Abstract
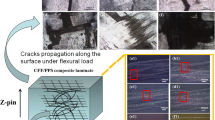
The present study investigates the thermal, mechanical and microscopic properties of polyphenylene sulphide/carbon fiber (PPS/CF) composites by incremental number of fiber layers. The composites were prepared by hand lay-up technique followed by compression molding. A superior matrix-reinforcement adhesion was attained without the use of coupling agent and mechanical stability of the composites improved with increasing fiber layers. Transverse rupture strength and bending modulus were improved by 59.84 and 125.21 %, respectively, without loss in toughness. Impact strength and hardness values were enhanced while storage modulus, loss modulus and dam** factor were dropped by increases in fiber layers. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) indicated a gradual rise in thermal stability (16.84 %) of the composite as compared to pure matrix. Surface morphology and crack propagation were studied by optical microscopy. It was found that crack was propagated in a linear plane by applying load. In addition, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) illustrated steady alignment of fibers and uniform distribution of the matrix around reinforcement. Based on the obtained results, fiber layers showed great potential for enhancement of thermal and mechanical properties of the composites.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suresh A, Harsha AP, Ghosh MK (2009) Solid particle erosion studies on polyphenylene sulfide composites and prediction on erosion data using artificial neural networks. Wear 266:184–193
Nejhad MNG, Parvizi-Majidi A (1990) Impact behaviour and damage tolerance of woven carbon fibre-reinforced thermoplastic composites. Composites 21:155–168
Sinmazçelik T, Fidan S, Günay V (2008) Residual mechanical properties of carbon/polyphenylenesulphide composites after solid particle erosion. Mater Des 29:1419–1426
Jiang Z, Gyurova LA, Schlarb AK, Friedrich K, Zhang Z (2008) Study on friction and wear behavior of polyphenylene sulfide composites reinforced by short carbon fibers and sub-micro TiO2 particles. Compos Sci Technol 68:734–742
Jang BP, Kowbel W, Jang BZ (1992) Impact behavior and impact-fatigue testing of polymer composites. Compos Sci Technol 44:107–118
Pandya KS, Veerraju C, Naik NK (2011) Hybrid composites made of carbon and glass woven fabrics under quasi-static loading. Mater Des 32:4094–4099
Sınmazçelika T, Taşkiran İ (2007) Erosive wear behaviour of polyphenylenesulphide (PPS) composites. Mater Des 28:2471–2477
Yýlmaz T, Sýnmazçelik T (2007) Investigation of load bearing performances of pin connected carbon/polyphenylene sulphide composites under static loading conditions. Mater Des 28:520–527
Naffakh M, Díez-Pascual AM (2014) Thermoplastic polymer nanocomposites based on inorganic fullerene-like nanoparticles and inorganic nanotubes. Inorganics 2:291–312
Wang J, Li KX, He HW, Wang JL, Sun GH (2011) Kinetic and thermodynamics analysis of water absorption in unidirectional fiber reinforced composites by polyethersulphone and polyphenylence sulfide. Colloids Surf A 377:330–335
Ferreira JAM, Costa JDM, Reis PNB (1999) Static and fatigue behaviour of glass fibre-reinforced polypropylene composites. Theor Appl Fract Mech 31:67–74
Shi H, Villages IF, Bersee HEN (2013) Strength and failure modes in resistance welded thermoplastic composite joints: effect of fibre–matrix adhesion and fibre orientation. Compos A 55:1–10
Vieille B, Taleb L (2011) About the influence of temperature and matrix ductility on the behavior of carbon woven-ply PPS or epoxy laminates: notched and unnotched laminates. Compos Sci Technol 71:998–1007
Vieille B, Aucher J, Taleb L (2011) Carbon fiber fabric reinforced pps laminates: influence of temperature on mechanical properties and behavior. Adv Polym Technol 30:80–95
Ye L, Chen ZR, Lu M, Hou M (2005) De-consolidation and re-consolidation in CF/PPS thermoplastic matrix composites. Compos A 36:915–922
Benoit V, Cédric L, Alexis C (2014) Post fire behavior of carbon fibers Polyphenylene Sulfide-and epoxy-based laminates for aeronautical applications: a comparative study. Mater Des 63:56–68
