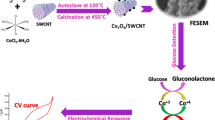
Abstract
Photo-electrochemical sensing is a new strategy for the development of clinical and environmental monitoring. Here, we present a new nanocomposite of cadmium sulfide decorated on cobalt oxide nano-dandelion (CoOx NDs/CdS NPs) aimed at glucose monitoring. Firstly, CoOx NDs are simply synthesized through hydrothermal technique; then, the resulted dandelion structures of CoOx are decorated with CdS nanoparticles through hydrothermal technique. The morphology of CoOx NDs/CdS NPs nanocomposite is characterized by transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties and sensing ability is investigated by various voltammetric techniques. Beside of electrocatalytic activity, a remarkable photoelectrocatalytic activity toward oxidation of glucose under visible light irradiation is observed. Consequently, the limit of detection of the fabricated sensor toward glucose is 0.23 μM with a sensitivity of 0.46 μA/μM in the dark and 0.09 μM with 1.1 μA/μM under visible light irradiation, respectively. Furthermore, this sensor has displays respectable stability, fast response time, and interference tolerance. This proposed composite can be used in develo** other photo-electrochemical sensors, bio anodes, and related biodevices.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Ogurtsova, J.D. da Rocha Fernandes, Y. Huang, U. Linnenkamp, L. Guariguata, N.H. Cho, D. Cavan, J.E. Shaw, L.E. Makaroff, IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 128, 40–50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024
Y. Yamakoshi, M. Ogawa, T. Yamakoshi, M. Satoh, M. Nogawa, S. Tanaka, T. Tamura, P. Rolfe, K. Yamakoshi, A new non-invasive method for measuring blood glucose using instantaneous differential near infrared spectrophotometry, in Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology—Proceedings (2007), pp. 2964–2967. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4352951
P.N. Wahjudi, M.E. Patterson, S. Lim, J.K. Yee, C.S. Mao, W.N.P. Lee, Measurement of glucose and fructose in clinical samples using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Clin. Biochem. 43, 198–207 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2009.08.028
E. Favre, P. Pugeaud, P. Péringer, Automated HPLC monitoring of glucose, glutamine, lactate and alanine on suspended mammalian cell reactors. Biotechnol. Tech. 4, 315–320 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157428
E. Sharifi, A. Salimi, E. Shams, A. Noorbakhsh, M.K. Amini, Shape-dependent electron transfer kinetics and catalytic activity of NiO nanoparticles immobilized onto DNA modified electrode: fabrication of highly sensitive enzymeless glucose sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 56, 313–319 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.01.010
C.W. Hsu, F.C. Su, P.Y. Peng, H.T. Young, S. Liao, G.J. Wang, Highly sensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose biosensor using a photolithography fabricated micro/nano hybrid structured electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 230, 559–565 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.02.109
A. Korani, A. Salimi, Fabrication of High performance bioanode based on fruitful association of dendrimer and carbon nanotube used for design O2/glucose membrane-less biofuel cell with improved bilirubine oxidase biocathode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 50, 186–193 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.05.047
A. Korani, A. Salimi, H. Hadadzadeh, Nickel-phendione complex covalently attached onto carbon nanotube/cross linked glucose dehydrogenase as bioanode for glucose/oxygen compartment-less biofuel cell. J. Power Sources 282, 586–595 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.02.009
J. Yuan, K. Wang, X. **a, Highly ordered platinum-nanotubule arrays for amperometric glucose sensing. Adv. Func. Mater. 15, 803–809 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200400321
A. Arabzadeh, A. Salimi, M. Ashrafi, S. Soltanian, P. Servati, Enhanced visible light driven photoelectrocatalytic oxidation of ethanol at reduced graphene oxide/CdS nanowires decorated with Pt nanoparticles. Catal. Sci. Technol. 6, 3485–3496 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cy01693b
Y. Bai, W. Yang, Y. Sun, C. Sun, Enzyme-free glucose sensor based on a three-dimensional gold film electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 134, 471–476 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2008.05.028
J.X. Wang, X.W. Sun, A. Wei, Y. Lei, X.P. Cai, C.M. Li, Z.L. Dong, Zinc oxide nanocomb biosensor for glucose detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 10–13 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2210078
Y. Mu, D. Jia, Y. He, Y. Miao, H.L. Wu, Nano nickel oxide modified non-enzymatic glucose sensors with enhanced sensitivity through an electrochemical process strategy at high potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 2948–2952 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.11.042
