Abstract
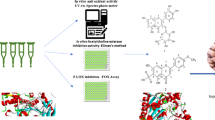
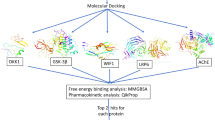
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most occurring neurodegenerative disorder that destroys learning, memory, and thinking skills. Although the pathophysiology of the disease is least understood, the post-mortem brain of AD patients as well as animal models revealed the part of down regulated Wnt signalling in progression of the disease. The deficit in the Wnt signalling leads to the accumulation of amyloid beta peptides, phosphorylation of tau proteins, and synaptic dysfunctions, which are regarded as the major pathological features of AD. As the available drugs for AD are only able to mitigate the symptoms and are also associated with several side effects, the therapeutic potential of the bioactive compounds is being explored for their efficacies in managing the major pathologies. Consequently, a few bioactive compounds fundamentally isolated from Garcinia species are established as promising neuroprotective agents in AD, however; their potential to regulate the Wnt signalling pathway is yet to be discovered. Considering the neuroprotective properties, in the present study efficiency of six small bioactive compounds viz., amentoflavone, isovitexin, orientin, apigenin, kaempferol, and garcinol have been investigated in modulating the receptor proteins (LRP6, DKK1, WIF1 and GSK3β) of the Wnt signalling pathway by molecular docking technique. While all the bioactive compounds could efficiently interact with the target proteins, amentoflavone, orientin, and isovitexin interact with all the target proteins viz., LRP6, DKK1, WIF1, and GSK3β with higher free energy of binding, more number of interactions, and similar mode of binding in comparison to their known or reported modulators. Thus, the present study set forth the investigated small bioactive molecules as potential drug candidates in AD therapeutics.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bhat R, Xue Y, Berg S, Hellberg S, Ormö M, Nilsson Y, Radesäter AC, Jerning E, Markgren PO, Borgegård T, Nylöf M, Giménez-Cassina A, Hernández F, Lucas JJ, Díaz-Nido J, Avila J (2003) Structural insights and Biological effects of Glycogen synthase kinase 3-specific inhibitor AR-A014418. J Biol Chem https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M306268200
Bhowmik D, Nandi R, Prakash A, Kumar D (2021) Evaluation of flavonoids as 2019-nCoV cell entry inhibitor through molecular docking and pharmacological analysis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06515. Heliyon
Buechler J, Salinas PC (2018) Deficient wnt signaling and synaptic vulnerability in Alzheimer’s Disease: emerging roles for the LRP6 receptor. Front Synaptic Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2018.00038
Cai Z, Zhao Y, Zhao B (2012) Roles of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr Alzheimer Res https://doi.org/10.2174/156720512802455386
Cao B, Zeng M, Zhang Q, Zhang B, Cao Y, Wu Y, Feng W, Zheng X (2021) Amentoflavone ameliorates memory deficits and abnormal autophagy in Aβ 25 – 35-Induced mice by mTOR Signaling. Neurochem Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03223-8
Caraci F, Busceti C, Biagioni F, Aronica E, Mastroiacovo F, Cappuccio I, Battaglia G, Bruno V, Caricasole A, Copani A, Nicoletti F (2008) The wnt antagonist, Dickkopf-1, as a target for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9710-0
Caricasole A, Copani A, Caraci F, Aronica E, Rozemuller AJ, Caruso A, Storto M, Gaviraghi G, Terstappen GC, Nicoletti F (2004) Induction of Dickkopf-1, a negative modulator of the wnt pathway, is associated with neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer’s brain. J Neurosci https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1381-04.2004
da Rosa MM, de Amorim LC, Alves JV, de Aguiar O, Oliveira IF, da Silva FG, dos Santos MV (2022) M.T.C., The promising role of natural products in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Disord https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dscb.2022.100049
Dong X, Zhou S, Nao J (2023) Kaempferol as a therapeutic agent in Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from preclinical studies. Ageing Res Rev https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2023.101910
Fortress AM, Schram SL, Tuscher JJ, Frick KM (2013) Canonical wnt signaling is necessary for object recognition memory consolidation. J Neurosci https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0659-13.2013
