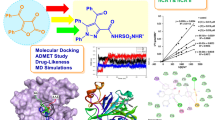
Abstract
The signalling pathways in human cells mostly rely on protein–protein interactions (PPI) for their function. Such a PPI site in 3 Phosphoinositide dependent Kinase-1 (PDK1) is targeted to design the small molecule modulators. Based on the hotspot residues in its PPI site, a pharmacophore with seven different features was developed and screened against 2.9 million lead like compounds in Zinc database. A phthalazine derivative was identified as a potent allosteric inhibitor through virtual screening, molecular docking and 100 ns dynamics simulations. The modified hit possessed hydrogen bonds with Lys115, Arg131, Thr148, Glu150 as well as pi–pi stacking interactions with Phe157 which are the key residues in the PIF pocket of PDK1. Comparison between the free energy profiles by metadynamics simulation with the presence and absence of the modified ligand (MH) in the binding pocket indicates that the binding of MH enhances the hinge motion making PDK1 to adopt open conformation also and stabilizes the fluctuation of the end-to-end distance in αB helix of PDK1. The modified hit compound was synthesized, characterized and found to be cytotoxic to cancerous cells that are rich in PDK1 expression. These results propose that MH can serve as a new scaffold template for the design of novel drugs targeting PDK1 as well as promising allosteric regulator of PDK1 targeting its protein–protein interface.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anant A, Ali A, Ali A, Gupta GD, Asati V (2021) A Computational approach to discover potential quinazoline derivatives against CDK4/6 kinase. J Mol Struct 1245:131079
Arencibia JM, Fröhner W, Krupa M, Pastor-Flores D, Merker P, Oellerich T et al (2017) An allosteric inhibitor scaffold targeting the PIF-pocket of atypical protein kinase C isoforms. ACS Chem Biol 12(2):564–573
Asati V, Agarwal S, Mishra M, Das R, Kashaw SK (2020) Structural prediction of novel pyrazolo-pyrimidine derivatives against PIM-1 kinase: In-silico drug design studies. J Mol Struct 1217:128375
Bai LY, Chiu CF, Kapuriya NP, Shieh TM, Tsai YC, Wu CY et al (2015) BX795, a TBK1 inhibitor, exhibits antitumor activity in human oral squamous cell carcinoma through apoptosis induction and mitotic phase arrest. Eur J Pharmacol [internet] 769:287–296
Beekman AM, Cominetti MMD, Walpole SJ, Prabhu S, O’Connell MA, Angulo J et al (2019) Identification of selective protein-protein interaction inhibitors using efficient: in silico peptide-directed ligand design. Chem Sci 10(16):4502–4508
Bhattacharya S, Asati V, Mishra M, Das R, Kashaw V, Kashaw SK (2021) Integrated computational approach on sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors for the development of novel antidiabetic agents. J Mol Struct 1227:129511
Bhattacharya S, Asati V, Ali A, Ali A, Gupta GD (2022) In-silico studies for the development of novel RET inhibitors for cancer treatment. J Mol Struct 1251:132040
Biondi RM, Komander D, Thomas CC, Lizcano JM, Deak M, Alessi DR et al (2002) High resolution crystal structure of the human PDK1 catalytic domain defines the regulatory phosphopeptide docking site. EMBO J 21(16):4219–4228
Busschots K, Lopez-Garcia LA, Lammi C, Stroba A, Zeuzem S, Piiper A et al (2012) Substrate-selective inhibition of protein kinase PDK1 by small compounds that bind to the PIF-pocket allosteric docking site. Chem Biol 19(9):1152–1163
Cukuroglu E, Engin HB, Gursoy A, Keskin O (2014) Hot spots in protein-protein interfaces: towards drug discovery. Prog Biophys Mol Biol Internet. 116(2–3):165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.06.003
Emmanouilidi A, Falasca M (2017) Targeting PDK1 for chemosensitization of cancer cells. Cancers (basel). 9:140
Engel M, Hindie V, Lopez-Garcia LA, Stroba A, Schaeffer F, Adrian I et al (2006) Allosteric activation of the protein kinase PDK1 with low molecular weight compounds. EMBO J 25(23):5469–5480
Gagic Z, Ruzic D, Djokovic N, Djikic T, Nikolic K (2020) In silico methods for design of kinase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Front Chem 7(January):1–25
Guo W, Wisniewski JA, Ji H (2014) Hot spot-based design of small-molecule inhibitors for protein-protein interactions. Bioorg Med Chem Lett [internet]. 24(11):2546–2554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.03.095
Komander D, Kular GS, Bain J, Elliott M, Alessi DR, Van ADMF (2003) Structural basis for UCN-01 (7-hydroxystaurosporine) specificity and PDK1 (3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1) inhibition. Biochem J 375:255–262
Leroux AE, Biondi RM (2020) Renaissance of allostery to disrupt protein kinase interactions. Trends Biochem Sci Internet 45(1):27–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2019.09.007
