Abstract
Purpose
To date, many genes have been associated with congenital hypothyroidism (CH). Our aim was to identify the mutational spectrum of 23 causative genes in Turkish patients with permanent CH, including thyroid dysgenesis (TD) and dyshormonogenesis (TDH) cases.
Methods
A total of 134 patients with permanent CH (130 primary, 4 central) were included. To identify the genetic etiology, we screened 23 candidate genes associated with CH by next-generation sequencing. For confirmation and to detect the status of the specific familial variant in relatives, Sanger sequencing was also performed.
Results
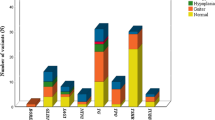
Possible pathogenic variants were found in 5.2% of patients with TD and in 64.0% of the patients with normal-sized thyroid or goiter. In all patients, variants were most frequently found in TSHR, followed by TPO and TG. The same homozygous TSHB variant (c.162 + 5G > A) was identified in four patients with central CH. In addition, we detected novel variants in the TSHR, TG, SLC26A7, FOXE1, and DUOX2.
Conclusion
Genetic causes were determined in the majority of CH patients with TDH, however, despite advances in genetics, we were unable to identify the genetic etiology of most CH patients with TD, suggesting the effect of unknown genes or environmental factors. The previous studies and our findings suggest that TSHR and TPO mutations is the main genetic defect of CH in the Turkish population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cherella CE, Wassner AJ (2017) Congenital hypothyroidism: insights into pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol 2017:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13633-017-0051-0
Dilli D, Çzbaş S, Acıcan D, Yamak N, Ertek M, Dilmen U (2013) Establishment and development of a national newborn screening programme for congenital hypothyroidism in Turkey. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 5(2):73–79. https://doi.org/10.4274/Jcrpe.929
Szinnai G (2014) Clinical genetics of congenital hypothyroidism. Endocr Dev 26:60–78. https://doi.org/10.1159/000363156
Persani L, Rurale G, de Filippis T, Galazzi E, Muzza M, Fugazzola L (2018) Genetics and management of congenital hypothyroidism. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 32(4):387–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2018.05.002
Targovnik HM, Citterio CE, Rivolta CM (2011) Thyroglobulin gene mutations in congenital hypothyroidism. Horm Res Paediatr 75:311–321. https://doi.org/10.1159/000324882
Persani L, Cangiano B, Bonomi M (2019) The diagnosis and management of central hypothyroidism in 2018. Endocr Connect 8(2):R44–R54. https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-18-0515
Nicholas AK, Jaleel S, Lyons G, Schoenmakers E, Dattani MT, Crowne E, Bernhard B, Kirk J, Roche EF, Chatterjee VK, Schoenmakers N (2017) Molecular spectrum of TSHβ subunit gene defects in central hypothyroidism in the UK and Ireland. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 86(3):410–418. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13149
Vuissoz JM, Deladoëy J, Buyukgebiz A, Cemeroglu P, Gex G, Gallati S, Mullis PE (2001) New autosomal recessive mutation of the TSH-beta subunit gene causing central isolated hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(9):4468–4471. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.86.9.7876
Borck G, Topaloglu AK, Korsch E, Martiné U, Wildhardt G, Onenli-Mungan N, Yuksel B, Aumann U, Koch G, Ozer G, Pfäffle R, Scherberg NH, Refetoff S, Pohlenz J (2004) Four new cases of congenital secondary hypothyroidism due to a splice site mutation in the thyrotropin-beta gene: phenotypic variability and founder effect. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(8):4136–4141. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-0494
Özhan B, BozAnlaş Ö, Sarıkepe B, Albuz B, SemerciGündüz N (2017) Congenital central hypothyroidism caused by a novel thyroid-stimulating hormone-beta subunit gene mutation in two siblings. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 9(3):278–282. https://doi.org/10.4274/jcrpe.4595