Giese KP (2009) GSK-3: a key player in neurodegeneration and memory. IUBMB Life https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.187
Gordon MD, Nusse R (2006) Wnt signaling: multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J Biol Chem https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R600015200
Guimarães CC, Oliveira DD, Valdevite M, Saltoratto ALF, Pereira SIV, França SdeC, Pereira AMS, Pereira PS (2015) The glycosylated flavonoids vitexin, isovitexin, and quercetrin isolated from Serjania Erecta Radlk (Sapindaceae) leaves protect PC12 cells against amyloid-β25–35 peptide-induced toxicity. Food Chem Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2015.09.002
Hernández F, Gómez de Barreda E, Fuster-Matanzo A, Lucas JJ, Avila J (2010) GSK3: a possible link between beta amyloid peptide and tau protein. Exp Neurol https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.09.011
Inestrosa NC, Varela-Nallar L, Grabowski CP, Colombres M (2007) Synaptotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease: the wnt signaling pathway as a molecular target. IUBMB Life https://doi.org/10.1080/15216540701242490
Inestrosa NC, Montecinos-Oliva C, Fuenzalida M (2012) Wnt signaling: role in Alzheimer disease and schizophrenia. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-012-9417-5
Jackson GR, Wiedau-Pazos M, Sang TK, Wagle N, Brown CA, Massachi S, Geschwind DH, Neuron (2002) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00706-7
Jia L, Piña-Crespo J, Li Y (2019) Restoring Wnt/β-catenin signaling is a promising therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Brain https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-019-0525-5
Jones ME, Büchler J, Dufor T, Palomer E, Teo S, Martin-Flores N, Boroviak K, Metzakopian E, Gibb A, Salinas PC (2023) A genetic variant of the wnt receptor LRP6 accelerates synapse degeneration during aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Adv https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abo7421
Kirby LA, Schott JT, Noble BL, Mendez DC, Caseley PS, Peterson SC, Routledge TJ, Patel NV (2012) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) inhibitor, SB-216763, promotes pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039329
Komiya Y, Habas R (2008) Wnt signal transduction pathways https://doi.org/10.4161/org.4.2.5851. Organogenesis
Lane CA, Hardy J, Schott JM (2018) Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13439
Lauretti E, Dincer O, Praticò D (2020) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Res https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118664
Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, Désiré L, Mira H, Consiglio A, Lein ES, Jessberger S, Lansford H, Dearie AR, Gage FH (2005) Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04108
Liu CC, Tsai CW, Deak F, Rogers J, Penuliar M, Sung YM, Maher JN, Fu Y, Li X, Xu H, Estus S, Hoe HS, Fryer JD, Kanekiyo T, Bu G (2014) Deficiency in LRP6-Mediated wnt signaling contributes to Synaptic Abnormalities and Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.08.048. Neuron
Liu H, Luo K, Luo D (2018) Guanosine monophosphate reductase 1 is a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21256-6
Malinauskas T, Aricescu AR, Lu W, Siebold C, Jones EY (2011) Modular mechanism of wnt signaling inhibition by wnt inhibitory factor 1. Nat Struct Mol Biol https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2081
Manandhar S, Sankhe R, Priya K, Hari G, Kumar B, Mehta H, Nayak CH, Pai UY, K.S.R (2022) Molecular dynamics and structure-based virtual screening and identification of natural compounds as wnt signaling modulators: possible therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Divers 26 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-022-10395-8
Mazumder MK, Paul R, Phukan BC, Dutta A, Chakrabarty J, Bhattacharya P, Borah A (2018) Garcinol, an effective monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Med Hypotheses 117:54–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEHY.2018.06.009
Mazumder MK, Borah A, Choudhury S (2020) Inhibitory potential of plant secondary metabolites on anti-parkinsonian drug targets: relevance to pathophysiology, and motor and non-motor behavioural abnormalities. Med Hypotheses https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109544
National Institute on Aging (2018) How Is Alzheimer’s Disease Treated? [WWW Document]. Online
Nejabati HR, Roshangar L (2022) Kaempferol as a potential neuroprotector in Alzheimer’s disease. J Food Biochem https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.14375
