Abstract
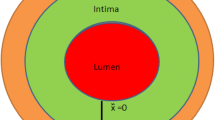
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease which occurs due to plaque accumulation in the intima, the innermost layer of the artery. In this paper, a simple reaction–diffusion mathematical model of the plaque formation process comprising of oxidized LDL and macrophages has been developed. Linear stability analysis of the non-spatial model leads to the existence of global stability of the kinetic system. This reveals that the non-spatial system can withstand a substantial change in the significant model parameter values which can be taken forward for further clinical investigations. Numerical bifurcation analysis of the non-spatial system confirms the existence of Hopf bifurcation with respect to two significant model parameters. The biological importance of these bifurcation diagrams is discussed in detail. The significance of the model presented in this research paper provides a clear insight into the role of the key constituents, oxidized LDL and macrophages, involved in the plaque-forming process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abi Younes G, El Khatib N (2022) Math Model Nat Phenom 17:5
Alimohammadi S (2017) Proc Inst Mech Eng Part H J Eng Med 231(5):378
Anlamlert W, Lenbury Y, Bell J (2017) Adv Differ Equ 2017(1):195
Bulelzai MA, Dubbeldam JL (2012) J Theor Biol 297:1
Calvez V, Ebde A, Meunier N, Raoult A (2009) ESAIM Proc (EDP Sci) 28:1–12
Chalmers AD, Cohen A, Bursill CA, Myerscough MR (2015) J Math Biol 71(6–7):1451
Cobbold C, Sherratt J, Maxwell S (2002) Bull Math Biol 64(1):65
Cohen A, Myerscough MR, Thompson RS (2014) Bull Math Biol 76(5):1117
Crowther MA (2005) ASH Educ Program Book 2005(1):436
Friedman A, Hao W (2015) Bull Math Biol 77(5):758
Gijsen FJ, Wentzel JJ, Thury A, Mastik F, Schaar JA, Schuurbiers JC, Slager CJ, van der Giessen WJ, de Feyter PJ, van der Steen AF (2008) Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295(4):H1608
Hale J (1969) Ordinary differential equations. Pure and applied mathematics. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Hao W, Friedman A (2014) PLoS One 9(3):e90497
Homma S, Hirose N, Ishida H, Ishii T, Araki G et al (2001) STROKE-DALLAS- 32(4):830
Ibragimov A, McNeal C, Ritter L, Walton J (2005) Math Med Biol 22(4):305
Kozusko F, Bourdeau M (2007) Cell Prolif 40(6):824
Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A (2002) Circulation 105(9):1135
Malek AM, Alper SL, Izumo S (1999) JAMA 282(21):2035
Marušić M, Vuk-Pavlovic S, Freyer JP et al (1994) Bull Math Biol 56(4):617
Mel’nyk T (2019) Int J Biomath 12(02):1950014
Ougrinovskaia A, Thompson RS, Myerscough MR (2010) Bull Math Biol 72(6):1534
Parton A, McGilligan V, O’kane M, Baldrick FR, Watterson S (2015) Brief Bioinform 17(4):562
Ross R, Glomset J, Harker L (1977) Am J Pathol 86(3):675
Simonetto C, Heier M, Peters A, Kaiser JC, Rospleszcz S (2022) Am J Epidemiol 191 (10):1766 From atherosclerosis to myocardial infarction–a process-oriented model investigating the role of risk factors. 191(10):1766–1775
Acknowledgements
All the authors are highly grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their fruitful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, D., Mukherjee, A. Analysis and numerical simulation of a reaction–diffusion mathematical model of atherosclerosis. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 9, 3517–3526 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01664-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01664-4