Cangul H, Aycan Z, Olivera-Nappa A, Saglam H, Schoenmakers NA, Boelaert K, Cetinkaya S, Tarim O, Bober E, Darendeliler F, Bas V, Demir K, Aydin BK, Kendall M, Cole T, Högler W, Chatterjee VK, Barrett TG, Maher ER (2013) Thyroid dyshormonogenesis is mainly caused by TPO mutations in consanguineous community. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 79(2):275–281. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.12127
Rodrigues C, Jorge P, Soares JP, Santos I, Salomão R, Madeira M, Osorió RV, Santos R (2005) Mutation screening of the thyroid peroxidase gene in a cohort of 55 Portuguese patients with congenital hypothyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol 152(2):193–198. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje.1.01826
Löf C, Patyra K, Kuulasmaa T, Vangipurapu J, Undeutsch H, Jaeschke H, Pajunen T, Kero A, Krude H, Biebermann H, Kleinau G, Kühnen P, Rantakari K, Miettinen P, Kirjavainen T, Pursiheimo JP, Mustila T, Jääskeläinen J, Ojaniemi M, Toppari J, Ignatius J, Laakso M, Kero J (2016) Detection of novel gene variants associated with congenital hypothyroidism in a Finnish patient cohort. Thyroid 26(9):1215–1224. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2016.0016
Avbelj M, Tahirovic H, Debeljak M, Kusekova M, Toromanovic A, Krzisnik C, Battelino T (2007) High prevalence of thyroid peroxidase gene mutations in patients with thyroid dyshormonogenesis. Eur J Endocrinol 156(5):511–519. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-07-0037
Bruellman RJ, Watanabe Y, Ebrhim RS, Creech MK, Abdullah MA, Dumitrescu AM, Refetoff S, Weiss RE (2020) Increased prevalence of TG and TPO mutations in Sudanese children with congenital hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 105(5):1564–1572. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgz297
Park KJ, Park HK, Kim YJ, Lee KR, Park JH, Park JH, Park HD, Lee SY, Kim JW (2016) DUOX2 mutations are frequently associated with congenital hypothyroidism in the Korean population. Ann Lab Med 36(2):145–153. https://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.2.145
Yu B, Long W, Yang Y, Wang Y, Jiang L, Cai Z, Wang H (2018) Newborn screening and molecular profile of congenital hypothyroidism in a Chinese population. Front Genet 9:509. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00509
Chen X, Kong X, Zhu J, Zhang T, Li Y, Ding G, Wang H (2018) Mutational spectrum analysis of seven genes associated with thyroid dyshormonogenesis. Int J Endocrinol 2018:8986475. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8986475
Wang H, Kong X, Pei Y, Cui X, Zhu Y, He Z, Wang Y, Zhang L, Zhuo L, Chen C, Yan X (2020) Mutation spectrum analysis of 29 causative genes in 43 Chinese patients with congenital hypothyroidism. Mol Med Rep 22(1):297–309. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11078
Sun F, Zhang JX, Yang CY, Gao GQ, Zhu WB, Han B, Zhang LL, Wan YY, Ye XP, Ma YR, Zhang MM, Yang L, Zhang QY, Liu W, Guo CC, Chen G, Zhao SX, Song KY, Song HD (2018) The genetic characteristics of congenital hypothyroidism in China by comprehensive screening of 21 candidate genes. Eur J Endocrinol 178(6):623–633. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-17-1017
Nicholas AK, Serra EG, Cangul H, Alyaarubi S, Ullah I, Schoenmakers E, Deeb A, Habeb AM, Almaghamsi M, Peters C, Nathwani N, Aycan Z, Saglam H, Bober E, Dattani M, Shenoy S, Murray PG, Babiker A, Willemsen R, Thankamony A, Lyons G, Irwin R, Padidela R, Tharian K, Davies JH, Puthi V, Park SM, Massoud AF, Gregory JW, Albanese A, Pease-Gevers E, Martin H, Brugger K, Maher ER, Chatterjee VK, Anderson CA, Schoenmakers N (2016) Comprehensive screening of eight known causative genes in congenital hypothyroidism with gland-in-Situ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101(12):4521–4531. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2016-1879
