Abstract
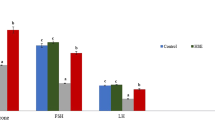
Protein hydrolysates, the so-called bioactive peptides, are specific protein fragments that have positive effects on several body functions and may improve human health. Marine organism-derived protein hydrolysates and bioactive peptides have shown to possess many physiological functions. Seahorses, used in traditional medicine, are generally ground to powder form either for direct application or for application following dissolution in warm water. In this present study, we purified, hydrolyzed, and characterized two bioactive peptides (ALC and PEP) obtained from seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis). The hydrolysates derived from seahorse significantly upregulated the expression of cyclin D and cyclin E and increased cell proliferation and testosterone level in the TM3 mouse Leydig cell line. These findings suggest that the hydrolysates stimulate the proliferation of TM3 cells via the AKT, ERK, and JNK pathways. The decline in the circulating testosterone levels in older men is associated with various adverse health effects. Following daily intake of hydrolysates for 12 weeks, the circulating level of testosterone and the sperm count in mice were measured. We found increased sperm motility (sperm count) as well as an increase in the testosterone level in male mice following a 12-week intake of hydrolysates derived from H. abdominalis. Hence, it can be suggested that seahorse-derived hydrolysates play an important role in improving male health by improving the serum testosterone level.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akpantah A, Oremosu A, Ajala M, Noronha C, Okanlawon A (2003) The effect of crude extract of Garcinia Kola seed on the histology and hormonal milieu of male sprague-dawley rats’ reproductive organs. Niger J Health Biomed Sci 2:40–46
Barqawi A, Crawford E (2006) Testosterone replacement therapy and the risk of prostate cancer. Is there a link? Int J Impotence Res 18:323–328
Bertoli C, Skotheim JM, de de Bruin RA (2013) Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:518–528
Bhasin S, Woodhouse L, Storer TW (2001) Proof of the effect of testosterone on skeletal muscle. J Endocrinol 170:27–38
Bui NT, Ho MT, Kim YM, Lim Y, Cho M (2014) Flavonoids promoting HaCaT migration: II. Molecular mechanism of 4′, 6, 7-trimethoxyisoflavone via NOX2 activation. Phytomedicine 21:570–577
Butler CM, Shaw G, Clark J, Renfree MB (2008) The functional development of Leydig cells in a marsupial. J Anat 212:55–66
Carrell D, Aston K, Oliva R, Emery B, De Jonge C (2016) The “omics” of human male infertility: integrating big data in a systems biology approach. Cell Tissue Res 363:295–312
Dudek SM, Chiang ET, Camp SM, Guo Y, Zhao J, Brown ME, Singleton PA, Wang L, Desai A, Arce FT, Lal R, Van Eyk JE, Imam SZ, Garcia JG (2010) Abl tyrosine kinase phosphorylates nonmuscle Myosin light chain kinase to regulate endothelial barrier function. Mol Biol Cell 21:4042–4056
Ebomoyi M, Ahumibe K (2014) Serum testosterone and testicular morphology in garlic-fed wistar rats following chronic garlic feeding. J Physiol Pathol 1(3):39–43
Erdmann K, Cheung BW, Schröder H (2008) The possible roles of food-derived bioactive peptides in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. J Nutr Biochem 19:643–654
Gakunga NJ, Mugisha K, Owiny D, Waako P (2014) Effects of crude aqueous leaf extracts of Citropsis articulata and Mystroxylon aethiopicum on sex hormone levels in male albino rats. Int J Pharm Sci Invent 3:5–17
Griswold SL, Behringer RR (2009) Fetal Leydig cell origin and development. Sex Dev 3:1–15
Haider SG (2004) Cell biology of Leydig cells in the testis. Int Rev Cytol 233:181–241
Hales DB, Allen JA, Shankara T, Janus P, Buck S, Diemer T, Hales KH (2005) Mitochondrial function in Leydig cell steroidogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1061:120–134
Himaya S, Ryu B, Qian Z, Kim S (2012) Paeonol from Hippocampus kuda Bleeler suppressed the neuro-inflammatory responses in vitro via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Taxicol Vitro 26:878–887
Horstman AM, Dillon EL, Urban RJ, Sheffield-Moore M (2012) The role of androgens and estrogens on healthy aging and longevity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 67:1140–1152
