Abstract
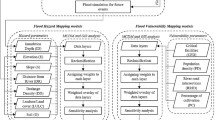
In large-scale group decision-making (LSGDM) for dry hot rock exploration location selection, decision-makers are limited by their professional fields and knowledge background, and it is difficult to provide complete evaluation information. However, brainstorming is the main advantage of LSGDM. To maximize the professional contributions of various decision-makers, a multi-attribute LSGDM method based on three-way decision (TWD) and intuitionistic fuzzy concept-oriented (IFC) is proposed. Firstly, according to the characteristics of IFC, a description of the LSGDM problem based on IFC is given; then, an LSGDM model based on TWD is proposed to classify and rank alternatives. Two algorithmic descriptions are given, namely consensus reaching process algorithm and algorithm for classifying and ranking alternatives. Then, taking dry hot rock exploration location selection as an example, the execution steps of this model were elaborated in detail, and the final classification and ranking results were obtained. Finally, the effectiveness and feasibility of this model were analyzed based on experimental results, and the influence of various parameters on the results was also studied.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed in this study may be provided by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
Code can be provided if required.
References
Atanassov, K.T.: Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 80, 87–96 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(86)80034-3
Ayyildiz, E.: Interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy analytic hierarchy process-based green supply chain resilience evaluation methodology in post covid-19 era. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16972-y
Chai, J.: Thoughts on the current situation and development path of clean energy in china. Sci. Technol. Innov. Herald 17, 119–120 (2019). https://doi.org/10.16660/j.cnki.1674-098X.2019.17.119
Chen, S., Cheng, S., Chiou, C.: Fuzzy multiattribute group decision making based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets and evidential reasoning methodology. Inf. Fusion 27, 215–227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2015.03.002
Chen, S.M., Han, W.H.: Multiattribute decision making based on nonlinear programming methodology, particle swarm optimization techniques and interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy values. Inf. Sci. 471, 252–268 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.08.021
Dai, J.H., Chen, T., Zhang, K.: The intuitionistic fuzzy concept-oriented three-way decision model. Inf. Sci. 619, 52–83 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.11.017
Gao, J.W., Guo, F.J., Ma, Z.Y., et al.: Multi-criteria decision-making framework for large-scale rooftop photovoltaic project site selection based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Appl. Soft Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107098
Jia, F., Liu, Y.Y., Wang, X.Y.: An extended mabac method for multi-criteria group decision making based on intuitionistic fuzzy rough numbers. Expert Syst. Appl. 127, 241–255 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.03.016
**g, T.Y., Zhao, W.T., Gao, S.W.: Practice and technical feasibility study of hot dry rock geothermal development. Sino-Global Energy 23(11), 17–22 (2018)
Joshi, R., Kumar, S.: A novel fuzzy decision-making method using entropy weights-based correlation coefficients under intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 232–242 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0538-8
Li, S.T., Zhang, S.Q., Jia, X.F.: Index system research of project site selection for dry hot rocks exploration. Geol. Surv. China 5(2), 64–72 (2018). https://doi.org/10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2018.02.10
Liang, D., Wang, M., Xu, Z., et al.: Risk appetite dual hesitant fuzzy three-way decisions with todim. Inf. Sci. 507, 585–605 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.12.017
Liang, D.C., Wang, M.W., Xu, Z.S.: Heterogeneous multi-attribute nonadditivity fusion for behavioral three-way decisions in interval type-2 fuzzy environment. Inf. Sci. 496, 242–263 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.05.044
Lin, W.J., Gan, H.N., Wang, G.L., et al.: Occurrence prospect of hdr and target site selection study in southeastern of china. Acta Geol. Sin. 90(8), 2043–2058 (2016)
Liu, B., Shen, Y., Chen, X., et al.: A partial binary tree dea-da cyclic classification model for decision makers in complex multi-attribute large-group interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy decision-making problems. Inf. Fusion 18, 119–130 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2013.06.004
Liu, F., Li, T.R., Wu, J., et al.: Modification of the bwm and mabac method for magdm based on q-rung orthopair fuzzy rough numbers. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 12, 2693–2715 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01357-x
Liu, H.W.: New similarity measures between intuitionistic fuzzy sets and between elements. Math. Comput. Model. 42, 61–70 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2005.04.002
Liu, P., Wang, Y., Jia, F., et al.: A multiple attribute decision making three-way model for intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 119, 177–203 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2019.12.020
Liu, Y., Liu, J., Qin, Y.: Dynamic intuitionistic fuzzy multiattribute decision making based on evidential reasoning and mdifwg operator. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 36, 5973–5987 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-181777
Wang, G.L., Zhang, W., Lin, W.J., et al.: Project progress of survey, evaluation and exploration demonstration of national geothermal resource. Geol. Surv. China 5(2), 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2018.02.01
Wang, W.J., Zhan, J.M., Mi, J.S.: A three-way decision approach with probabilistic dominance relations under intuitionistic fuzzy information. Inf. Sci. 582, 114–145 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.09.018
Wu, J., Liu, Y., Liu, F., et al.: Comprehensive evaluation of land reclamation schemes in mining areas based on linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy group decision-making. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29(58), 87,380-87,392 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20952-1
Xu, Y., Wen, X., Zhang, W.: A two-stage consensus method for large-scale multi-attribute group decision making with an application to earthquake shelter selection. Comput. Ind. Eng. 116, 113–129 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2017.11.025
Xu, Z.S.: Intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 15, 1179–1187 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/tfuzz.2006.890678
Xu, Z.S., Wu, J.: Intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 21, 580–590 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-4132.2010.04.009
Yao, Y.Y.: Three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. Inf. Sci. 180, 341–353 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2009.09.021
Ye, J., Zhan, J., Xu, Z.: A novel decision-making approach based on three-way decisions in fuzzy information systems. Inf. Sci. 541, 362–390 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.06.050
Zeng, S.Z., Chen, S.M., Fan, K.Y.: Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multiple attribute decision making based on nonlinear programming methodology and topsis method. Inf. Sci. 506, 424–442 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.08.027
Zhan, J., Jiang, H., Yao, Y.: Three-way multi-attribute decision-making based on outranking relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tfuzz.2020.3007423
Zhao, M., Gao, M., Li, Z.: A consensus model for large-scale multi-attribute group decision making with collaboration-reference network under uncertain linguistic environment. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 37, 4133–4156 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-190276
Zhong, X., Xu, X., Pan, B.: A non-threshold consensus model based on the minimum cost and maximum consensus-increasing for multi-attribute large group decision-making. Inf. Fusion 77, 90–106 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2021.07.006
Zhong, X., Xu, X., Yin, X.: A multi-stage hybrid consensus reaching model for multi-attribute large group decision-making: integrating cardinal consensus and ordinal consensus. Comput. Ind. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107443
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by Open Research Fund Program of Data Recovery Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (No. DRN2105, DRN19014); Scientific Research Innovation Team of Neijiang Normal University (No. 2021TD04); Scientific Research Project of Neijiang Normal University (No. 2021YB21); and Application basic research project of Sichuan Province (No. 2021YJ0108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by YL, JW, and ZZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by FL and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical Approval
Ethics approval is not involved in this study.
Consent to Participate
All authors agree to participate.
Consent for Publication
All authors agree to publish this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Zhou, Z., Wu, J. et al. Location Selection for Dry Hot Rock Exploration Based on Large-Scale Group Decision-Making with Three-way Decision. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-024-01690-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-024-01690-7