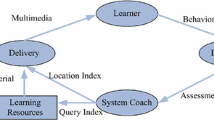
Abstract
In recent years, the main problem in e-learning has shifted to personalization of learning environment by Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITSs). Therefore, by designing personalized teaching models, learners are able to have a successful and satisfying experience in achieving their learning goals. Affective Tutoring Systems (ATSs) are some kinds of ITS that can recognize and respond to affective states of learners. In this study, we have designed, implemented, and evaluated an ATS named ATTENDEE (AffecTive Tutoring system based on facial EmotioN recognition and heaD posE Estimation) to personalize the learning environment based on the facial emotions recognition, head pose estimation, and cognitive style of learners. First, a unit called Intelligent Analyzer (IA) created which was responsible for recognizing facial expression and head angles of learners. Next, the ATS was built which mainly made of two units: ITS, IA. Results indicated that with the ATS, participants needed less efforts to pass the tests. In other words, we observed when the IA unit was activated, learners could pass the final tests in fewer attempts than those for whom the IA unit was deactivated. In addition, we have examined the effect of the IA unit on the educational achievement and satisfaction of learners.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainley, M. (2006). Connecting with learning: Motivation, affect and cognition in interest processes. Educational Psychology Review, 18(4), 391–405.
Alexander, S. T. V. (2007a). An affect-sensitive intelligent tutoring system with an animated pedagogical agent that adapts to student emotion like a human tutor,. In Doctoral Thesis in Philosophy in Computer Science.
Alexander, S. T. V. (2007b). An affect-sensitive intelligent tutoring system with an animated pedagogical agent that adapts to student emotion like a human tutor: a thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Computer Science . Massey University.
Alkhatlan, A., & Kalita, J. (2018). Intelligent tutoring systems: A comprehensive historical survey with recent developments. Ar**v Preprint. https://doi.org/10.48550/ar**v.1812.09628
Ba, S., & Hu, X. (2023). Measuring emotions in education using wearable devices: A systematic review. Computers & Education, 200, 104797.
Barrón-Estrada, M. L., Zatarain-Cabada, R., Oramas-Bustillos, R., & Gonzalez-Hernandez, F. (2017). Sentiment analysis in an affective intelligent tutoring system. 2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT), 394–397.
Cárdenas-López, H. M., Zatarain-Cabada, R., Barrón-Estrada, M. L., & Mitre-Hernández, H. (2023). Semantic fusion of facial expressions and textual opinions from different datasets for learning-centered emotion recognition. Soft Computing, 27, 1–11.
Chan, A. T. S., Wang, P. C., Guan, F., Soo, S. H., & Li, H. L. H. (2023). Integration of Virtual Reality with Intelligent Tutoring for High Fidelity Air Traffic Control Training.
Cunha-Pérez, C., Arevalillo-Herráez, M., Marco-Giménez, L., & Arnau, D. (2018). On incorporating affective support to an intelligent tutoring system: An empirical study. IEEE Revista Iberoamericana De Tecnologias Del Aprendizaje, 13(2), 63–69.
Dougalis, A., & Plexousakis, D. (2022). A logic based affective tutoring system that uses reinforcement learning for discovering teaching strategies. EDULEARN22 Proceedings, 4535–4543.
Duffy, M. C., Lajoie, S. P., Pekrun, R., & Lachapelle, K. (2020). Emotions in medical education: Examining the validity of the Medical Emotion Scale (MES) across authentic medical learning environments. Learning and Instruction, 70, 101150.
Ekman, P. (1999). Basic emotions. Handbook of Cognition and Emotion, 98(45–60), 16.
Garcia, M. B., & Garcia, P. S. (2023). Intelligent Tutoring System as an Instructional Technology in Learning Basic Nutrition Concepts: An Exploratory Sequential Mixed Methods Study. In Handbook of Research on Instructional Technologies in Health Education and Allied Disciplines (pp. 265–284). IGI Global.
Gupta, A., Jaiswal, R., Adhikari, S., & Balasubramanian, V. (2016). DAISEE: dataset for affective states in e-learning environments. Ar**v Preprint. https://doi.org/10.48550/ar**v.1609.01885
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 770–778.
Huang, Y., Brusilovsky, P., Guerra, J., Koedinger, K., & Schunn, C. (2023). Supporting skill integration in an intelligent tutoring system for code tracing. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 39(2), 477–500.
Isen, A. M., & Means, B. (1983). The influence of positive affect on decision-making strategy. Social Cognition, 2(1), 18–31.
Kaklauskas, A., Kuzminske, A., Zavadskas, E. K., Daniunas, A., Kaklauskas, G., Seniut, M., Raistenskis, J., Safonov, A., Kliukas, R., & Juozapaitis, A. (2015). Affective tutoring system for built environment management. Computers & Education, 82, 202–216.
Lin, H.-C.K., Wu, C.-H., & Hsueh, Y.-P. (2014). The influence of using affective tutoring system in accounting remedial instruction on learning performance and usability. Computers in Human Behavior, 41, 514–522.
Loderer, K., Pekrun, R., & Lester, J. C. (2020). Beyond cold technology: A systematic review and meta-analysis on emotions in technology-based learning environments. Learning and Instruction, 70, 101162.