Cangül H, Doğan M, Sağlam Y, Kendall M, Boelaert K, Barrett TG, Maher ER (2014) One base deletion (c.2422delT) in the TPO gene causes severe congenital hypothyroidism. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 6(3):169–173. https://doi.org/10.4274/Jcrpe.1404
Cangul H, Aydin BK, Bas F (2015) A homozygous TPO gene duplication (c.1184_1187dup4) causes congenital hypothyroidism in three siblings born to a consanguineous family. J Pediatr Genet 4(4):194–198. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1565268
Cangul H, Liao XH, Schoenmakers E, Kero J, Barone S, Srichomkwun P, Iwayama H, Serra EG, Saglam H, Eren E, Tarim O, Nicholas AK, Zvetkova I, Anderson CA, Frankl FEK, Boelaert K, Ojaniemi M, Jääskeläinen J, Patyra K, Löf C, Williams ED, UK10K Consortium, Soleimani M, Barrett T, Maher ER, Chatterjee VK, Refetoff S, Schoenmakers N (2018) Homozygous loss-of-function mutations in SLC26A7 cause goitrous congenital hypothyroidism. JCI Insight 3(20):e99631. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.99631
Cangul H, Boelaert K, Dogan M, Saglam Y, Kendall M, Barrett TG, Maher ER (2014) Novel truncating thyroglobulin gene mutations associated with congenital hypothyroidism. Endocrine 45(2):206–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-0027-7
Cangül H, Doğan M, Üstek D (2015) A homozygous nonsense thyroid peroxidase mutation (R540X) consistently causes congenital hypothyroidism in two siblings born to a consanguineous family. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 7(4):323–328. https://doi.org/10.4274/jcrpe.1920
Mutlu M, Karagüzel G, Alıyazicioğlu Y, Eyüpoğlu I, Okten A, Aslan Y (2012) Reference intervals for thyrotropin and thyroid hormones and ultrasonographic thyroid volume during the neonatal period. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 25(2):120–124. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2011.561894
Aydıner Ö, KarakoçAydıner E, Akpınar İ, Turan S, Bereket A (2015) Normative data of thyroid volume-ultrasonographic evaluation of 422 subjects aged 0–55 years. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 7(2):98–101. https://doi.org/10.4274/jcrpe.1818
Lek M, Karczewski KJ, Minikel EV et al (2016) Exome aggregation consortium. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 536(7616):285–291. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19057
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL, ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American college of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular pathology. Genet Med 17(5):405–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.30
Fan X, Fu C, Shen Y, Li C, Luo S, Li Q, Luo J, Su J, Zhang S, Hu X, Chen R, Gu X, Chen S (2017) Next-generation sequencing analysis of twelve known causative genes in congenital hypothyroidism. Clin Chim Acta 468:76–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2017.02.009
Yamaguchi T, Nakamura A, Nakayama K, Hishimura N, Morikawa S, Ishizu K, Tajima T (2020) Targeted next-generation sequencing for congenital hypothyroidism with positive neonatal TSH screening. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 105(8):dgaa308. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa308
Mio C, Grani G, Durante C, Damante G (2020) Molecular defects in thyroid dysgenesis. Clin Genet 97(1):222–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.13627
Zou M, Alzahrani AS, Al-Odaib A, Alqahtani MA, Babiker O, Al-Rijjal RA, BinEssa HA, Kattan WE, Al-Enezi AF, Al Qarni A, Al-Faham MSA, Baitei EY, Alsagheir A, Meyer BF, Shi Y (2018) Molecular analysis of congenital hypothyroidism in Saudi Arabia: SLC26A7 mutation is a novel defect in thyroid dyshormonogenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103(5):1889–1898. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-02202
Khan A, Umair M, Sharaf RA, Khan MI, Ullah A, Abbas S, Shaheen N, Bilal M, Ahamd F (2020) Novel homozygous variant in the TPO gene associated with congenital hypothyroidism and mild-intellectual disability. Hum Genome Var 7(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41439-020-00129-3
