Abstract
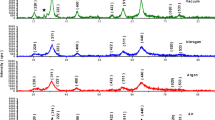
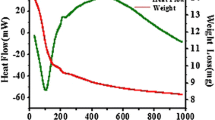
Co–SiO2 nano composite has been synthesized via sol–gel technique using dextrose [C6H12O6] as a reducer and tetraethyl orthosilicate [Si(OCH2CH3)4] as oxide forming agent, respectively. The dried gel has been subsequently calcined at different temperature (850 and 900 °C) for 30 min in an inert atmosphere by N2 purging. The synthesized materials have been characterized by X-ray diffraction, high resolution transmission microscope, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, UV–Vis spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope, field emission microscope, atomic force microscope and physical property measurement system. The crystallite sizes of the face centered cubic cobalt nano composite materials have been found to be in the range of 14–28 nm. The crystallite size of the material found to be increased at higher calcination temperature due to the grain growth. The surface morphology of the obtained material has been found to be agglomerated but spherical in nature. This agglomeration tendency could be attributed to magnetic interaction between particles, large surface area as well as high surface energy. The band gap value of the obtained material has been determined to be 1.92 eV. The saturation magnetization (Ms) and the coercivity (Hc) of the composite material were found to be 29.45 emu g−1and 23.2 Oe, respectively. This technique has thus been found to be a convenient and effective method to prepare pure metallic cobalt nanoparticles with uniform size and homogeneous distribution throughout the matrix.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Somorjai, T. Feng, J.Y. Park, The nanoscience revolution: merging of colloid science, catalysis and nanaelectronics. Top. Catal. 47(1–2), 15–21 (2008)
R. Schloögl, S.B.A. Hamid, Nanocatalysis: mature science revisited or something really new? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43(13), 1628–1637 (2004)
S.H. Wu, D.H. Chen, Synthesis and characterization of nickel nanoparticles in ternary W/O microemulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 259(2), 282–286 (2003)
C.T. Black, C.B. Murray, R.L. Sandstrom, S.H. Sun, Spin-dependent tunneling in self-assembled cobalt-nanocrystal superlattices. Science 290(5494), 1131–1134 (2000)
H.Q. Cao, Z. Xu, H. Sang, D. Sheng, C.Y. Tie, Template synthesis and magnetic behavior of an array of cobalt nanowires encapsulated in polyaniline nanotubues. Adv. Mater. 13(2), 121–123 (2001)
J.P. Wilcoxon, B.L. Abrams, Synthesis, structure and properties of metal nanoclusters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 35, 1162–1194 (2006)
K. Yakushiji, F. Ernult, H. Imamura, K. Yamane, S. Mitani, K. Takanashi, S. Takahashi, S. Maekawa, H. Fujimori, Enhanced spin accumulation and novel magnetotransport in nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 4(1), 57–61 (2005)
Y. Xu, M. Mahmood, Z.R. Li, E. Dervishi, S. Trigwell, V.P. Zharov, N. Ali, V. Saini, A.R. Biris, D. Lupu, D. Boldor, A.S. Biris, Cobalt nanoparticles coated with graphitic shells as localized radio frequency absorbers for cancer therapy. Nanotechnology 19(43), 435102 (2008)
V.F. Puntes, K.M. Kirshnan, A.P. Alivisatos, Colloidal nanocrystal shape and size control: the case of cobalt, colloidal nanocrystal shape and size control: the case of cobalt. Science 291(5511), 2115–2117 (2001)
M. Todorovic, S. Schultz, J. Wong, A. Scherer, Writing and reading of single magnetic domain per bit perpendicular patterned media. Appl. Phys. Lett. 74(17), 2516–2518 (1999)
G. Reiss, A. Hutten, Magnetic nanoparticles: applications beyond data storage. Nat. Mater. 4(10), 725–726 (2005)
X.H. Liu, W. Liu, W.J. Hu, S. Guo, X.K. Lv, W.B. Cui, X.G. Zhao, Z.D. Zhang, Giant reversible magnetocaloric effect in cobalt hydroxide nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93(20), 202502–202505 (2008)
J. Kim, Y. Piao, T. Hyeon, Multifunctional nanostructured materials for multimodal imaging, and simultaneous imaging and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 372–390 (2009)
D.L. Zhao, H.L. Zhang, X.W. Zeng, Q.S. **a, J.T. Tang, Inductive heat property of Fe3O4/polymer composite nanoparticles in an ac magnetic field for localized hyperthermia. Biomed. Mater. 1(4), 198–201 (2006)
R. Qiu, D. Zhang, P. Wang, X.L. Zhang, Y.S. Kang, Tunable electrochemical preparation of cobalt micro/nanostructures and their morphology-dependent wettability property. Electrochim. Acta 58, 699–706 (2011)
S. Hatamie, S.D. Dhole, J. Ding, S.N. Kale, Encapsulation of cobalt nanoparticles in cross-linked-polymer cages. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321(14), 2135–2138 (2009)
Q. **e, Y.T. Qian, S.Y. Zhang, S.Q. Fu, W.C. Yu, A hydrothermal reduction route to single crystalline hexagonal cobalt nanowires. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006(12), 2454–2459 (2006)
Y. Soumare, C. Garcia, T. Maurer, G. Chaboussant, F. Ott, F. Fievet, J.Y. Piquemal, G. Viau, Kinetically controlled synthesis of hexagonally close-packed cobalt nanorods with high magnetic coercivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19(12), 1971–1977 (2009)
