Abstract
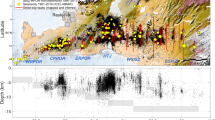
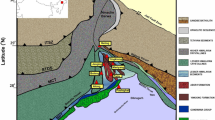
In this study, we attempted to derive a seismotectonic model for the High-Middle Atlas Junction area, in the central part of Morocco, by determining new earthquake focal mechanisms and tectonic stress tensor parameters. For that, we have analyzed high-quality seismic waveform data of moderate earthquakes that were collected by local broadband seismological networks between the time period from 2008 to 2014. The focal mechanisms of well-relocated earthquakes were determined using the P-wave first-motion polarities that were retrieved from the earthquake seismograms. The tectonic stress parameters were then inferred by applying a stress tensor inversion to the calculated focal mechanisms. The results that we found show that most earthquakes are characterized by predominant pure reverse faulting to reverse faulting with a minor strike-slip component. The average trend of P- and T-axes is 223.94°±95.6° and 17.68°±13.02°, respectively, and the average plunge of P- and T-axes is 183.02°±95.22° and 56.32°±28.41°, respectively. The estimated stress tensor parameters, describing the principal stress directions show that the axis of σ1 has the trend of 178.0° and dip** southward of 2.0° and an axis of σ2 has the trend of 268.0° and dip** westward of 3.0°, indicating that both of σ1 and σ2 axes are sub-horizontal. The third stress axis, σ3, has the trend of 46.0° and the plunge of 87.0°, and tends to be sub-vertical. The stress shape ratio, R, is equal to 0.61 in the whole area. These results strongly suggest that the reverse-faulting regime is predominant over the study area, and the P-axes and the stress orientations are steeply consistent with the GPS velocities field pattern derived from recent geodetic models. The seismotectonic model proposed in this study is consistent with the NW–SE displacement vector of the Nubia plate with respect to Eurasia plate and currently accommodating the central High Atlas tectonic deformation system, enhancing the slight crustal shortening process at the northern active tectonic boundary of the study area.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulnaby W, Al-Mohmed R, Mahdi M (2016) Seismicity and recent stress regime of Diyala City, Iraq–Iran border. Model Earth Syst Environ 2:142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0201-z
Ait Brahim L, Chotin P (1984) Mise en évidence d’un changement de direction de compression dans l’avant pays rifain (Maroc) au cours du Tertiaire et du Quatemaire. Buil Soc go/ Fr 4:681–689
Ait Brahim L, Chotin P, Hinaj S, Abdelouafi A, El Adraoui A, Nakcha C, Dhont D, Charroud M, Alaoui FS, Amrhar A, Bouaza A, Tabyaoui H, Chaouni A (2002) Paleostress evolution in the Moroccan African marginfrom Triassic to Present. Tectonophysics 357:187–205
Angelier J (1984) Tectonic analysis of fault slip data sets. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 89(B7):5835–5848
Ayarza P, Carbonell R, Teixell A, Palomeras I, Martí D, Kchikach A, Harnafi M, Levander A, Gallart J, Arboleya ML, Alcalde J (2014) Crustal thickness and velocity structure across the moroccan Atlas from long offset wide-angle reflection seismic data: the SIMA experiment. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 15(5):1698–1717
Bensaid I, Buforn E, Cherkaoui TE, Medina F, Hahou Y (2011) New fault-plane solutions of moroccan earthquakes for the 2005–2008 period. Bull Inst Sci sect Sci Terre 33:47–52
Bernini M, Boccaletti M, Moratti G, Papani G (2000) Structural development of the Taza-Guercif Basin as a constraint for the Middle Atlas Shear Zone tectonic evolution. Mar Pet Geol 17(3):391–408
Bezada MJ, Humphreys ED, Davila JM, Carbonell R, Harnafi M, Palomeras I, Levander A (2014) Piecewise delamination of moroccan lithosphere from beneath the Atlas Mountains. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 15:975–985. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GC005059
Boulanouar A, El Moudnib L, Padhy S, Harnafi M, Villasenor A, Gallart J, Pazos A, Rahmouni A, Boukalouch M, Sebbani J (2018) Estimation of coda wave attenuation in Northern Morocco. Pure Appl Geophys 175:883–897
Buforn E, Sanz de Galdeano C, Udías A (1995) Seismotectonics of the Ibero-Maghrebian Region. Tectonophysics 248:247–261
Buforn E, Bezzeghoud M, Udías A, Pro C (2004) Seismic sources on the Iberia-African plate boundary and their tectonic implications. Pure appl Geophys 161(3):623–646
Cherkaoui T-E, El Hassani A (2012) Seismicity and seismic hazard in Morocco: 1901–2010. Bulletin de l’Institut Scientifique. Rabat Sect Sci de la Terre 34:45–55
