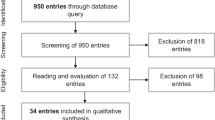
Abstract
Resilience is challenging for small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), as their structure hinders them from overcoming external disturbances. This article used control to model how these perspectives can lead SMEs to equilibrium. We adopted a systemic approach, which addresses organizational complexity via linear modeling. First, using social network analysis (SNA), we revised the understanding of organizational resilience in the SME literature, identified groups with similar components, and used this information to feed our model. Second, we developed a conceptual model via a causal loop diagram, and third, we simulated scenarios using system dynamics. Our results indicate that organizational resilience is associated with feedforward, buffering, and feedback controls as critical factors demanding continuous coordination between core operations and management mechanisms. A limitation regarding system dynamics is that it models a system’s behavior rather than predicting it statistically. Even though the focus of this work is on the organizational context and Mexican SMEs, the versatility of the systemic approach may allow for the application of these ideas in other sectors. Our results may help managers and academics rethink resilience by restructuring relationships in operational and strategic units, increasing their autonomy, strengthening strategic planning as well as feedback means. The revised studies used statistical modeling to evaluate factors that foster SMEs’ organizational resilience. The present article contributes to this area by framing the problem in terms of system dynamics methodology and evaluating the adopted scenario.

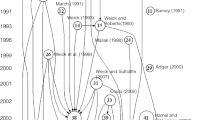
Source: Seld-elaboration using the igraph package in Rstudio