F. Dumestre, B. Chaudret, C. Amiens, M. Respaud, P. Fejes, P. Renaud, P. Zurcher, Unprecedented crystalline super-lattices of monodisperse cobalt nanorods. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42(42), 5213–5216 (2003)
R. Xu, T. **e, Y.G. Zhao, Y.D. Li, Single-crystal metal nanoplatelets: cobalt, nickel, copper, and silver. Cryst. Growth Des. 7(9), 1904–1911 (2007)
J.G. Li, J.J. Huang, Y. Qin, F. Ma, Magnetic and microwave properties of cobalt nanoplatelets. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 138(3), 199–204 (2007)
L. Guo, F. Liang, N. Wang, D.S. Kong, S.M. Wang, L. He, C.P. Chen, X.M. Meng, Z.Y. Wu, Preparation and characterization of ring-shaped Co nanomaterials. Chem. Mater. 20(16), 5163–5168 (2008)
L. Guo, S. Yang, C. Chen, Uniform magnetic chains of hollow cobalt mesospheres from one-pot synthesis and their assembly in solution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17(3), 425–430 (2007)
Y. Bao, M. Beerman, A.B. Pakhomov, K.M. Krishnan, Controlled crystalline structure and surface stability of cobalt nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 109(15), 7220–7222 (2005)
L. Liu Sha, X. Kai-huant, Preparation of nano-crystalline Co powder from CoCO3. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 27(1), 61–65 (2009)
R.U. Ribeiro, J.W.C. Liberatori, H. Winnishofer, J.M.C. Bueno, D. Zanchet, Colloidal Co nanoparticles supported on SiO2: synthesis, characterizationand catalytic properties for steam reforming of ethanol. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 91(3–4), 670–678 (2009)
M. Rivera, C.H. Rios-Reyes, L.H. Mendoza-Huizar, Morphological and magnetic properties of cobalt nanoclusters electrodeposited onto HOPG. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(5), 1754–1758 (2008)
B. Tamami, S. Ghasemi, Modified cross linked polyacrylamide anchored Schiff base–cobalt complex: a novel nano-sized heterogeneous catalyst for selective oxidation of olefins and alkyl halides with hydrogen peroxide in aqueous media. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 393(1–2), 242–250 (2011)
J. Yan, T. Wei, J. Feng, Z. Fan, L. Zhang, F. Wei, One step synthesis of nanoparticles of cobalt in a graphitic shell anchored on graphene sheets. Carbon 50(6), 2356–2358 (2012)
L.P. Zhu, H.M. **ao, W.D. Zhang, Y. Yang, S.Y. Fu, Synthesis and characterization of novel three-dimensional metallic Co dendritic superstructures by a simple hydrothermal reduction route. Cryst. Growth Des. 8(4), 1113–1118 (2008)
R. Torchio, C. Meneghini, S. Mobilio, G. Capellini, A.G. Prieto, J. Alonso, M.L. Fdez-Gubieda, V.T. Liveri, A. Longo, A.M. Ruggirello, T. Neisius, Microstructure and magnetic properties of colloidal cobalt nano-clusters. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322(21), 3565–3571 (2010)
Y. Lu, X.M. Lu, B.T. Mayers, T. Herricks, Y.N. ** surfactants. J. Solid State Chem. 181(7), 1530–1538 (2008)
G. Seong, S. Takami, T. Arita, K. Minami, D. Hojo, A.R. Yavari, T. Adschiri, Supercritical hydrothermal synthesis of metallic cobalt nanoparticles and its thermodynamic analysis. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 60, 113–120 (2011)
H. Meng, F. Zhao, Z. Zhang, Preparation of cobalt nanoparticles by direct current arc plasma evaporation method. Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 31, 224–229 (2012)
H.-X. Wu, C.-X. Zhang, L. **, H. Yang, S.-P. Yang, Preparation and magnetic properties of cobalt nanoparticles with dendrimers as templates. Mater. Chem. Phys. 121(1–2), 342–348 (2010)
S.S. Nair, V. Sunny, M.R. Anantharaman, Tuning of magnetic parameters in cobalt–polystyrene nanocomposites by reduction cycling. Mater. Res. Bull. 46(9), 1610–1614 (2011)
A.J. Majewski, J. Wood, W. Bujalski, Nickele–silica core@shellcatalyst for methane reforming. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 38(34), 14531–14541 (2013)
N. Sahiner, H. Ozay, O. Ozay, N. Aktas, A soft hydrogel reactor for cobalt nanoparticle preparation and use in the reduction of nitrophenols. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 101(1–2), 137–143 (2010)
X. Liu, R. Yi, Y. Wang, G. Qiu, N. Zhang, X. Li, Highly ordered snowflakelike metallic cobalt microcrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(1), 163–167 (2007)
Q. **e, Y.T. Qian, S.Y. Zhang, S.Q. Fu, W.C. Yu, A hydrothermal reduction route to single-crystalline hexagonal cobalt nanowires. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006(12), 2454–2459 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This Paper was presented at the "Indian Workshop and Symposium on Modelling, Experimentation and Simulation on Complex Systems (Mescos 2015)" Held at HIT, Haldia during August 5–7, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, M., Mukherjee, S., Gayen, A. et al. Micro Structural, Optical and Magnetic Properties of Co–SiO2 Nanocomposite Synthesized by Sol–Gel Technique. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 98, 91–99 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-016-0116-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-016-0116-x