Abstract
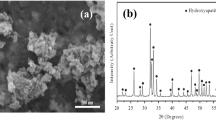
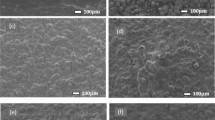
Polyimide is a promising shell polymer for platinum electrodes because of good biocompatibility, excellent corrosion resistance, mechanical, thermal and chemical stabilities. Herein, hydroxyapatite (HAP) nanoparticles were coated on polyimide encapsulated platinum electrodes to overcome the adverse effects of electrical stimulation. SEM, TEM, XRD and EDS analyses indicated that the coating was homogeneous and dense consisting of nano-hydroxyapatite. The HAP/polyimide coating presented good stability under the conditions of moist heat, high temperature or high shear stress (10 dyn/cm2). Differential thermal analysis revealed that the nano-hydroxyapatite coating could significantly reduce the thermal diffusion from electrical stimulation its thermal elimination rate was about 96 times and 310 times smaller than that of polyimide encapsulated platinum electrode and bare platinum electrode, respectively. Atomic absorption spectroscopy measurement showed that the nano-hydroxyapatite coatings could prohibit the diffusion of platinum ions caused by electrical stimulation. CCK-8 test, neutral red uptake measurement and Tunel analysis revealed that the nano-hydroxyapatite coating could significantly attenuate the cytotoxicity of heavy metal ion from long-term stimulation. The in vivo biocompatibility evaluation by H&E measurement in a rabbit subcutaneous implantation model clearly showed that the nano-hydroxyapatite coating had good tissue response in 6 months. All these data supported that the nano-hydroxyapatite coating improved the biocompatibility of platinum electrodes by prohibiting thermal injury and heavy metal ions diffusion.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Su, Y., Routhu, S., Moon, K.S., Lee, S.Q., Youm, W., Ozturk, Y.: A wireless 32-channel implantable bidirectional brain machine interface. Sensors 16(10), 1582 (2016)
Baek, C., Kim, J., Lee, Y., Seo, J.-M.: Fabrication and evaluation of cyclic olefin copolymer-based implantable neural electrode. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 67(9), 2542–2551 (2020)
Feiner, R., Dvir, T.: Tissue-electronics interfaces: from implantable devices to engineered tissues. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3, 17076 (2018)
Agren, R., Bartek, J., Jr., Johansson, A., Blomstedt, P., Fytagoridis, A.: Pulse width and implantable pulse generator longevity in pallidal deep brain stimulation for dystonia: a population-based comparative effectiveness study. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 98(5), 331–336 (2020)
Suaning, G.J., Lovell, N.H., Kwok, C.Y.: Fabrication of platinum spherical electrodes in an intra-ocular prosthesis using high-energy electrical discharge. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 108, 155–161 (2003)
Lee, Y.J., Kim, H.J., Do, S.H., Kang, J.Y., Lee, S.H.: Characterization of nerve-cuff electrode interface for biocompatible and chronic stimulating application. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 237, 924–934 (2016)
McDonald, J.W.: Repairing the damaged spinal cord. Sci. Am. 281(3), 64–73 (1999)
Schlosshauer, B., Brinker, T., Wuller, H.W., Meyer, J.U.: Towards micro electrode implants: in vitro guidance of rat spinal cord neurites through polyimide sieves by Schwann cells. Brain Res. 903(1–2), 237–241 (2001)
Humayun, M.S., Jr., Juan, E.D., Weiland, J.D., Dagnelie, G., Katona, S., Greenberg, R., Suzuki, S.: Pattern electrical stimulation of the human retina. Vis. Res. 39(15), 2569–2576 (1999)
He, F., Lycke, R., Ganji, M., **e, C., Luan, L.: Ultraflexible neural electrodes for long-lasting intracortical recording. iScience 23(8), 101387 (2020)
Jang, J., Kim, J.Y., Kim, Y.C., Kim, S., Chou, N., Lee, S., Choung, Y.H., Kim, S., Brugger, J., Choi, H., Jang, H.J.: A 3D microscaffold cochlear electrode for steroid elution. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 8(20), e1900379 (2019)