Source: Self-elaboration base o stakeholder approaches and literature review

Source: self-elaboration using Vensim PLE Plus for Machintosh Version 8.2.0

Source: self-elaboration using deSolve package in RStudio version 1.2.5

Source: self-elaboration using deSolve package in RStudio version 1.2.5

Source: self-elaboration using deSolve package in RStudio version 1.2.5

Source: self-elaboration using deSolve package in RStudio version 1.2.5

Source: self-elaboration using deSolve package in RStudio version 1.2.5

Source: self-elaboration using deSolve package in RStudio version 1.2.5

Source: self-elaboration using deSolve package in Rstudio version 1.2.2
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann, F., Andersen, D. F., Eden, C., & Richardson, G. P. (2010). Using a group decision support system to add value to group model building. System Dynamics Review, 26(4), 335–346. https://doi.org/10.1002/sdr.444
Alefari, M., Almanei, M., & Salonitis, K. (2020). A system dynamics model of employees’ performance. Sustainability, 12(16), 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166511
Amin, S. M., & Horowitz, B. M. (2008). Toward agile and resilient large-scale systems: adaptive robust national/international infrastructures. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 9(1), 27–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03396536
Angeles, A., Perez-Encinas, A., & Villanueva, C. E. (2022). Characterizing organizational lifecycle through strategic and structural flexibility: Insights from MSMEs in Mexico. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 23(2), 271–290.
Beech, N., Devins, D., Gold, J., & Beech, S. (2020). In the family way: An exploration of family business resilience. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 28(1), 160–182. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-02-2019-1674
Beer, S. (1984). The viable system model: Its provenance, development, methodology and pathology. The Journal of the Operational Research Society, 35(1), 7–25. https://doi.org/10.2307/2581927
Beer, S. (2004). What is cybernetics? Kybernetes, 33(3/4), 853–863.
Belay, A. M., Torp, O., Thodesen, C., & Odeck, J. (2016). A framework for organizing a resilient cost benefit analysis for construction projects. Procedia Engineering, 145, 1169–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.04.151
Brauch, M., & Größler, A. (2022). Holistic versus analytic thinking orientation and its relationship to the bullwhip effect. System Dynamics Review, 38(1), 121–134. https://doi.org/10.1002/sdr.1702
Carayannis, E. G., Grigoroudis, E., & Wurth, B. (2022). OR for entrepreneurial ecosystems: A problem-oriented review and agenda. European Journal of Operational Research, 300(3), 791–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2021.10.030
Checkland, P. (2001). Systems thinking, systems practice (2nd ed.). Wiley.
Coyle, G. (2000). Qualitative and quantitative modelling in system dynamics: Some research questions. System Dynamics Review, 16(3), 225–244.
Crovini, C. (2019). Risk management in small and medium enterprises. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429276316
Cserep, K. & Imbsen, C. (2022). Enhancing Resilience to Drive sustainability in destinations.
Duchek, S. (2020). Organizational resilience: A capability-based conceptualization. Business Research, 13(1), 215–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40685-019-0085-7
Duggan, J. (2016). System dynamics modeling with R. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-34043-2
Duggan, J. (2019). Using R libraries to facilitate sensitivity analysis and to calibrate system dynamics models. System Dynamics Review, 35(3), 255–282. https://doi.org/10.1002/sdr.1638
Elf, M., Putilova, M., von Koch, L., & Öhrn, K. (2007). Using system dynamics for collaborative design: A case study. BMC Health Services Research, 7(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-7-123
Elias, A. (2021). Kerala’s innovations and flexibility for covid-19 recovery: storytelling using systems thinking. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 22(1), 33–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-021-00268-8
Fandiño, A. M., Formiga, N. S., & de Menezes, R. M. (2019). Organizational social capital, resilience and innovation validation of a theoretical model for specialized workers. Journal of Strategy and Management, 12(1), 137–152. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSMA-05-2018-0041
Forrester, J. (1990). Principles of systems. Productivity Press.
François, C. (2004). International encyclopedia of systems and cybernetics. Part 1 (2a ed.). K. G. Saur München.
Freeman, R., McMahon, C., & Godfrey, P. (2017). An exploration of the potential for re-distributed manufacturing to contribute to a sustainable, resilient city. International Journal of Sustainable Engineering, 10(4–5), 260–271. https://doi.org/10.1080/19397038.2017.1318969
Gershenson, C. (2020). Guiding the self-organization of cyber-physical systems. Frontiers in Robotics and A, I, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2020.00041
Gomez, C., González, A., Baroud, H., & Bedoya-Motta, C. (2019). Integrating operational and organizational aspects in interdependent infrastructure network recovery. Risk Analysis, 39(9), 1913–1929. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.13340
Hallak, R., Assaker, G., O’Connor, P., & Lee, C. (2018). Firm performance in the upscale restaurant sector: The effects of resilience, creative self-efficacy, innovation and industry experience. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 40, 229–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.10.014
Hanifah, H., Abdul Halim, H., Ahmad, N. H., & Vafaei-Zadeh, A. (2019). Emanating the key factors of innovation performance: Leveraging on the innovation culture among SMEs in Malaysia. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 13(4), 559–587. https://doi.org/10.1108/JABS-04-2018-0130
