Abstract
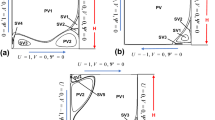
In the present study, numerical simulations of two-dimensional steady-state incompressible Newtonian fluid flow in one-sided and four-sided lid-driven square cavities are reported. For the one-sided lid-driven cavity, the upper wall is moved to the right with up to 5000 Reynolds numbers under a grid size of up to \( 501\times 501\). This lends support to previous findings in the literature. Two cases are used in this article for the four-sided lid-driven square cavity specifically. In case-I, the top and lower walls are moved to the right, while the left and right walls are moved upward and downward, respectively. In case II, the top wall is moved to the left, the lower wall to the right, the left wall is moved upward, and the right wall is moved downward, with all three walls moving at the same speed one and the bottom wall moving at two. Conventional numerical solutions show that the unique solutions exist for all Reynolds numbers for both the geometries. All possible flow solutions are studied in the present article, as velocity profiles and streamline contours for the same Reynolds number using a finite volume SIMPLE technique. The work done in this paper includes flow properties such as the location of primary and secondary vortices, velocity components, and numerical values for benchmarking purposes, and it is in excellent agreement with previous findings in the literature. A PARAM Shavak, high-performance computing computer, was used to execute the calculations.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Abbreviations
- 2D :
-
Two dimensional
- SIMPLE:
-
Semi implicit method for pressure linked equation
- HPC:
-
High performance computing
- FVM:
-
Finite volume technique
- PV:
-
Primary vortex
- Right-SV:
-
Right secondary vortex
- Left-SV:
-
Left secondary vortex
- Left-USV:
-
Left upper secondary vortex
- UPV:
-
Upper primary vortex
- LPV:
-
Left primary vortex
- RPV:
-
Right primary vortex
- BPV:
-
Bottom primary vortex
- BSV:
-
Bottom secondary vortex
- u :
-
x-axis velocity component (m/s)
- \(u^*\) :
-
x-axis approximate velocity component (m/s)
- \(u^\prime \) :
-
x-axis correction velocity component (m/s)
- v :
-
y-axis velocity component (m/s)
- \(v^*\) :
-
y-axis approximate velocity component (m/s)
- \(v^\prime \) :
-
y-axis correction velocity component (m/s)
- p :
-
Pressure (\(\mathrm{N/m}^2\))
- \(p^*\) :
-
Guessed pressure (\(\mathrm{N/m}^2\))
- \(p^\prime \) :
-
Correction pressure (\(\mathrm{N/m}^2\))
- i :
-
x-direction node location
- j :
-
y-direction node location
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- \(\Delta x\) :
-
x-direction spatial step
- \(\Delta y\) :
-
y-direction spatial step
References
Ozisik, M.N.: Heat Transfer: A Basic Approach. McGraw-Hill, New York (1985)
Anderson, J.D., Wendt, J.: Computational Fluid Dynamics. Springer, Berlin (1995)
Moukalled, F., Mangani, L., Darwish, M.: The Finite Volume Method in Computational Fluid Dynamics, p. 113. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Kundu, PK., Cohen, IM.: Fluid mechanics. (2002)
Peng, H.F., Yang, K., Cui, M., Gao, X.W.: Radial integration boundary element method for solving two-dimensional unsteady convection-diffusion problem. Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem. 102, 39–50 (2019)
Anley, E.F., Zheng, Z.: Finite difference approximation method for a space fractional convection-diffusion equation with variable coefficients. Symmetry 12(3), 485 (2020)
Appadu, A.R., Djoko, J.K., Gidey, H.: A computational study of three numerical methods for some advection-diffusion problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 272, 629–647 (2016)
Mazumder, S.: Numerical Methods For Partial Differential Equations: Finite Difference And Finite Volume Methods. Academic Press, Cambridge (2015)
Suhas, P.: Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. Hemisphere publishing corporation, Etas-Unis d’Amérique (1980)
Ghia, U., Ghia, K.N., Shin, C.: High-Re solutions for incompressible flow using the Navier-Stokes equations and a multigrid method. J. Comput. Phys. 48(3), 387–411 (1982)
Erturk, E.: Discussions on driven cavity flow. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 60(3), 275–294 (2009)
Von Terzi, DA.: Numerical investigation of transitional and turbulent backward-facing step flows. PhD thesis. The University of Arizona (2004)
Versteeg, H.K., Malalasekera, W.: An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: the Finite Volume Method. Pearson education, London (2007)
Indukuri, J.V., Maniyeri, R.: Numerical simulation of oscillating lid-driven square cavity. Alex. Eng. J. 57(4), 2609–2625 (2018)
Patel, M.R., Pandya, J.U.: Numerical study of a one and two-dimensional heat flow using finite volume. Mater. Today Proc. 51(1), 48–57 (2021)
Ding, P.: Solution of lid-driven cavity problems with an improved SIMPLE algorithm at high Reynolds numbers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 115, 942–954 (2017)