Keiler, J., Schulze, M., Sombetzki, M., Heller, T., Tischer, T., Grabow, N., Wree, A., Bansch, D.: Neointimal fibrotic lead encapsulation-clinical challenges and demands for implantable cardiac electronic devices. J. Cardiol. 70, 7–17 (2017)
Hibbert, D.B., Weitzner, K., Tabor, B., Carter, P.: Mass changes and dissolution of platinum during electrical stimulation in artificial perilymph solution. Biomaterials 21(21), 2177–2182 (2000)
de Haro, C., Mas, R., Abadal, G., Munoz, J., Perez-Murano, F., Dominguez, C.: Electrochemical platinum coatings for improving performance of implantable microelectrode arrays. Biomaterials 23(23), 4515–4521 (2002)
Widge, A.S., Jeffries-El, M., Cui, X.Y., Lagenaur, C.F., Matsuoka, Y.: Self-assembled monolayers of polythiophene conductive polymers improve biocompatibility and electrical impedance of neural electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 22(8), 1723–1732 (2007)
Mailley, S., Hyland, M., Mailley, P., McLaughlin, J.A., McAdams, E.T.: Thin film platinum cuff electrodes for neurostimulation: in vitro approach of safe neurostimulation parameters. Bioelectrochemistry 63(1–2), 359–364 (2004)
Lin, C.Y., Lou, W.S., Chen, J.C., Weng, K.Y., Shih, M.C., Hung, Y.W., Chen, Z.Y., Wang, M.C.: Biocompatibility and bio-insulation of implantable electrode prosthesis ameliorated by A-174 silane primed parylene-C deposited embedment. Micromachines 11(12), 1064 (2020)
Lacour, S.P., Atta, R., FitzGerald, J.J., Blamire, M., Tarte, E., Fawcett, J.: Polyimide micro-channel arrays for peripheral nerve regenerative implants. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 147(2), 456–463 (2008)
Fukuzawa, M., Ikedou, H., Iwamoto, M.: Electrical breakdown of ultra-thin polyimide langmuir-blodgett films under a needle-plane electrode system. Thin Solid Films 438–439, 243–247 (2003)
Andreeva, D.V., Gorin, D.A., Mohwald, H., Sukhorukov, G.B.: Novel type of self-assembled polyamide and polyimide nanoengineered shells-fabrication of microcontainers with shielding properties. Langmuir 23(17), 9031–9036 (2007)
Richardson, R.R., Jr., Miller, J.A., Reichert, W.M.: Polyimides as biomaterials: preliminary biocompatibility testing. Biomaterials 14(8), 627–635 (1993)
Lago, N., Ceballos, D., Rodriguez, F.J., Stieglitz, T., Navarro, X.: Long term assessment of axonal regeneration through polyimide regenerative electrodes to interface the pheripheral nerve. Biomaterials 26(14), 2021–2031 (2005)
Seo, J.M., Kim, S.J., Chung, H., Kim, E.T., Yu, H.G., Yu, Y.S.: Biocompatibility of polyimide microelectrode array for retinal stimulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 24, 185–189 (2004)
Zhang, X., Tang, Y., Zhang, F., Lee, C.: A novel aluminum-graphite dual-ion battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 6(11), 1502588 (2016)
Ji, B., Zhang, F., Song, X., Tang, Y.: A novel potassium-ion-based dual-ion battery. Adv. Mater. 29(19), 1700519 (2017)
Mu, S., Liu, Q., Kidkhunthod, P., Zhou, X., Wang, W., Tang, Y.: Molecular grafting towards high-fraction active nanodots implanted in N-doped carbon for sodium dual-ion batteries. Natl. Sci. Rev. 8(7), nwaa178 (2021)
Zhu, H., An, Y., Shi, M., Li, Z., Chen, N., Yang, C., **ao, P.: Porous N-doped carbon/MnO2 nanoneedles for high performance ionic liquid-based supercapacitors. Mater. Lett. 296, 129837 (2021)
Liu, J., Sui, M., Song, S., Huang, L., Belfiore, L.A., Tang, J.: Towards applicable photoacoustic micro-fluidic pumps: tunable excitation wavelength and improved stability by fabrication of Ag-Au alloying nanoparticles. J. Alloy Compd. 884, 161091 (2021)
Liu, W., Zheng, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Yang, J., Chen, M., Wei, L.: Ultrasensitive exhaled breath sensors based on anti-resonant hollow core fiber with in situ grown ZnO-Bi2O3 nanosheets. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 8(6), 2001978 (2021)
Guo, W., Liu, J., Zhang, P., Song, L., Wang, X., Hu, Y.: Multi-functional hydroxyapatite/polyvinyl alcohol composite aerogels with self-cleaning, superior fire resistance and low thermal conductivity. Compos. Sci. Technol. 158, 128–136 (2018)
Brazdis, R.I., Fierascu, I., Avramescu, S.M., Fierascu, R.C.: Recent progress in the application of hydroxyapatite for the adsorption of heavy metals. Materials 14(22), 6898 (2021)