Hwang T, Liao T, Lin J, Lin Y, Lee S, Lai Y, Kao S (2011) Low-dose testosterone treatment decreases oxidative damage in TM3 Leydig cells. Asian J Androl 13:432–437
Ibañez E, Herrero M, Mendiola JA, Castro-Puyana M (2012) Extraction and characterization of bioactive compounds with health benefits from marine resources: macro and micro algae, cyanobacteria, and invertebrates. In: Hayes M (ed) Marine bioactive compounds, anonymous. Springer, New York, pp 55–98
Ibebunjo C, Eash JK, Li C, Ma Q, Glass DJ (2011) Voluntary running, skeletal muscle gene expression, and signaling inversely regulated by orchidectomy and testosterone replacement. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 300:E327–E340
Kasuga S, Uda N, Kyo E, Ushijima M, Morihara N, Itakura Y (2001) Pharmacologic activities of aged garlic extract in comparison with other garlic preparations. J Nut 131:1080S–1104S
Ketnawa S, Benjakul S, Martínez-Alvarez O, Rawdkuen S (2014) Three-phase partitioning and proteins hydrolysis patterns of alkaline proteases derived from fish viscera. Sep Purif Technol 132:174–181
Khaki A, Fathiazad F, Nouri M, Afshin Khaki A, Ozanci CC, Ghafari-Novin M, Hamadeh M (2009) The effects of Ginger on spermatogenesis and sperm parameters of rat. Int J Reprod Biomed 7:7–12
Kilinc F, Kayaselcuk F, Aygun C, Guvel S, Egilmez T, Ozkardes H (2004) Experimental varicocele induces hypoxia inducible factor-1α, vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis in the rat testis. J Urol 172:1188–1191
Kim S (2013) Marine proteins and peptides: biological activities and applications. Wiley, New York
Kwon YK, Choi SJ, Kim CR, Kim JK, Kim Y, Choi JH, Song S, Kim C, Park GG, Park C (2016) Antioxidant and cognitive-enhancing activities of Arctium lappa L. roots in Aβ1-42-induced mouse model. Appl Biol Chem 59:553–565
Liu Y, Su X, Hao J, Chen M, Liu W, Liao X, Li G (2016) Overexpression of PRL7D1 in Leydig Cells Causes Male Reproductive Dysfunction in Mice. Int J Mol Sci 17:96
Lopes S, Sun J, Jurisicova A, Meriano J, Casper RF (1998) Sperm deoxyribonucleic acid fragmentation is increased in poor-quality semen samples and correlates with failed fertilization in intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil Steril 69:528–532
Lordan S, Ross RP, Stanton C (2011) Marine bioactives as functional food ingredients: potential to reduce the incidence of chronic diseases. Mar Drugs 9:1056–1100
Lucas TF, Nascimento AR, Pisolato R, Pimenta MT, Lazari MFM, Porto CS (2014) Receptors and signaling pathways involved in proliferation and differentiation of sertoli cells. Spermatogenesis 4:e28138
Mahabadi JA, Nikzad H, Taherian A, Mohammadi F (2013) The effects of vasectomy on epididymal morphology and sperm parameters in Adult Male Balb/c mice. Int J Morphol 31(4):1349–1354
Matsumoto AM (2002) Andropause: clinical implications of the decline in serum testosterone levels with aging in men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 57:M76–M99
Mendoza MC, Er EE, Blenis J (2011) The Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem Sci 36:320–328
Naughton CK, Nangia AK, Agarwal A (2001) Pathophysiology of varicoceles in male infertility. Hum Reprod Update 7:473–481
Nigro N, Christ-Crain M (2012) Testosterone treatment in the aging male: myth or reality. Swiss Med Wkly 142:w13539
Noh Y, Kim D, Kim JY, Park J, Kim OH, Han D, Kim W, Kim S, Lee M, Heo S (2012) Improvement of andropause symptoms by dandelion and rooibos extract complex CRS-10 in aging male. Nutr Res Pract 6:505–512
Ofem OE (2014) Enhancement of some sex hormones concentrations by consumption of leaves extract of Viscum album (mistletoe) in rats. Asian J Med Sci 5:87–90
O’Shaughnessy PJ, Fowler PA (2011) Endocrinology of the mammalian fetal testis. Reproduction 141:37–46
Pang L, Zhu K, Feng X, Liu W, Peng D, Qiu L, Gao X, Deng J, Li Y, Zhao X (2015) Protective effect of liensinine on periodontitis through its antioxidant effect in mice. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 58:927–936
Park JS, Han K (2013) The spermatogenic effect of yacon extract and its constituents and their inhibition effect of testosterone metabolism. Biomed Ther 21:153–160
Poutahidis T, Springer A, Levkovich T, Qi P, Varian BJ, Lakritz JR, Ibrahim YM, Chatzigiagkos A, Alm EJ, Erdman SE (2014) Probiotic microbes sustain youthful serum testosterone levels and testicular size in aging mice. PLoS ONE 9:e84877