Turkkahraman D, Alper OM, Pehlivanoglu S, Aydin F, Yildiz A, Luleci G, Akcurin S, Bircan I (2010) Analysis of TPO gene in Turkish children with iodide organification defect: identification of a novel mutation. Endocrine 37(1):124–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-009-9280-1
Pannain S, Weiss RE, Jackson CE, Dian D, Beck JC, Sheffield VC, Cox N, Refetoff S (1999) Two different mutations in the thyroid peroxidase gene of a large inbred Amish kindred: power and limits of homozygosity map**. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(3):1061–1071. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.84.3.5541
Bikker H, Vulsma T, Baas F, de Vijlder JJ (1995) Identification of five novel inactivating mutations in the human thyroid peroxidase gene by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Hum Mutat 6(1):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.1380060104
Ishii J, Suzuki A, Kimura T, Tateyama M, Tanaka T, Yazawa T, Arimasu Y, Chen IS, Aoyama K, Kubo Y, Saitoh S, Mizuno H, Kamma H (2019) Congenital goitrous hypothyroidism is caused by dysfunction of the iodide transporter SLC26A7. Commun Biol 2:270. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-019-0503-6
Petrovic S, Barone S, Xu J, Conforti L, Ma L, Kujala M, Kere J, Soleimani M (2004) SLC26A7: a basolateral Cl-/HCO3- exchanger specific to intercalated cells of the outer medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286(1):F161–F169. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00219.2003
De Felice M, Ovitt C, Biffali E, Rodriguez-Mallon A, Arra C, Anastassiadis K, Macchia PE, Mattei MG, Mariano A, Schöler H, Macchia V, Di Lauro R (1998) A mouse model for hereditary thyroid dysgenesis and cleft palate. Nat Genet 19(4):395–398. https://doi.org/10.1038/1289
Carré A, Hamza RT, Kariyawasam D, Guillot L, Teissier R, Tron E, Castanet M, Dupuy C, El Kholy M, Polak M (2014) A novel FOXE1 mutation (R73S) in Bamforth-Lazarus syndrome causing increased thyroidal gene expression. Thyroid 24(4):649–654. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2013.0417
Castanet M, Polak M (2010) Spectrum of human Foxe1/TTF2 mutations. Horm Res Paediatr 73(6):423–429. https://doi.org/10.1159/000281438
Castanet M, Park SM, Smith A, Bost M, Léger J, Lyonnet S, Pelet A, Czernichow P, Chatterjee K, Polak M (2002) A novel loss-of-function mutation in TTF-2 is associated with congenital hypothyroidism, thyroid agenesis and cleft palate. Hum Mol Genet 11(17):2051–2059. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/11.17.2051
Baris I, Arisoy AE, Smith A, Agostini M, Mitchell CS, Park SM, Halefoglu AM, Zengin E, Chatterjee VK, Battaloglu E (2002) A novel missense mutation in human TTF-2 (FKHL15) gene associated with congenital hypothyroidism but not athyreosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(10):4183–4187. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-0405
Narumi S, Muroya K, Abe Y, Yasui M, Asakura Y, Adachi M, Hasegawa T (2009) TSHR mutations as a cause of congenital hypothyroidism in Japan: a population-based genetic epidemiology study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(4):1317–1323. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-1767
Lee ST, Lee DH, Kim JY, Kwon MJ, Kim JW, Hong YH, Lee YW, Ki CS (2011) Molecular screening of the TSH receptor (TSHR) and thyroid peroxidase (TPO) genes in Korean patients with nonsyndromic congenital hypothyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 75(5):715–721. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04156.x
de Filippis T, Gelmini G, Paraboschi E, Vigone MC, Di Frenna M, Marelli F, Bonomi M, Cassio A, Larizza D, Moro M, Radetti G, Salerno M, Ardissino D, Weber G, Gentilini D, Guizzardi F, Duga S, Persani L (2017) A frequent oligogenic involvement in congenital hypothyroidism. Hum Mol Genet 26(13):2507–2514. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx145