J. Luo, S. Jiang, H. Zhang, J. Jiang, X. Liu, A novel non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on Cu nanoparticle modified graphene sheets electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 709, 47–53 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.10.025
A. Navaee, M. Narimani, A. Korani, R. Ahmadi, A. Salimi, S. Soltanian, Bimetallic Fe15Pt85 nanoparticles as an effective anodic electrocatalyst for non-enzymatic glucose/oxygen biofuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 208, 325–333 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.05.033
H. Okabe, J. Akimitsu, T. Kubodera, M. Matoba, T. Kyomen, M. Itoh, Low-temperature magnetoresistance of layered cobalt oxides NaxCoO2. Phys B 378–380, 863–864 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2006.01.319
H.J. Qiu, L. Liu, Y.P. Mu, H.J. Zhang, Y. Wang, Designed synthesis of cobalt-oxide-based nanomaterials for superior electrochemical energy storage devices. Nano Res. 8, 321–339 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0589-6
X.H. **a, J.P. Tu, J. Zhang, X.H. Huang, X.L. Wang, W.K. Zhang, H. Huang, Enhanced electrochromics of nanoporous cobalt oxide thin film prepared by a facile chemical bath deposition. Electrochem. Commun. 10, 1815–1818 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2008.09.025
A. Salimi, R. Hallaj, S. Soltanian, H. Mamkhezri, Nanomolar detection of hydrogen peroxide on glassy carbon electrode modified with electrodeposited cobalt oxide nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 594, 24–31 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.05.010
M. Ashrafi, A. Salimi, A. Arabzadeh, Photoelectrocatalytic enzymeless detection of glucose at reduced graphene oxide/CdS nanocomposite decorated with finny ball CoOx nanostructures. J. Electroanal. Chem. 783, 233–241 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.11.015
M. Manickam, V. Ponnuswamy, C. Sankar, R. Mariappan, R. Suresh, Influence of substrate temperature on the properties of cobalt oxide thin films prepared by nebulizer spray pyrolysis (NSP) technique. Silicon 8, 351–360 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-015-9316-5
L. Kang, D. He, L. Bie, P. Jiang, Nanoporous cobalt oxide nanowires for non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 220, 888–894 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.06.015
D. Bimberg, Quantum dot based nanophotonics and nanoelectronics. Electron. Lett. 44, 390 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:20080395
J.K. Jaiswal, S.M. Simon, Potentials and pitfalls of fluorescent quantum dots for biological imaging. Trends Cell Biol. 14, 497–504 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2004.07.012
N. Qutub, S. Sabir, Optical, thermal and structural properties of CdS quantum dots synthesized by a simple chemical route. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8, 111–120 (2012)
J.J. Zhang, T.F. Kang, Y.C. Hao, L.P. Lu, S.Y. Cheng, Electrochemiluminescent immunosensor based on CdS quantum dots for ultrasensitive detection of microcystin-LR. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 214, 117–123 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.019
R. Agarwal, C.J. Barrelet, C.M. Lieber, Lasing in single cadmium sulfide nanowire optical cavities. Nano Lett. 5, 917–920 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl050440u
M. Antoniadou, D.I. Kondarides, D.D. Dionysiou, P. Lianos, Quantum dot sensitized titania applicable as photoanode in photoactivated fuel cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 16901–16909 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp305098m
R. Grinyte, J. Barroso, L. Saa, V. Pavlov, Modulating the growth of cysteine-capped cadmium sulfide quantum dots with enzymatically produced hydrogen peroxide. Nano Res. 10, 1932–1941 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1378-1
J.A. Ho, Y.C. Lin, L.S. Wang, K.C. Hwang, P.T. Chou, Carbon nanoparticle enhanced immunoelectrochemical detection for protein tumor marker with CdS biotracer. Anal. Chem. 81, 1340–1346 (2009)
C.J. Lin, L.C. Kao, Y. Huang, M.A. Bañares, S.Y.H. Liou, Uniform deposition of coupled CdS and CdSe quantum dots on ZnO nanorod arrays as electrodes for photoelectrochemical solar water splitting. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 40, 1388–1393 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.11.070
I.L. Medintz, H.T. Uyeda, E.R. Goldman, H. Mattoussi, Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 4, 435–446 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1390
M. Molaei, M. Marandi, E. Saievar-Iranizad, N. Taghavinia, B. Liu, H.D. Sun, X.W. Sun, Near-white emitting QD-LED based on hydrophilic CdS nanocrystals. J. Lumin. 132, 467–473 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2011.08.038
W. Shangguan, Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water on nanocomposites incorporating cadmium sulfide into the interlayer. J. Phys. Chem. B 9, 12227–12230 (2002)