Marondedze EF, Govender KK, Govender PP (2020) Ligand-based pharmacophore modelling and virtual screening for the identification of amyloid-beta diagnostic molecules. J Mol Graph Model [internet]. 101:107711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2020.107711
Medina JR, Blackledge CW, Heerding DA, Campobasso N, Ward P, Briand J et al (2010) Aminoindazole PDK1 inhibitors: a case study in fragment-based drug discovery. ACS Med Chem Lett 1(8):439–442
Meharena HS, Fan X, Ahuja LG, Keshwani MM, McClendon CL, Chen AM et al (2016) Decoding the interactions regulating the active state mechanics of eukaryotic protein kinases. PLoS Biol 14(11):e2000217
Najafov A, Shpiro N, Alessi DR (2012) Akt is efficiently activated by PIF-pocket- and PtdIns(3,4,5) P3-dependent mechanisms leading to resistance to PDK1 inhibitors. Biochem J [internet]. 448(2):285–295. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20121287
Qin J, Cao M, Hu X, Tan W, Ma B, Cao Y et al (2023) Dual inhibitors of ASK1 and PDK1 kinases: design, synthesis, molecular docking and mechanism studies of N-benzyl pyridine-2-one containing derivatives as anti-fibrotic agents. Eur J Med Chem 247:115057
Ra**i A, Nookaraju M, Reddy IAK, Venkatathri N (2017) Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity studies of a novel titanium dodecylamino phosphate. J Saudi Chem Soc [internet]. 21:S77-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2013.10.005
Rathore A, Asati V, Mishra M, Das R, Kashaw V, Kashaw SK (2022) Computational approaches for the design of novel dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptor dual antagonist towards schizophrenia. In Silico Pharmacol [internet]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-022-00121-5
Rettenmaier TJ, Sadowsky JD, Thomsen ND, Chen SC, Doak AK, Arkin MR et al (2014) A small-molecule mimic of a peptide docking motif inhibits the protein kinase PDK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci Internet. 111(52):18590–18595. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1415365112
Saha M, Gupta S, Dhiman S, Asati V, Ali A, Ali A (2023) Field and atom-based 3D-QSAR models of chromone (1-benzopyran-4-one) derivatives as MAO inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn [internet]. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2023.2166122
Sarvagalla S, Cheung CHA, Tsai JY, Hsieh HP, Coumar MS (2016) Disruption of protein-protein interactions: hot spot detection, structure-based virtual screening and: in vitro testing for the anti-cancer drug target-survivin. RSC Adv [internet]. 6(38):31947–31959. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA22927H
Schrodinger Release 2021–3: Bioluminate, Schrodinger, LLC Newyork, NY,2021. New York: NY: LLC; 2015
Schulze JO, Saladino G, Busschots K, Neimanis S, Süß E, Odadzic D et al (2016) Bidirectional allosteric communication between the ATP-binding site and the regulatory PIF pocket in PDK1 protein kinase. Cell Chem Biol 23(10):1193–1205
Singh KD, Kirubakaran P, Nagarajan S, Sakkiah S, Muthusamy K, Velmurgan D et al (2012) Homology modeling, molecular dynamics, e-pharmacophore map** and docking study of Chikungunya virus nsP2 protease. J Mol Model 1:39–51
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A, McMahon J, Vistica D et al (1990) New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for. J Natl Cancer Inst 82(13):1107–1112
Sterling T, Irwin JJ (2015) ZINC 15—ligand discovery for everyone. J Chem Inf Model 55(11):2324–2337
Wang X, Ni D, Liu Y, Lu S (2021) Rational design of peptide-based inhibitors disrupting protein-protein interactions. Front Chem [internet] 9:682675
Zhang J, Yang C, Zhou F, Chen X (2018) PDK1 inhibitor GSK2334470 synergizes with proteasome inhibitor MG-132 in multiple myeloma cells by inhibiting full AKT activity and increasing nuclear accumulation of the PTEN protein. Oncol Rep 39(6):2951–2959
Acknowledgements
The Senior Research Associateship from CSIR, Govt. of India by Scientists’ pool scheme is greatly acknowledged by KNV. The cell cytotoxicity assays from ACTREC, Mumbai, India is also acknowledged by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VKN: idea, analysis, manuscript writing SB: synthesis of the compound and characterization, EKP: idea, results and Manuscript evaluation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that “There are no conflicts to declare”.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kailasam Natesan, V., Balaraman, S. & KuppannaGounder Pitchaimuthu, E. Insilico design of an allosteric modulator targeting the protein–protein interaction site of 3 Phosphoinositide dependent Kinase-1: design, synthesis and biological activity. In Silico Pharmacol. 11, 26 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-023-00160-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-023-00160-6