Abstract
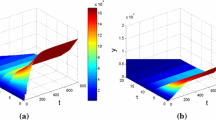
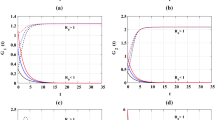
Some viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus, can infect several types of cell populations. The age of infection can also affect the dynamics of infected cells and the production of viral particles. In this work, we study a virus model with infection age and different types of target cells that takes into account the saturation effect in antibody-immune response and a general non-linear infection rate. We construct suitable Lyapunov functionals to show that the global dynamics of the model is completely determined by two parameters: the basic reproduction number of virus and the reproductive number of antibody response.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briggs, C.J., Godfray, H.C.J.: The dynamics of insect-pathogen interactions in stage-structured populations. Am. Nat. 145(6), 855–887 (1995)
Culshaw, R.V., Ruan, S.: A delay-differential equation model of HIV infection of CD4+ T-cells. Math. Biosci. 165(1), 27–39 (2000)
Djidjou Demasse, R., Ducrot, A.: An age-structured within-host model for multistrain malaria infections. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 73(1), 572–593 (2013)
Duan, X., Yuan, S.: Global dynamics of an age-structured virus model with saturation effects. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 40(6), 1851–1864 (2017)
Duffin, R.P., Tullis, R.H.: Mathematical models of the complete course of HIV infection and AIDS. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 4(4), 215–221 (2002)
Elaiw, A.M.: Global properties of a class of HIV models. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(4), 2253–2263 (2010)
Elaiw, A.M.: Global properties of a class of virus infection models with multitarget cells. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(1), 423–435 (2012)
Elaiw, A.M., Azoz, S.A.: Global properties of a class of HIV infection models with Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 36(4), 383–394 (2013)
Georgescu, P., Hsieh, Y.H.: Global stability for a virus dynamics model with nonlinear incidence of infection and removal. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 67(2), 337–353 (2006)
Hale, J.K.: Asymptotic Behavior of Dissipative Systems. American Mathematical Society, Providence (2010)
Hale, J.K., Waltman, P.: Persistence in infinite-dimensional systems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 20(2), 388–395 (1989)
Li, D., Ma, W.: Asymptotic properties of a HIV-1 infection model with time delay. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 335(1), 683–691 (2007)
Magal, P., Thieme, H.R.: Eventual compactness for semiflows generated by nonlinear age-structured models. Commun. Pure Appl. Anal. 3(4), 695–727 (2004)
Nelson, P.W., Gilchrist, M.A., Coombs, D., Hyman, J.M., Perelson, A.S.: An age-structured model of HIV infection that allows for variations in the production rate of viral particles and the death rate of productively infected cells. Math. Biosci. Eng. 1(2), 267–288 (2004)
Pawelek, K.A., Liu, S., Pahlevani, F., Rong, L.: A model of HIV-1 infection with two time delays: mathematical analysis and comparison with patient data. Math. Biosci. 235(1), 98–109 (2012)
Rong, L., Feng, Z., Perelson, A.S.: Mathematical analysis of age-structured HIV-1 dynamics with combination antiretroviral therapy. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 67(3), 731–756 (2007)
Song, X., Neumann, A.U.: Global stability and periodic solution of the viral dynamics. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 329(1), 281–297 (2007)
Tian, X., Wang, J.: Stability analysis for viral infection model with multitarget cells, Beddington–DeAngelis functional response, and humoral immunity. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2015, 654507 (2015)
Wang, J., Lang, J., Li, F.: Constructing Lyapunov functionals for a delayed viral infection model with multitarget cells, nonlinear incidence rate, state-dependent removal rate. J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 9, 524–536 (2016)
Wang, J., Lang, J., Zou, X.: Analysis of an age structured HIV infection model with virus-to-cell infection and cell-to-cell transmission. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 34, 75–96 (2017)
Wang, J., Pang, J., Kuniya, T., Enatsu, Y.: Global threshold dynamics in a five-dimensional virus model with cell-mediated, humoral immune responses and distributed delays. Appl. Math. Comput. 241, 298–316 (2014)
Wang, J., Tian, X., Wang, X.: Stability analysis for delayed viral infection model with multitarget cells and general incidence rate. Int. J. Biomath. 9(01), 1650007 (2016)
Wang, S., Wu, J., Rong, L.: A note on the global properties of an age-structured viral dynamic model with multiple target cell populations. Math. Biosci. Eng. 14(3), 805–820 (2017)
Wang, X., Chen, Y., Liu, S., Song, X.: A class of delayed virus dynamics models with multiple target cells. Comput. Appl. Math. 32(2), 211–229 (2013)
Wang, X., Lou, Y., Song, X.: Age-structured within-host HIV dynamics with multiple target cells. Stud. Appl. Math. 138(1), 43–76 (2017)
Wasserstein-Robbins, F.: A mathematical model of HIV infection: simulating T4, T8, macrophages, antibody, and virus via specific anti-HIV response in the presence of adaptation and tropism. Bull. Math. Biol. 72(5), 1208–1253 (2010)
Xu, S.: Global stability of the virus dynamics model with Crowley–Martin functional response. Electron. J. Qual. Theory Differ. Equ. 2012(9), 1–10 (2012)
Yang, Y., Ruan, S., **ao, D.: Global stability of an age-structured virus dynamics model with Beddington–DeAngelis infection function. Math. Biosci. Eng. 12, 859–877 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This article was supported by Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán and Conacyt SNI under Grant Number 15284.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avila-Vales, E., Pérez, Á.G.C. Global properties of an age-structured virus model with saturated antibody-immune response, multi-target cells, and general incidence rate. Bol. Soc. Mat. Mex. 27, 26 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40590-021-00315-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40590-021-00315-5