Rutherfurd-Markwick KJ, Moughan PJ (2005) Bioactive peptides derived from food. J AOAC Int 88:955–966
Ryan JT, Ross RP, Bolton D, Fitzgerald GF, Stanton C (2011) Bioactive peptides from muscle sources: meat and fish. Nutrients 3:765–791
Saito K, O’Donnell L, McLachlan RI, Robertson DM (2000) Spermiation failure is a major contributor to early spermatogenic suppression caused by hormone withdrawal in adult rats 1. Endocrinology 141:2779–2785
Saleh RA, HCLD AA (2002) Oxidative stress and male infertility: from research bench to clinical practice. J Androl 23:737–752
Sattler F, Bhasin S, He J, Chou CP, Castaneda-Sceppa C, Yarasheski K, Binder E, Schroeder ET, Kawakubo M, Zhang A, Roubenoff R, Azen S (2011) Testosterone threshold levels and lean tissue mass targets needed to enhance skeletal muscle strength and function: the HORMA trial. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 66:122–129
Schwartz E, Holtorf K (2011) Hormone replacement therapy in the geriatric patient: current state of the evidence and questions for the future. Estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and thyroid hormone augmentation in geriatric clinical practice: part 1. Clin Geriatr Med 27:541–559
Shahidi F, Zhong Y (2008) Bioactive peptides. J AOAC Int 91:914–931
Steidle C, Schwartz S, Jacoby K, Sebree T, Smith T, Bachand R (2003) AA2500 testosterone gel normalizes androgen levels in aging males with improvements in body composition and sexual function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:2673–2681
Sukcharoen N, Keith J (1996) Evaluation of the percentage of sperm motility at 24 h and sperm survival ratio for prediction of in vitro fertilization. Andrologia 28:203–210
Szulcek R, Bogaard HJ, van Nieuw Amerongen GP (2014) Electric cell-substrate impedance sensing for the quantification of endothelial proliferation, barrier function, and motility. J Vis Exp 85:e51300
Toth G, Zenick H, Smith M (1989) Effects of epichlorohydrin on male and female reproduction in Long-Evans rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol 13:16–25
Travison TG, Basaria S, Storer TW, Jette AM, Miciek R, Farwell WR, Choong K, Lakshman K, Mazer NA, Coviello AD, Knapp PE, Ulloor J, Zhang A, Brooks B, Nguyen AH, Eder R, LeBrasseur N, Elmi A, Appleman E, Hede-Brierley L, Bhasin G, Bhatia A, Lazzari A, Davis S, Ni P, Collins L, Bhasin S (2011) Clinical meaningfulness of the changes in muscle performance and physical function associated with testosterone administration in older men with mobility limitation. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 66:1090–1099
Vermeulen A, Kaufman J (1995) Ageing of the hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis in men. Horm Res Paediatr 43:25–28
Vincent AC (1995) Trade in seahorses for traditional Chinese medicines, aquarium fishes and curios. Taffic Bull-Wild Trade Monit Unit 15:125–128
Vincent A, Foster S, Koldewey H (2011) Conservation and management of seahorses and other Syngnathidae. J Fish Biol 78:1681–1724
Weinbauer GF, Luetjens CM, Simoni M, Nieschlag E (2010) Physiology of testicular function. In: Nieschlag E (ed) Andrology, anonymous. Springer, Berlin, pp 11–59
World Health Organisation (1999) WHO laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and sperm-cervical mucus interaction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Zhang W, Liu HT (2002) MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res 12:9–18
Zhang N, Xu B, Mou C, Yang W, Wei J, Lu L, Zhu J, Du J, Wu X, Ye L (2003) Molecular profile of the unique species of traditional Chinese medicine, Chinese seahorse (Hippocampus kuda Bleeker). FEBS Lett 550:124–134
Zirkin BR, Chen H (2000) Regulation of Leydig cell steroidogenic function during aging. Biol Reprod 63:977–981
Acknowledgements
This research was a part of the Project titled “Development of functional foods using the form hippocampus” (No. 20150343), funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.M., Jeon, Y.J., Huh, J.S. et al. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysate from seahorse Hippocampus abdominalis on testosterone secretion from TM3 Leydig cells and in male mice. Appl Biol Chem 59, 869–879 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-016-0237-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-016-0237-9