Mao, X., & Li, Z. (2010). Agent based affective tutoring systems: A pilot study. Computers & Education, 55(1), 202–208.
Mayer, R. E. (2020). Searching for the role of emotions in e-learning. Learning and Instruction, 70, 101213.
Mollahosseini, A., Hasani, B., & Mahoor, M. H. (2017). Affectnet: A database for facial expression, valence, and arousal computing in the wild. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 10(1), 18–31.
Nye, B., Karumbaiah, S., Tokel, S. T., Core, M. G., Stratou, G., Auerbach, D., & Georgila, K. (2017). Analyzing learner affect in a scenario-based intelligent tutoring system. International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, 544–547.
Pourmirzaei, M., Montazer, G. A., & Esmaili, F. (2021). How self-supervised learning can be used for fine-grained head pose estimation? Ar**v Preprint. https://doi.org/10.48550/ar**v.2108.04893
Pourmirzaei, M., Montazer, G. A., & Esmaili, F. (2021). Using self-supervised auxiliary tasks to improve fine-grained facial representation. Ar**v Preprint. https://doi.org/10.48550/ar**v.2105.06421
Riding, R., & Cheema, I. (1991). Cognitive styles—an overview and integration. Educational Psychology, 11(3–4), 193–215.
Ruiz, N., Chong, E., & Rehg, J. M. (2018). Fine-grained head pose estimation without keypoints. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2074–2083.
Russell, J. A. (1980). A circumplex model of affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 39(6), 1161.
Santos, O. C. (2016). Emotions and personality in adaptive e-learning systems: an affective computing perspective. In Emotions and personality in personalized services (pp. 263–285). Springer.
Schmitz-Hübsch, A., Stasch, S.-M., Becker, R., Fuchs, S., & Wirzberger, M. (2022). Affective response categories—toward personalized reactions in affect-adaptive tutoring systems. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 5, 873056.
Soltani, M., Zarzour, H., Babahenini, M. C., & Chemam, C. (2018). An affective tutoring system for massive open online courses. International Conference on the Sciences of Electronics, Technologies of Information and Telecommunications, 202–211.
Tan, M., & Le, Q. (2019). Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. International Conference on Machine Learning, 6105–6114.
Wang, C.-H., & Lin, H.-C.K. (2018). Constructing an affective tutoring system for designing course learning and evaluation. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 55(8), 1111–1128.
Wang, H., Tlili, A., Huang, R., Cai, Z., Li, M., Cheng, Z., Yang, D., Li, M., Zhu, X., & Fei, C. (2023). Examining the applications of intelligent tutoring systems in real educational contexts: A systematic literature review from the social experiment perspective. Education and Information Technologies, 28, 1–36.
Wang, T.-H., Lin, H.-C.K., Chen, H.-R., Huang, Y.-M., Yeh, W.-T., & Li, C.-T. (2021). Usability of an affective emotional learning tutoring system for mobile devices. Sustainability, 13(14), 7890.
Wang, T., Zheng, J., Tan, C., & Lajoie, S. P. (2023). Computer-based scaffoldings influence students’ metacognitive monitoring and problem-solving efficiency in an intelligent tutoring system. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 39, 1652.
Wu, C. H., Lin, H.-C.K., Wang, T.-H., Huang, T.-H., & Huang, Y.-M. (2022). Affective mobile language tutoring system for supporting language learning. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 833327.
Yasin, M., & Utomo, R. A. (2023). Design of intelligent tutoring system (ITS) based on augmented reality (AR) for three-dimensional geometry material. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2569(1).
Zhang, S., Zhu, X., Lei, Z., Shi, H., Wang, X., & Li, S. Z. (2017). Faceboxes: A CPU real-time face detector with high accuracy. IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), 2017, 1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The research presented in this manuscript, which focused on evaluating two groups of people using an E-learning system, adhered to the highest ethical standards as prescribed by Tarbiat Modares University. In this study, informed consent was obtained from all participants, ensuring they were fully aware of the study's nature and their involvement. The research was conducted in accordance with the ethical guidelines of Tarbiat Modares University's Institutional Review Board, with a particular emphasis on respecting participant privacy and data confidentiality. All participant information has been anonymized to maintain confidentiality. We confirm that there were no conflicts of interest affecting this research, and all procedures were conducted ethically and responsibly.
Ethical Statement
We declare that this manuscript, titled “ATTENDEE: an AffecTive Tutoring system based on facial EmotioN recognition and heaD posE Estimation to personalize e-learning environment,” represents our original research and collective effort. The development and assessment of the affective tutoring system have been conducted with adherence to ethical research standards, including the informed consent of all involved parties and the protection of their privacy. No personal data were misused, and facial expressions and head pose data were anonymized. This work has not been published elsewhere, nor is it under consideration by another publication. The undersigned authors share joint responsibility for the cont ent and adherence to ethical guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pourmirzaei, M., Montazer, G.A. & Mousavi, E. ATTENDEE: an AffecTive Tutoring system based on facial EmotioN recognition and heaD posE Estimation to personalize e-learning environment. J. Comput. Educ. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-023-00303-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-023-00303-w