Frizon De Lamotte D, Crespo-Blanc A, Saint-Bezar B, Comas M, Fernandez M, Zeyen H, Ayarza P, Robert-Charrue C, Chalouan A, Zizi M, Teixell A, Arboleya ML, Alvarez-Lobato F, Julivert M, Micard A (2004) TRANSMED-transect I (Betics, Alboran Sea, Rif, Moroccan Meseta, High Atlas, Jbel Saghro, Tindouf basin. In: W Cavazza, F Roure, W Spakman, GM Stampfli, pA Ziegler (eds) The TRANSMED Atlas: the Mediterranean region from crust to mantle. Springer, Berlin. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00069189/
Dooley TP, Hudec MR (2020) Extension and inversion of salt-bearing rift systems. Solid Earth 11:1187–1204
Fekkak A, H. Ouanaimi H, Michard A, Soulaimani A, Ettachfini EM, Berrada I, El Arabi H, Lagnaoui A, Saddiqi O, (2018) Thick-skinned tectonics in a Late Cretaceous-Neogene intracontinental belt (High Atlas Mountains, Morocco): The flat-ramp fault control on basement shortening and cover folding. J Afr Earth Sci 140:169–188
Frizon de Lamotte D, Saint Bézar B, Bracène R, Mercier E (2000) The two main steps of the Atlas building and geodynamics of the western Mediterranean. Tectonics 19:740–761
Frohlich C, Apperson KD (1992) Earthquake focal mechanisms, moment tensors, and the consistency of seismic activity near plate boundaries. Tectonics 11(2):279–296
Gephart JW, Forsyth DW (1984) An improved method for determining the regional stress tensor using earthquake focal mechanism data: application to the San Fernando Earthquake sequence. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 89(11):9305–9320
Gomez F, Barazangi M, Bensaid M (1996) Active tectonism in the intracontinental Middle Atlas Mountains of Morocco: synchronous crustal shortening and extension. J Geol Soc 153(3):389–402
Hallo M, Opršal I, Asano K, Gallovič F (2019) Seismotectonics of the 2018 Northern Osaka M6.1 earthquake and its aftershocks: joint movements on strike-slip and reverse faults in inland Japan. Earth Planet Space 71:34
Havskov J, Ottemoller L (1999) SeisAn earthquake analysis software. Seismol Res Lett 70(5):532–534
Jacobshagen V (1988) The Atlas system (Morocco). Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 481–499
Kariche J, Meghraoui M, Timoulali Y, Cetin E, Toussaint R (2018) The Al Hoceima earthquake sequence of 1994, 2004 and 2016: Stress transfer and poroelasticity in the Rif and Alboran Sea region. Geophys J Int 212:42–53
Kissling E, Ellsworth WL, Eberhart-Phillips D, Kradolfer U (1994) Initial reference models in local earthquake tomography. J Geophys Res 99:19635–19646
Koulali A, Ouazar D, Tahayt A, King RW, Vernant P, Reilinger RE (2011) New GPS constraints on active deformation along the Africa–Iberia plate boundary. Earth Planet Sci Lett 308(1–2):211–217
Laville E, Piqué A (1992) Jurassic penetrative deformation and cenozoic uplift in the central high Atlas (Morocco): a tectonic model. Structural and orogenic inversions. Geol Rundsch 81:157–170
Lee H, Bezada MJ, Faccenda M (2021) Can sub-slab low-velocity anomalies be an artifact caused by anisotropy? A case study from the Alboran slab area in the western Mediterranean. Tectonophysics 229080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2021.229080
Lee HM, Bezada MJ, Kim YH (2022) The origin of the low-velocity anomalies beneath the rootless atlas mountains: insights gained from modeling of anisotropy developed by the travel of canary plume. JGR Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022JB024622
Lienert BRE, Havskov J (1995) A computer program for locating earthquakes both locally and globally. Seismol Res Lett 66(5):26–36
Makris J, Demnati A, Klussmann J (1985) Deep seismic soundings in Morocco and a crust and upper mantle model deduced from seismic and gravity data. Ann Geophys 3:369–380
Martín R, Stich D, Morales J, Mancilla F (2015) Moment tensor solutions for the Iberian-Maghreb region during the Iberarray deployment. Tectonophysics 663:261–274
Mckenzie DP (1969) The relation between Fault Plane solution for earthquakes and the directions of the principal stresses. Bull Seismol Soc Am 59:591–601
Medina F (2008) Catalogue of focal mechanisms of the moroccan earthquakes for the period 1959–2007. Doc Inst Sci Rabat 23:58
Medina F, Cherkaoui TE (1991) Focal mechanisms of the Atlas earthquakes, and their tectonic implications. Geol Rundsch 80:639–648
Medina F, Cherkaoui TE (1992) Mécanismes au foyer des séismes du Maroc et des régions voisines (1901–1986). Implications tectoniques. Eclogae Geol Helv 85:(2):433–457
Medina F, Cherkaoui TE (2021) The Midelt earthquake of November 17th 2019, and its implications on the present-day tectonics of the junction of the High and Middle Atlas (Morocco). Arab J Geosci 14:1717
Medina F, Bensaid I, Tangi A (2011) Catalogue of focal mechanisms of Moroccan earthquakesf or the period 1959–2007; analysis of parameters. Bulletin de l’Institut Scientifique Rabat section Sciences de la Terre 33:37–46
Michael AJ (1984) Determination of stress from slip data: faults and folds. J Geophys Res 89:(11):517–526