Hartmann, S., Weiss, M., Newman, A., & Hoegl, M. (2020). Resilience in the workplace: A multilevel review and synthesis. Applied Psychology, 69(3), 913–959. https://doi.org/10.1111/apps.12191
Helfgott, A. (2018). Operationalising systemic resilience. European Journal of Operational Research, 268(3), 852–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2017.11.056
Hillmann, J. (2021). Disciplines of organizational resilience: Contributions, critiques, and future research avenues. Review of Managerial Science, 15(4), 879–936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-020-00384-2
Hillmann, J., & Guenther, E. (2021). Organizational resilience: A valuable construct for management research? International Journal of Management Reviews, 23(1), 7–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12239
ILO. (2021). World employment and social outlook. Trends 2022, Switzerland, International Labour Organization.
Jaaron, A., & Backhouse, C. J. (2014). Building antifragility in service organisations: Going beyond resilience. International Journal of Services and Operations Management, 19(4), 491. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSOM.2014.065671
Jones, M. (2018). Strategic environmental assessment for wetlands: Resilience thinking. In The wetland book (pp. 2105–2115). Springer. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9659-3_283
Katic, M., & Agarwal, R. (2018). The flexibility paradox: achieving ambidexterity in high-variety, low-volume manufacturing. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 19(S1), 69–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-018-0184-x
Kleijnen, J. (1995). Sensitivity analysis and optimization of system dynamics models: Regression analysis and statistical design of experiments. System Dynamics Review, 1(4), 275–288.
Kolaczyk, E. D., & Csárdi, G. (2020). Statistical analysis of network data with R. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44129-6
Lafuente, E., Szerb, L., & Rideg, A. (2020). A system dynamics approach for assessing SMEs’ competitiveness. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 27(4), 555–578. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-06-2019-0204
Lassl, W. (2019). The viability of organizations (Vol. 1). Cham, Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12014-6
Leerapan, B., Teekasap, P., Urwannachotima, N., Jaichuen, W., Chiangchaisakulthai, K., Udomaksorn, K., Meeyai, A., Noree, T., & Sawaengdee, K. (2021). System dynamics modelling of health workforce planning to address future challenges of Thailand’s Universal Health Coverage. Human Resources for Health, 19(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12960-021-00572-5
Ma, Z., **ao, L., & Yin, J. (2018). Toward a dynamic model of organizational resilience. Nankai Business Review International, 9(3), 246–263. https://doi.org/10.1108/NBRI-07-2017-0041
Mabula, J., Dong**, H., & Chivundu-Ngulube, C. (2020). SME manager’s perceived cooperative support, commitment and trust on learning and entrepreneurship orientation for firm innovation. Human Systems Management, 39(2), 233–250. https://doi.org/10.3233/HSM-190735
Machado, C., Morandi, M., & Sellitto, M. (2019). System dynamics and learning scenarios for process improvement and regional resilience: a study in the footwear industry of southern Brazil. Systemic Practice and Action Research, 32(6), 663–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11213-019-9480-4
Malesios, C., De, D., Moursellas, A., Dey, P. K., & Evangelinos, K. (2020). Sustainability performance analysis of small and medium sized enterprises: Criteria, methods and framework. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2020.100993
Mamouni Limnios, E., Mazzarol, T., Ghadouani, A., & Schilizzi, S. (2014). The resilience architecture framework: Four organizational archetypes. European Management Journal, 32(1), 104–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2012.11.007
Mokline, B., & ben Abdallah, M. (2021). Individual resilience in the organization in the face of crisis: Study of the concept in the context of COVID-19. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 22(3), 219–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-021-00273-x
Mokline, B., & Ben Abdallah, M. A. (2022). The Mechanisms of Collective Resilience in a Crisis Context: The Case of The ‘COVID-19’Crisis. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management,, 23(1), 151–163.
Ng, T., & Sy, C. (2014). A resilience optimization approach for workforce-inventory control dynamics under uncertainty. Journal of Scheduling, 17(5), 427–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10951-013-0330-4
Núñez-Ríos, J. E., Aguilar-Gallegos, N., Sánchez-García, J. Y., & Cardoso-Castro, P. P. (2020a). Systemic design for food self-sufficiency in urban areas. Sustainability, 12(18), 7558–7583. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187558
Núñez-Ríos, J. E., Sánchez-García, J. Y., López-Hernández, C., Soto-Pérez, M., & Cardoso-Castro, P. Pablo. (2022). A systems science approach to organizational integrity. Case: Services small and medium enterprises. Cybernetics and Systems, 53(2), 238–255. https://doi.org/10.1080/01969722.2021.1983698
Núñez-Ríos, J. E., Sánchez-García, J. Y., Soto-Pérez, M., Olivares-Benitez, E., & Rojas, O. G. (2022b). Components to foster organizational resilience in tourism SMEs. Business Process Management Journal, 28(1), 208–235. https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-12-2020-0580
Núñez-Ríos, J. E., Sánchez-García, J. Y., & Tejeida-Padilla, R. (2020b). Human capital management in tourism SMEs from a cyber-systemic approach. Systemic Practice and Action Research, 33(5), 527–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11213-019-09499-4
OECD. (2019). OECD SME and entrepreneurship outlook 2019. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Oluwatayo, A. A., & Adetoro, O. (2020). Influence of employee attributes, work context and human resource management practices on employee job engagement. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 21(4), 295–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-020-00249-3