Y. Huang, F. Sun, H. Wang, Y. He, L. Li, Z. Huang, Q. Wu, J.C. Yu, Photochemical growth of cadmium-rich CdS nanotubes at the air–water interface and their use in photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 6901 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b907871a
S. Liu, N. Zhang, Z.R. Tang, Y.J. Xu, Synthesis of one-dimensional CdS@TiO2 core-shell nanocomposites photocatalyst for selective redox: the dual role of TiO2 shell. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 6378–6385 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/am302074p
A. Arabzadeh, A. Salimi, One dimensional CdS nanowire@TiO2 nanoparticles core-shell as high performance photocatalyst for fast degradation of dye pollutants under visible and sunlight irradiation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 479, 43–54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.06.036
F. Jafari, A. Salimi, A. Navaee, Electrochemical and photoelectrochemical sensing of dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and glucose based on noncovalently functionalized reduced graphene oxide-cadmium sulfide quantum dots/poly-nile blue nanocomposite. Electroanalysis 26, 1782–1793 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201400164
T. Maiyalagan, K.A. Jarvis, S. Therese, P.J. Ferreira, A. Manthiram, Spinel-type lithium cobalt oxide as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution and oxygen reduction reactions. Nat. Commun. 5, 3949 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4949
A. Khan, CdS nanoparticles with a thermoresponsive polymer: synthesis and properties. J. Nanomater. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/451506
A. Salimi, H. Mamkhezri, R. Hallaj, S. Soltanian, Electrochemical detection of trace amount of arsenic(III) at glassy carbon electrode modified with cobalt oxide nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 129, 246–254 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2007.08.017
N. Zhang, S. Liu, X. Fu, Y.J. Xu, A simple strategy for fabrication of “plum-pudding” type Pd@CeO2 semiconductor nanocomposite as a visible-light-driven photocatalyst for selective oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 22901–22909 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp205821b
X. Dong, H. Xu, X. Wang, Y. Huang, M.B. Chan-park, H. Zhang, 3D Graphene À cobalt oxide electrode for high-performance supercapacitor and enzymeless glucose detection. ACS Nano (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn300097q
Y. Ding, Y. Wang, L. Su, M. Bellagamba, H. Zhang, Y. Lei, Electrospun Co3O4 nanofibers for sensitive and selective glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 542–548 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.07.050
R.A. Soomro, A. Nafady, Z.H. Ibupoto, S.S.T.H. Sirajuddin, M. Willander, M.I. Abro, Non-enzymatic glucose sensor using complex nanostructures of cobalt oxide. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 34, 373–381 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.02.055
C. Hou, Q. Xu, L. Yin, X. Hu, Metal-organic framework templated synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles for direct glucose and H2O2 detection. Analyst 137, 5803–5808 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an35954e
C. Guo, X. Zhang, H. Huo, C. Xu, X. Han, Co3O4 microspheres with free-standing nanofibers for high performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Analyst 138, 6727–6731 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an01403g
C.W. Kung, C.Y. Lin, Y.H. Lai, R. Vittal, K.C. Ho, Cobalt oxide acicular nanorods with high sensitivity for the non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 27, 125–131 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.06.033
Y. Su, B. Luo, J.Z. Zhang, Controllable cobalt oxide/Au hierarchically nanostructured electrode for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Anal. Chem. 88, 1617–1624 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03396
H. Zhang, S. Liu, A combined self-assembly and calcination method for preparation of nanoparticles-assembled cobalt oxide nanosheets using graphene oxide as template and their application for non-enzymatic glucose biosensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 485, 159–166 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.09.041
G. Ma, M. Yang, C. Li, H. Tan, L. Deng, S. **e, F. Xu, L. Wang, Y. Song, Preparation of spinel nickel-cobalt oxide nanowrinkles/reduced graphene oxide hybrid for nonenzymatic glucose detection at physiological level. Electrochim. Acta 220, 545–553 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.10.163
Acknowledgments
The financial supports of the Iranian Nanotechnology inventive and Research Office of the University of Kurdistan (Grant Number 4.160231) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ashrafi, M., Salimi, A. Dandelion-like CoOx nanostructures decorated with CdS nanoparticles toward the photoelectrocatalytic enzymeless glucose oxidation and detection. J IRAN CHEM SOC 20, 1061–1072 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-022-02728-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-022-02728-z