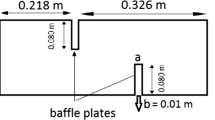
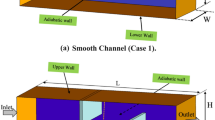
Abstract
Numerically, we have studied different characteristics of turbulent air flow (flow structure, axial velocity profiles, dimensionless coefficient of skin friction, normalized friction factor),and heat transfer (local Nusselt number, and average Nusselt number) phenomena through a rectangular channel having trapezoidal baffles attached on its walls, and along the centerline of it. The governing equations have been solved using the finite volume method and to visualize the simulation results, fluent software has been employed. It is shown that the maximum value of pressure drop occurs on the upstream, and minimum value attains in the downstream section of the channel. It is ensured that an increase in the Reynolds number (Re) causes increase in normalize friction factor (F), and average Nusselt number (Nuav). The simulation results of this work will help to design and monitor flow phenomena through many thermal applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Abbreviations
- \(C\) :
-
Empirical constant, \(C_{\mu }\) = 0.09, \(C_{1\epsilon }\) = 1.44, \(C_{2\epsilon }\) = 1.92, \(\sigma_{k}\) = 1.0, \(\sigma_{\epsilon } = 1.3\)
- \(C_{p}\) :
-
Average pressure coefficient
- Cf(x):
-
Skin friction coefficient
- f0 :
-
Friction factor of smooth channel [Petukhov[1]] = \(\left( {0.79 \ln {\text{Re}} - 1.64} \right)^{ - 2}\) for \(\le {\text{Re}} \le 500,000\)
- F:
-
Average friction factor = \(\frac{2\Delta p H}{{L \rho u_{0 }^{2} }}\)
- F:
-
Normalize friction factor = \(\frac{f}{{f_{0} }}\)
- \(G_{k}\) :
-
Production rate of kinetic energy due to
- h(x):
-
Coefficient of heat transfer
- H:
-
Channel width (m)
- HT:
-
Heat transfer
- kf :
-
Thermal conductivity (Wm−1 K−1)
- \(k\) :
-
Turbulent kinetic energy = \(\frac{1}{2}\overline{{u_{i}^{{\prime }} u_{j}^{{\prime }} }}\)
- L:
-
Length of channel
- M:
-
Meter
- Ne :
-
Total number of elements
- p:
-
Pressure
- p1 :
-
Pressure at inlet
- p2 :
-
Pressure at outlet
- \(\Delta p\) :
-
Absolute pressure drop =|(p2-p1)|
- T:
-
Temperature
- Tw :
-
Wall temperature = 375 K
- \(u_{i}^{\prime } ,u_{j}^{\prime }\) :
-
Fluctuation velocity components in in xi and xj directions
- u0 :
-
Input velocity [ms−1]
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity [Pa.s]
- Re:
-
Reynolds number = \(\frac{{u_{0 } \rho H}}{\mu }\)
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- \(Nu\left( x \right)\) :
-
Local Nusselt number \(= \frac{h\left( x \right)L}{{k_{f} }}\)
- Nuav :
-
Average Nusselt number = \(\frac{1}{L}\mathop \smallint \limits_{0}^{L} Nu\left( x \right) dx\)
- \(Nu_{0}\) :
-
Average Nusselt number of smooth channel [Dittus and Boelter [2]] = \(0.023 {\text{Re}}^{0.8} \Pr^{0.4}\) for \({\text{Re}} \ge 10,000\)
- Nuna :
-
Normalized average Nusselt number
- NCf(x):
-
Normalize skin friction coefficient = Cf(x)/f0
- FVM:
-
Method of finite volume
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- \(\frac{\mu }{Pr}\) :
-
Molecular diffusivity
- \(\frac{{\mu_{t} }}{{Pr_{t} }}\) :
-
Turbulent thermal diffusivity
- \(\mu_{t}\) :
-
Turbulent viscosity = \(\rho C_{\mu } \frac{{k^{2} }}{\epsilon }\)
- \(\delta_{ij}\) :
-
Kronecker delta
- \(Y^{ + }\) :
-
Normalize distance of the walls
- \(k_{p}\) :
-
Kinetic energy of turbulence at position P
- \(y_{p}\) :
-
Distance from position P to the wall
- E:
-
= 9.81
- r:
-
= 0.42
- v:
-
Velocity in y direction
- x:
-
Y, Cartesian coordinate
- ui :
-
Uj, components of mean velocity [ms−1] in xi and xj directions