Pohlenz J, Dumitrescu A, Aumann U, Koch G, Melchior R, Prawitt D, Refetoff S (2002) Congenital secondary hypothyroidism caused by exon skip** due to a homozygous donor splice site mutation in the TSHbeta-subunit gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(1):336–339. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.87.1.8154
Heinrichs C, Parma J, Scherberg NH, Delange F, Van Vliet G, Duprez L, Bourdoux P, Bergmann P, Vassart G, Refetoff S (2000) Congenital central isolated hypothyroidism caused by a homozygous mutation in the TSH-beta subunit gene. Thyroid 10(5):387–391. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2000.10.387
Stoupa A, Kariyawasam D, Muzza M, de Filippis T, Fugazzola L, Polak M, Persani L, Carré A (2021) New genetics in congenital hypothyroidism. Endocrine 71(3):696–705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02646-9
van de Graaf SA, Cammenga M, Ponne NJ, Veenboer GJ, Gons MH, Orgiazzi J, de Vijlder JJ, Ris-Stalpers C (1999) The screening for mutations in the thyroglobulin cDNA from six patients with congenital hypothyroidism. Biochimie 81(5):425–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-9084(99)80091-1
Makretskaya N, Bezlepkina O, Kolodkina A, Kiyaev A, Vasilyev EV, Petrov V, Kalinenkova S, Malievsky O, Dedov II, Tiulpakov A (2018) High frequency of mutations in ‘dyshormonogenesis genes’ in severe congenital hypothyroidism. PLoS ONE 13(9):e0204323. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204323
de Roux N, Misrahi M, Brauner R, Houang M, Carel JC, Granier M, Le Bouc Y, Ghinea N, Boumedienne A, Toublanc JE, Milgrom E (1996) Four families with loss of function mutations of the thyrotropin receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81(12):4229–4235. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.81.12.8954020
Tenenbaum-Rakover Y, Grasberger H, Mamanasiri S, Ringkananont U, Montanelli L, Barkoff MS, Dahood AM, Refetoff S (2009) Loss-of-function mutations in the thyrotropin receptor gene as a major determinant of hyperthyrotropinemia in a consanguineous community. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(5):1706–1712. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-1938
Liu S, Zhang W, Zhang L, Zou H, Lu K, Li Q, **a H, Yan S, Ma X (2016) Genetic and functional analysis of two missense DUOX2 mutations in congenital hypothyroidism and goiter. Oncotarget 9(4):4366–4374. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10525
Qiu YL, Ma SG, Liu H, Yue HN (2016) Two novel TSHR gene mutations (p.R528C and c.392+4del4) associated with congenital hypothyroidism. Endocr Res 41(3):180–184. https://doi.org/10.3109/07435800.2015.1124438
Nagashima T, Murakami M, Onigata K, Morimura T, Nagashima K, Mori M, Morikawa A (2001) Novel inactivating missense mutations in the thyrotropin receptor gene in Japanese children with resistance to thyrotropin. Thyroid 11(6):551–559. https://doi.org/10.1089/105072501750302859
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the children and their parents who participated in this study. We also would like to thank Enago (www.enago.com) for the English language review.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SA, BÖ, SA, and GA conducted the study. SA and SG coordinated all steps of this study. SA, SG, GA, ÖN, FH, ÖK, BÖ, and BÖ contributed to the study conception and design and analysis and interpretation of and reviewed this paper. All of the authors approved the final version of this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the local ethics committee in light of the Helsinki Declaration (2020/12-03).
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the children and their parents before the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acar, S., Gürsoy, S., Arslan, G. et al. Screening of 23 candidate genes by next-generation sequencing of patients with permanent congenital hypothyroidism: novel variants in TG, TSHR, DUOX2, FOXE1, and SLC26A7. J Endocrinol Invest 45, 773–786 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01706-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01706-1