Pudjiarti, E., & Priagung Hutomo, P. (2020). The critical role of effective organizational learning to improve firm’s innovation and performance in a market turbulence condition. International Journal of Innovation Science, 12(3), 237–254. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJIS-08-2019-0079
Quintana-Romero, L., Mendoza-González, M. & Álvarez-García, J. (2021). Covid-19 and tourism in Mexico: Economic impacts and prospects. In Pandemics and travel (pp. 173–191). Emerald Publishing Limited. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-80071-070-220211011
Ricciardi, F., de Bernardi, P., & Cantino, V. (2020). System dynamics modeling as a circular process: The smart commons approach to impact management. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 151(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.119799
Rouwette, E., Bleijenbergh, I., & Vennix, J. (2016). Group model-building to support public policy: Addressing a conflicted situation in a problem neighbourhood. Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 33(1), 64–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/sres.2301
Rydzak, F., & Monus, P. (2018). Sha** organizational network structure to enable sustainable transformation. System Dynamics Review, 34(1–2), 255–283. https://doi.org/10.1002/sdr.1602
Salah, M., Saikouk, T. & Berrado, A. (2019). The impact of payment delays on the financial resilience of a multi-echelon supply chain: A system dynamics simulation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Pilsen, (pp 410–418).
Sánchez-García, J., Núñez-Ríos, J., & López-Hernández, C. (2020). Systemic complementarity, an integrative model of cooperation among small and medium-sized tourism enterprises in Mexico. International Journal of Business Innovation and Research, 23(3), 354. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBIR.2020.110968
Schwaninger, M. (2018). Systemic design for sustainability. Sustainability Science, 13(5), 1225–1234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-018-0538-5
Scott, R., Cavana, R., & Cameron, D. (2016). Recent evidence on the effectiveness of group model building. European Journal of Operational Research, 249(3), 908–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2015.06.078
Scuotto, V., del Giudice, M., & Carayannis, E. (2017). The effect of social networking sites and absorptive capacity on SMES’ innovation performance. The Journal of Technology Transfer, 42(2), 409–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-016-9517-0
Settembre-Blundo, D., González-Sánchez, R., Medina-Salgado, S., & García-Muiña, F. (2021). Flexibility and resilience in corporate decision making: A new sustainability-based risk management system in uncertain times. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 22(2), 107–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-021-00277-7
Sterman, J. (2000). Business dynamics: Systems thinking and modeling for a complex world. McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
UNWTO. (2022). UNWTO world tourism barometer and statistical annex, March 2022. UNWTO World Tourism Barometer, 20(2), 1–36. https://doi.org/10.18111/wtobarometereng.2022.20.1.2
Vennix, J. (1999). Group model-building: Tackling messy problems. System Dynamics Review, 15, 379–401.
Vik, M., Finnestrand, H., & Flood, R. (2022). Systemic problem structuring in a complex hospital environment using viable system diagnosis – kee** the blood flowing. Systemic Practice and Action Research, 35(2), 203–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11213-021-09569-6
Vojtko, V., Rolínek, L., & Plevný, M. (2019). System dynamics model of crises in small and medium enterprises. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 32(1), 168–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2018.1552176
Warfield, J. (2003). A proposal for systems science. Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 20(6), 507–520.
Watts, G. & Paciga, J. (2011). Conscious Adaptation: Building Resilient Organizations. AAAI Fall Symposium: Complex Adaptive Systems, 158–167.
Williams, A., Whiteman, G., & Kennedy, S. (2021). Cross-scale systemic resilience: implications for organization studies. Business & Society, 60(1), 95–124. https://doi.org/10.1177/0007650319825870
Zhang, T. (2021). Capturing the dynamics of interorganizational governance implementation: A process and cybernetic based conceptualization. Business Process Management Journal, 27(3), 722–741. https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-11-2020-0482
Funding
This research was supported by the Universidad Panamericana [Grant Number UP-CI- 2020-GDL-06-EMP].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JYS-G did conceptualization, supervision and formal analysis; JYS-G and JEN-R done methodology and writing (original draft preparation; CL-H and ARM collected the data; JEN-R validated the study; CL-H and ARM done writing (editing). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest and all agreed with the amendments to this article. The authors also declare that this is an original work and is not under review in another journal.
Ethical Approval
We are grateful to all participants that took part in this study. Their participation in this work was anonymous and no names or preferences were revealed. We only used organizational position in the development of our ideas.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-García, J.Y., Núñez-Ríos, J.E., López-Hernández, C. et al. Modeling Organizational Resilience in SMEs: A System Dynamics Approach. Glob J Flex Syst Manag 24, 29–50 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-022-00322-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-022-00322-z
Keywords
- Adaptability
- Learning organizations
- Organizational resilience
- Small- and medium-sized enterprises
- Tourism