Demirdžić, I., Lilek, Ž, Perić, M.: Fluid flow and heat transfer test problems for non-orthogonal grids: bench-mark solutions. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 15(3), 329–354 (1992)
Som, S.: Introduction to Heat Transfer. PHI learning Pvt Ltd (2008)
Wahba, E.M.: Multiplicity of states for two-sided and four-sided lid-driven cavity flows. Comput. Fluids 38, 247–253 (2009)
Dass, A.K., Perumal, D.A.: Multiplicity of steady solutions in two-dimensional lid-driven cavity flows by Lattice Boltzmann Method. Comput. Math. Appl. 61, 3711–3721 (2011)
Cadou, J.M., Guevel, Y., Girault, G.: Numerical tools for the stability analysis of 2D flows: application to the two- and four-sided lid-driven cavity. Fluid Dyn. Res. 44, 031403 (2012)
Chen, K.T., Tsai, C.C., Luo, W.J.: Multiplicity flow solutions in a four-sided lid-driven cavity. Appl. Mech. Mater. 368–370, 838–843 (2013)
Granados, J.M., Power, H., Bustamante, C.A., Florez, W.F., Hill, A.F.: A global particular solution meshless approach for the four-sided lid-driven cavity fow problem in the presence of magnetic fields. Comput. Fluids 160, 120–137 (2018)
Albensoeder, S., Kuhlmann, H., Rath, H.: Multiplicity of steady two-dimensional flows in twosided lid-driven cavities. Theoret. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 14, 223–241 (2001)
Syrakos, A., Georgiou, G., Alexandrou, A.: Solution of the square lid-driven cavity flow of a Bingham plastic using the finite volume method. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 195, 19–31 (2013)
Syrakos, A., Dimakopoulos, Y., Georgiou, G.C., Tsamopoulos, J.: Viscoplastic flow in an extrusion damper. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 232, 102–124 (2016)
Syrakos, A., Dimakopoulos, Y., Tsamopoulos, J.: A Finite Volume method for the simulation of elastoviscoplastic flows and its application to the lid-driven cavity case. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 275, 104216 (2020)
Azzouz, EA., Houat, S., Benhizia, O.: Numerical study of steady flow inside a lid-driven square cavity for Reynolds number up to 50000, 23ème Congrès Français de Mécanique, (2017)
Faridzadeh, M.R., Toghraie, D., Niroumand, A.: Analysis of laminar mixed convection in an inclined square lid-driven cavity with a nanofluid by using an artificial neural network. Heat Transf. Res. 45, 361–390 (2014)
Rahmati, A.R., Akbari, O.A., Marzban, A., Toghraie, D., Karimi, R., Pourfattah, F.: Simultaneous investigations the effects of non-Newtonian nanofluid flow in different volume fractions of solid nanoparticles with slip and no-slip boundary conditions. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 5, 263–277 (2018)
Dabiri, S., Khodabandeh, E., Poorfar, A.K., Mashayekhi, R., Toghraie, D., Zade, S.A.A.: Parametric investigation of thermal characteristic in trapezoidal cavity receiver for a linear Fresnel solar collector concentrator. Energy 153, 17–26 (2018)
Li, Z., Barnoon, P., Toghraie, D., Dehkordi, R.B., Afrand, M.: Mixed convection of non-Newtonian nanofluid in an H-shaped cavity with cooler and heater cylinders filled by a porous material: Two phase approach. Adv. Powder Technol. 30, 2666–2685 (2019)
Azzouz, E.A., Houat, S.: Numerical analysis and explore of asymmetrical fluid flow in a two-sided lid-driven cavity. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 14, 7269–7281 (2020)
Azzouz, E.A., Houat, S., Dellil, A.Z.: Numerical assessment of turbulent flow driving in a two-sided lid-driven cavity with antiparallel wall motion. DDF 406, 133–148 (2021)
Ferziger, J., Peric, M.: Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Smith, G.D.: Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations: Finite Difference Methods. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1985)
Yaghoubi, A.: High Order Finite Difference Schemes for Solving Advection-Diffusion Equation
Sastry, S.S.: Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis. PHI Learning Pvt Ltd (2012)
Patel, M.R., Pandya, J.U.: A research study on unsteady state convection diffusion flow with adoption of the finite volume technique. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Mech. 20(4), 65–76 (2021)
Hou, S., Zou, Q., Chen, S., Doolen, G., Cogley, A.C.: Simulation of cavity flow by the lattice Boltzmann method. J. Comput. Phys. 118(2), 329–347 (1995)
Gupta, M.M., Kalita, J.C.: A new paradigm for solving Navier-Stokes equations: streamfunction-velocity formulation. J. Comput. Phys. 207(1), 52–68 (2005)
Kamel, A.G., Haraz, E.H., Hanna, S.N.: Numerical simulation of three-sided lid-driven square cavity. Eng. Rep. 2(4), e12151 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express our special thanks and gratitude to DST, Gujcost, and C-DAC high-performance computing clusters, PARAM Shavak of KSV.
Funding
No funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, M.R., Pandya, J.U. & Patel, V.K. Numerical Analysis of Fluid Flow Behaviour in Four-Sided Square Lid-Driven Cavity Using the Finite Volume Technique. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 8, 153 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-022-01353-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-022-01353-x