- Tin :
-
Inlet temperature = 300 K
References
Petukhov, B.: Heat transfer and friction in turbulent pipe flow with variable physical properties. Adv Heat Tranf 6, 503–564 (1970)
Dittus, W.F., Boelter, M.L.K.: Heat transfer in automobile radiators of the tubular type. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 12(1), 03–22 (1985)
Wiemer, P.: Untersuchungber den Zugwiederstand von Wasserrohrkesseln. Dissertation, RWTH Aachen (1937)
Gunter, A.Y., Sennstrom, H.R., Kopp, S.: A study of flow patterns in baffled heat exchangers. ASME, 47-A-103 (1947)
Bergelin, O.P., Brown, G.A., Colburn, A.P.: Heat transfer and fluid friction during flow across banks of tubes-V: a study of a cylindrical baffles exchanger without internal leakage. ASME J. Heat Transf. 75, 841–850 (1953)
Gay, B., Williams, T.A.: Heat transfer on the shell-side of a cylindrical shelland-tube heat exchanger fitted with segmental baffles. Transf. Ins. Chem. Eng. 46, 95–100 (1968)
Gay, B., Mackley, N.V., Jenkins, J.D.: Heat transfer in baffled cylindrical shell-and-tube exchangers: an electrochemical transfer modelling technique. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 19(9), 995–1002 (1976)
Gay, B., Jenkins, J.D., Mackley, N.V.: Shell-side heat transfer coefficient in cylindrical heat exchangers: the influence of geometrical factors, I. The leakage case. Lett. Heat and Mass Transf. 4, 41–52 (1977)
Gay, B., Jenkins, J.D., Mackley, N.V.: Shell-side heat transfer coefficients in cylindrical heat exchangers: the influence of geometrical factors. Lett. Heat and Mass Transf. 8(6), 437–452 (1981)
Patankar, S.V., Liu, C.H., Sparrow, E.M.: Analysis of laminar forced convection heat transfer in ducts. J. Heat Transf. (1977)
Berner, C., Durst, F., McEligot, D.M.: Flow around baffles. J. Heat Transf. 106, 743–749 (1984)
Webb, G.W., Ramadhyani, S.: Fluid flow and heat transfer in a parallel platechannel with staggered baffles. J. Heat Mass Transf. 28(5), 471–495 (1985)
Webb, B.W., Ramadhyani, S.: Conjugate heat transfer in a channel with staggered ribs. Int. J. Heat and Mass Transf. 28(9), 1679–1687 (1985)
Habib, M.A., Attya, A.E., McEligot, D.M.: Calculation of turbulent flow and heattransfer in channels withstreamwise-periodic flow. ASME J. Turbomach. 110, 405–411 (1988)
Habib, M.A., Mobarak, A.M., Sallak, M.A., Hadi, E.A., Affy, R.I.: Experimental investigation of heat transfer and flow over Ba_es of Di_erent heights. J. Heat Transf. 116, 1609–1617 (1994)
Al-Atabi, M.T., Chin, S.B., Luo, X.Y.: Visualization of mixing of flow in circular tubes with segmental baffles. J. Vis. 8(2), 89–92 (2005)
Al-Atabi, M.T., Chin, S.B., Luo, X.Y.: Flow structure in circular tubes withsegmental baffles. J. Vis. Image Process 12, 301–311 (2005)
Bazdidi, F., Naderi, M.: Numerical analysis of laminar heat transfer in entrance region of a horizontal channel with transverse fins. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 31, 211–220 (2004)
Kelkar, K.M., Patankar, S.V.: Numerical prediction of flow and heat transfer in a parallel plate channel with staggered fins. J. Heat Transf. 109, 25–30 (1987)
Prusty, P., Rout, S., Barik, K.A.: Heat transfer correlation for a triangular protruded surface with a cross-flow jet. Sadhana 44(5), 1–14 (2019)
Saha, S., Biswas, P., Nath, S., Singh, L.: Numerical simulations of Newtonian fluid flow through a suddenly contracted rectangular channel with two different types of baffle plates. Soft Comput. 25, 9873–9885 (2021)