Olayinka JN, Okosun MO, Amadi MC, Ikpen JO (2022) Apigenin restores memory function in stressed mice. Alzheimer’s Dement https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.069135
Palomer E, Buechler J, Salinas PC (2019) Wnt signaling deregulation in the aging and Alzheimer’s brain. Front Cell Neurosci https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00227
Pérez M, Hernández F, Gómez-Ramos A, Smith M, Perry G, Avila J (2002) Formation of aberrant phosphotau fibrillar polymers in neural cultured cells. Eur J Biochem https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02794.x
Piller C (2022) Second death linked to potential antibody treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Insid
Purro SA, Dickins EM, Salinas PC (2012) The secreted wnt antagonist dickkopf-1 is required for amyloid β-mediated synaptic loss. J Neurosci https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4562-11.2012
Shadrina AAN, Herdiyati Y, Wiani I, Satari MH, Kurnia D (2021) Prediction mechanism of Nevadensin as Antibacterial Agent against S. Sanguinis: in vitro and in silico studies. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen https://doi.org/10.2174/1386207324666210707104440
Siddique YH, Rahul, Ara G, Afzal M, Varshney H, Gaur K, Subhan I, Mantasha I, Shahid M (2022) Beneficial effects of apigenin on the transgenic Drosophila model of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem Biol Interact https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110120
Sims-Robinson C, Kim B, Rosko A, Feldman EL (2010) How does diabetes accelerate Alzheimer disease pathology? Nat Rev Neurol https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2010.130
Sun X, Sato S, Murayama O, Murayama M, Park JM, Yamaguchi H, Takashima A (2002) Lithium inhibits amyloid secretion in COS7 cells transfected with amyloid precursor protein C100. Neurosci Lett https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(01)02583-6
Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N, DeTeresa R, Hill R, Hansen LA, Katzman R (1991) Physical basis of cognitive alterations in alzheimer’s disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410300410
Thysiadis S, Katsamakas S, Mpousis S, Avramidis N, Efthimiopoulos S, Sarli V (2018) Design and synthesis of gallocyanine inhibitors of DKK1/LRP6 interactions for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg Chem https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.06.018
Zhang M, Zhou S, Obaid NH, Altimari US, Adel Mohammed M, Kareem Obaid Aldulaim A, Salaam Abood E, Kotb H, Enayati A, Khori V, Mirzaei H, Salehi A, Soltani A, Sarjadi S, Rahman ML, M (2022) Chromenone-based GSK-3β inhibitors as potential therapeutic targets for cardiovascular diseases: in silico study, molecular dynamics, and ADMET profiles. Arab J Chem https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104288
Zhao L, Wang JL, Liu R, Li XX, Li JF, Zhang L (2013) Neuroprotective, anti-amyloidogenic and neurotrophic effects of apigenin in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Molecules https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089949
Zhao N, Sun C, Zheng M, Liu S, Shi R (2019) Amentoflavone suppresses amyloid β1–42 neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease through the inhibition of pyroptosis. Life Sci https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117043
Zhong Y, Zheng Qyu, Sun Cyan, Zhang Z, Han K, Jia N (2019) Orientin improves cognition by enhancing Autophagosome Clearance in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. J Mol Neurosci https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01353-5
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Assam University, Silchar for e-journal access through DBT e-Library Consortium (DeLCON).
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ankumoni Dutta (AD) contributed to the conceptualization, hypothesis formation, evaluation, and writing the original draft. Pallab Bhattacharya (PB) and Pavitra Chutia (PC) contributed to writing-editing and reviewing the manuscript. Anupom Borah (AB) contributed to the conceptualization, hypothesis formation, and evaluation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, A., Bhattacharya, P., Chutia, P. et al. Targeting of wnt signalling pathway by small bioactive molecules for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. In Silico Pharmacol. 12, 50 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-024-00226-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-024-00226-z