Ibrahim, M., Labaki, M., Giraudon, J.M., Lamonier, J.F.: Hydroxyapatite, a multifunctional material for air water and soil pollution control: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 383, 121139 (2020)
Zhang, Y.G., Zhu, Y.J., Chen, F., Sun, T.W.: Biocompatible, ultralight, strong hydroxyapatite networks based on hydroxyapatite microtubes with excellent permeability and ultralow thermal conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(9), 7918–7928 (2017)
Quilitz, M., Steingrover, K., Veith, M.: Effect of the Ca/P ratio on the dielectric properties of nanoscaled substoichiometric hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 21, 399–405 (2010)
Xu, Y., Zhao, A., Wang, X., Xue, H., Liu, F.: Influence of curing accelerators on the imidization of polyamic acids and properties of polyimide films. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 31(5), 1137–1143 (2016)
Hu, X., Shen, H., Cheng, Y., **ong, X., Wang, S., Fang, J., Wei, S.: One-step modification of nano-hydroxyapatite coating on titanium surface by hydrothermal method. Surf. Coat. Tech. 205, 2000–2006 (2010)
Schander, A., Gancz, J.M., Tintelott, M., Lang, W.: Towards long-term stable polyimide-based flexible electrical insulation for chronically implanted neural electrodes. Micromachines 12(11), 1279 (2021)
Rial, R., Gonzalez-Durruthy, M., Liu, Z., Ruso, J.M.: Advanced materials based on nanosized hydroxyapatite. Molecules 26(11), 3190 (2021)
Slack, G.A.: Platinum as a thermal conductivity standard. J. Appl. Phys. 35(2), 339–344 (1964)
Yang, C., Yang, P., Wang, W., Wang, J., Zhang, M., Lin, J.: Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of Ln (Eu3+, Tb3+) doped hydroxyapatite. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 328(1), 203–210 (2008)
Hashizume, M., Maeda, M., Iijima, K.: Biomimetic calcium phosphate coating on polyimide films by utilizing surface-selective hydrolysis treatments. J. Ceram. Soc. JPN 121(1417), 816–818 (2013)
Hong, G., Lieber, C.M.: Novel electrode technologies for neural recordings. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 20(6), 330–345 (2019)
Gross, K.A., Berndt, C.C., Herman, H.: Amorphous phase formation in plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 39(30), 407–414 (1998)
Lu, Y.P., Song, Y.Z., Zhu, R.F., Li, M.S., Lei, T.Q.: Factors influencing phase compositions and structure of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings during heat treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 206(1–4), 345–354 (2003)
Grill, W.M., Norman, S.E., Bellamkonda, R.V.: Implanted neural interfaces: biochallenges and engineered solutions. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 11, 1–24 (2009)
Wurth, S., Capogrosso, M., Raspopovic, S., Gandar, J., Federici, G., Kinany, N., Cutrone, A., Piersigilli, A., Pavlova, N., Guiet, R., Taverni, G., Rigosa, J., Shkorbatova, P., Navarro, X., Barraud, Q., Courtine, G., Micera, S.: Long-term usability and bio-intergration of polyimide-based intra-neural stimulating electrodes. Biomaterials 122, 114–129 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Basic Research Project of Natural Science in Henan Institute of Science and Technology (103010620002/012) and Med-Engineering Cross Foundation of Shanghai Jiao tong University (YG2019QNB28). Scientific and technological project of Henan Province (222102310005), Training Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China in Henan Institute of Science and Technology (105020221015/034) and Training Program of Basic Research Plan in Henan Institute of Science and Technology (10502022015/056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HJ., Yang, GG., Zhang, JM. et al. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles/polyimide-coated platinum electrodes for improved heat-insulating and heavy metal ion diffusion properties. J Nanostruct Chem 13, 563–575 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-022-00489-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-022-00489-y