Chhanda, S.N., Barik, K.A.: Conjugate heat transfer in a rectangular channel with perforated protrusion and cross-flow effect. Int. J. Control Theory Appl. 10(6), 91–100 (2017)
Barik, K.A., Rout, S., Mukherjee, A.: Numerical investigation of heat transfer enhancement from a protruded surface by cross-flow jet using Al2O3nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 110, 550–561 (2016)
Prithiviraj, M., Andrews, M.J.: Three dimensional numerical simulation of shell and tube heat exchangers. J. Numer. Heat Transf. 33(6), 799–816 (1988)
Prashanta, D., Akram, H.: Internal cooling augmentation in rectangular channel using inclined baffle plates. Int J. Heat Fluid Flow 26, 799–816 (2005)
Shivani, T., Gajusingh, A., Nasiruddin, S., Kamran, S.: The impact of a vortex induced by a baffle on the turbulent structure. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 34, 590–602 (2010)
Kang, K., Anand, N.K.: Use of porous baffles to enhance heat transfer in a rectangular channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46(22), 4191–4199 (2003)
Behera, P.P., Barik, K.A., Malik, K.R.: Heat transfer enhancement for a trapezoidal protruded surface with cross-flow jet. Int. J. Control Theory Appl. 10(6), 449–459 (2017)
Karwa, R., Maheshwari, K.B., Karwa, N.: Experimental study of heat transfer enhancement in an asymmetrically heatedrectangular duct with perforated baffles. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 32, 275–284 (2005)
Bhuiya, K.K.M., Chowdhury, U.S.M., Saha, M., Islam, T.M.: Heat transfer and friction factor characteristics in turbulent flow through a tube fitted with perforated twisted tape inserts. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 49–57 (2013)
Barik, K.A., Mukherjee, A., Patro, P.: Heat transfer enhancement from a small rectangular channel with different surface protrusions by a turbulent cross flow jet. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 98, 32–41 (2015)
Mukherjee, A., Rout, S., Barik, K.A.: Heat transfer and entropy generation analysis of a protruded surface in presence of a cross-flow jet using Al2O3-water nanofluid. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 5, 327–338 (2015)
Mukherjee, A., Barik, A.: Heat transfer enhancement from a ribbed surface in presence of a cross flow jet: a numerical investigation. J. Mater. Sci. Mech. Eng. 3(3), 172–178 (2016)
Demartini, L.C., Vielmo, H.A., Mller, S.V.: Numeric and experimental analysis of the turbulent flow through a channel with baffle plates. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 26(2), 153–159 (2004)
Nasiruddin, M.H., Siddiqui, K.: Heat transfer augmentation in a heat exchanger tube using a baffle. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 28(2), 318–328 (2007)
Launder, B.E., Spalding, D.B.: The numerical computation of turbulence. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 3(2), 269–289 (1974)
Saha, S.: Numerical simulation of turbulent airflow and heat transfer through a rectangular channel along with trapezoidal baffle plates. AIP Conf. Proc. 2341, 1–10 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the reviewers for their valuable suggestions, which helped a lot to improve this work.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, S., Biswas, P. & Das, A.N. Numerical Study of Turbulent Airflow Structure and Transfer of Heat Having Trapezoidal Baffles Attached on the Walls and Centerline of the Rectangular Channel. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 8, 104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-022-01252-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-022-01252-1