Michael AJ (1987) Use of focal mechanisms to determine stress: a control study. J Geophys Res 92:357–368
Miller MS, Allam AA, Becker TW, Di Leo JF, Wookey J (2013) Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the westernmost Mediterranean and northwestern Africa from shear wave splitting analysis. Earth Planet Sci Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.05.036
Missenard Y, Taki Z, Frizon de Lamotte D, Benammi M, Hafid M, Leturmy P, Sébrier M (2007) Tectonic styles in the Marrakesh High Atlas (Morocco): the role of heritage and mechanical stratigraphy. J Afr Earth Sci 48(4):247–266
Morel JL, Zouine M, Andrieux J, Faure-Muret A (2000) Déformations néogènes et quaternaires de la bordure nord haut atlasique (Maroc): Rôle du socle et conséquences structurales. J Afr Earth Sci 30:119–131
Mridekh A, Toto EA, Hafid M, El Ouataoui A (2000) Structure sismique de la plate-forme atlan-tique au large d’Agadir (Maroc sud-occidental). Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences de Paris. Sci de la Terre et des Planètes 331:387–392
Mutlu AH (2020) Seismicity, focal mechanism, and stress tensor analysis of the Simav region, western Turkey. Open Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1515/geo-2020-0010
Onana PNE, Toto EL, Zouhri L, Chaabane A, El Mouraouah A, Iben Brahim A (2011) Recent seismicity of Central High Atlas and Ouarzazate basin (Morocco). Bull Eng Geol Environ 70:633–641
Palomeras I, Thurner S, Levander A, Liu K, Villaseñor A, Carbonell R, Harnafi M (2014) Finite-frequency Rayleigh wave tomography of the western Mediterranean: map** its lithospheric structure. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 15:140–160
Palomeras I, Villaseñor A, Thurner S, Levander A, Gallart J, Harnafi M (2017) Lithospheric structure of Iberia and Morocco using finite-frequency Rayleigh wave tomography from earthquakes and seismic ambient noise. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 18:1824–1840
Sebrier M, Siame L, Zouine EM, Winter T, Missenard Y, Leturmy P (2006) Active tectonics in the moroccan high Atlas. C R Geosci 338(1–2):65–79
Serpelloni E, Vannucci G, Pondrelli S, Argnani A, Casula G, Anzidei M, Baldi P, Gasperini P (2007) Kinematics of the Western Africa–Eurasia plate boundary from focal mechanisms and GPS data. Geophys J Int 169:1180–1200
Sherif MA, Kamal A, Naif AO (2020) Tectonic stress regime and stress patterns from the inversion of earthquake focal mechanisms in NW Himalaya and surrounding regions. J King Saud Univ Sci 33(2)
Snoke JA, Munsey JW, Teague AG, Bollinger GA (1984) A program for focal mechanism determination by combined use of polarity and SV-P amplitude ratio data. Earthq Notes 5(2):165–171
Spieker S, Wölbern I, Thomas C, Harnafi M, El Moudnib L (2014) Crustal and upper-mantle structure beneath the western Atlas Mountains in SW Morocco derived from receiver functions. Geophys J Int 198(3):1474–1485
Stich D, Serpelloni E, Mancilla F, Morales J (2006) Kinematics of the Iberia-Maghreb plate contact from seismic moment tensors and GPS observations. Tectonophysics 426(3–4):295–317
Stich D, Martín R, Morales J (2010) Moment tensor inversion for Iberia-Maghreb earthquakes 2005–2008. Tectonophysics 483:390–398
Teixell A, Arboleya ML, Julivert M, Charroud M (2003) Tectonic shortening and topography in the central high Atlas (Morocco). Tectonics 22(5):1051
Timoulali Y, Bouiflane M, Bouskri G, Azguet R, El Fellah Y (2019) Lithosphere structures dynamics in the central high Atlas (Morocco) by seismic tomography and gravimetric data. Geodesy Geodyn 10(3):241–255
Vavryčuk V (2011) Principal earthquakes: theory and observations for the 2008 West Bohemia swarm. Earth Planet Sci Lett 305(3–4):290–296
Vavryčuk V (2014) Iterative joint inversion for stress and fault orientations from focal mechanisms. Geophys J Int 199(1):69–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggu224
Vernant P, Fadil A, Mourabit T, Ouazar D, Koulali A, Martin Davila J, Garate J, McClusky S, Reilinger R (2010) Geodetic constraints on active tectonics of the western Mediterranean: implications for the kinematics and dynamics of the Nubia- Eurasia plate boundary zone. J Geod 49:123–129
Wessel P, Smith WHF (1998) New improved version of the generic map** tools released. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 79(47):579
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moudnib, L.E., Timoulali, Y., Nouayti, A. et al. Seismotectonic model of High-Middle Atlas Junction (Morocco) derived from earthquake focal mechanism and stress tensor analysis. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 9, 2407–2423 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01630-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01630-0