‘unsuitable’ zone in this dry land. Finally, the present study provides a guideline to water managers, planners and decision maker in this dry land to ascertain availability of water resource that meet community demand through the Integrated Water Resource Management as lauded in the Bangladesh Water Act (2013).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
BAEC (Bangladesh) (1989) A study on aquifer condition and groundwater quality of the Barind in Rajshahi, Institute of Nuclear Science and Technology, Atomic Energy Establishment, Ganakbari, Savar, Dhaka
Banglapedia (2003) National encyclopedia of Bangladesh. Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, Dhaka
Berhanu B, Melesse AM, Seleshi Y (2013) GIS-based hydrological zones and soil geo-database of Ethiopia. CATENA 104:21–31
Dey S (2014) Delineation of ground water prospect zones using remote sensing, GIS techniques—a case study of Baghmundi development block of Puruliya district, West Bengal. Int J Geol Earth Environ Sci 4(2):62–72 (ISSN: 2277-2081 (online))
Dilon P, Gale I, Contreras S, Pavelic P, Evans P, Ward I (2009) Managing aquifer recharge and discharge to sustain irrigation livelihoods under water scarcity and climate change. In: IAHS & IAH conference, Hyderabad, India, vol 330. IAHS-AISH Publication, pp 1–12
Hammouri N, El-Naqa A, Barakat M (2012) An integrated approach to groundwater exploration using remote sensing and geographic information system. J Water Resourc Prot 4:717–724
Hasan, T.M. (2021) Study on Groundwater Resource Potentiality and Prospect of Artificial Groundwater Recharge in Barind Tract, Bangladesh: A Multi-criteria Decision Making Approach in GIS Environment, MS Thesis (Unpublished), University of Rajshahi, Bangladesh
Jahan CS, Ahmed M (1997) Flow of groundwater in the Barind area, Bangladesh: implication of structural framework. J Geol Soc India 50:743–752
Jahan CS, Islam MA, Mazumder QH, Asaduzzaman M, Islam MM, Islam MO, Sultana A (2007) Evaluation of depositional environment and aquifer condition in the Barind area, Bangladesh, using gamma ray well log data. J Geol Soc India 70:1070–1076
Jahan CS, Rahaman MF, Mazumder QH, Hossain MI (2021) MAR model: a blessing adaptation for hard-to-reach livelihood in thirsty Barind Tract, Bangladesh. In: Mukearjee (ed) GLOBAL GROUNDWATER source, scarcity, sustainability, security and solution. Elsevier Publications
Morgan JP, McIntire WG (1959) Quaternary geology of the Bengal Basin, East Pakistan and India. Geol Soc Am Bull 70:319–342
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hill, New York
Sener E, Davraz A, Ozcelik M (2005) An integration of GIS and remote sensing in groundwater investigations: a case study in Burdur, Turkey. Hydrogeol J 13(5–6):826–834
Strahler AN (1957) Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Trans Am Geophys Union 38:913–920
UNDP (United Nations Development Programme) (1982) Groundwater survey: the hydrogeological conditions of Bangladesh, united nations development programme (UNDP), technical report DP/UN/BGD-74-009/1, New York, p 113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hasan, M.T., Jahan, C.S., Rahaman, M.F. et al. Delineation of zones and sites for artificial recharge of groundwater in dry land Barind Tract, Bangladesh using MCDM technique in GIS environment. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 8, 147 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00713-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00713-1