Gull N, Khan SM, Munawar MA, Shafiq M, Anjum F, Butt MTZ, Jamil T (2015) Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide (ZnO) filled glass fiber reinforced polyester composites. Mater Des 67:313–317
EL-Dessouky HM, Lawrence CA (2013) Ultra-lightweight carbon fibre/thermoplastic composite material using spread tow technology. Compos B 50:91–97
**a LG, Li AJ, Wang WQ, Yin Q, Lin H, Zhao YB (2008) Effects of resin content and preparing conditions on the properties of polyphenylene sulfide resin/graphite composite for bipolar plate. J Power Sour 178:363–367
Kenny JM, Maffezzoli A (1991) Crystallization kinetics of poly(phenylene sulfide) (PPS) and PPS/carbon fiber composites. Polym Eng Sci 31:607–614
Zhang R, Huang Y, Min M, Gao Y, Yu X, Lu A, Lu Z (2009) Isothermal crystallization of pure and glass fiber reinforced poly(phenylene sulfide) composites. Polym Compos 30:460–466
** FL, Lee SY, Park SJ (2013) Polymer matrices for carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites. Carbon Lett 14:76–88
Stoeffler K, Andjelic S, Legros N, Roberge J, Steen B, Schougaard SB (2013) Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) composites reinforced with recycled carbon fiber. Compos Sci Technol 84:65–71
Yang Y, Duan H, Zhang S, Niu P, Zhang G, Long S, Wang X, Yang J (2013) Morphology control of nanofillers in poly (phenylene sulfide): a novel method to realize the exfoliation of nanoclay by SiO2 via melt shear flow. Compos Sci Technol 75:28–34
Chen Z, Li T, Yang Y, Liu X, Lv R (2004) Mechanical and tribological properties of PA/PPS blends. Wear 257:696–707
Wang H, Liu D, Yan L, Li M, Wang C, Zhu Y (2014) A computed model for tribological properties of porous self-lubricating PPS composites: numerical analysis and experimental verification. Wear 320:94–102
Desio GP, Rebenfeld L (1992) Crystallization of fiber-reinforced poly(phenylene sulfide) composites, I. Experimental studies of crystallization rates and morphology. J Appl Polym Sci 44:1989–2001
Díez-Pascual AM, Naffakh M, Marco C, Ellis G (2012) Mechanical and electrical properties of carbon nanotube/poly(phenylene sulphide) composites incorporating polyetherimide and inorganic fullerene-like nanoparticles. Compos A 43:603–612
Gonon L, Momtaz A, Van Hoyweghen D, Chabert B, Gérard JF, Gaertner R (1996) Physico-chemical and micromechanical analysis of the interface in a poly(phenylene sulfide)/glass fiber composite—a microbond study. Polym Compos 17:265–274
Liu B, Liu Z, Wang X, Zhang G, Long S, Yang J (2013) Interfacial shear strength of carbon fiber reinforced polyphenylene sulfide measured by the microbond test. Polym Test 32:724–730
Hemanth R, Sekar M, Suresha B (2014) Effects of fibers and fillers on mechanical properties of thermoplastic composites. Indian J Adv Chem Sci 2:28–35
Zhang K, Zhang G, Liu B, Wang X, Long S, Yang J (2014) Effect of aminated polyphenylene sulfide on the mechanical properties of short carbon fiber reinforced polyphenylene sulfide composites. Compos Sci Technol 98:57–63
Yamamoto Y, Hashimoto M (2004) Friction and wear of water lubricated PEEK and PPS sliding contacts: part 2. Composites with carbon or glass fibre. Wear 257:181–189
Wang S, Mei Z, Chung DDL (2001) Interlaminar damage in carbon fiber polymer-matrix composites, studied by electrical resistance measurement. Int J Adhes Adhes 21:465–471
Akonda MH, Lawrence CA, Weager BM (2012) Recycled carbon fibre-reinforced polypropylene thermoplastic composites. Compos A 43:79–86
Asundi A, Choi AYN (1997) Fiber metal laminates: an advanced material for future aircraft. J Mater Process Tech 63:384–394
Sinmazçelik T, Avcu E, Bora MÖ, Çoban O (2011) A review: fibre metal laminates, background, bonding types and applied test methods. Mater Des 32:3671–3685
Folgueras LC, Alves MA, Rezende MC (2014) Evaluation of a nanostructured microwave absorbent coating applied to a glass fiber/polyphenylene sulfide laminated composite. Mater Res 17:197–202
Saad NA, Hamzah MS, Hamzah AF (2013) Study of fatigue behavior of composite materials with the basis of polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) reinforced with glass fiber and carbon. Int J Eng Technol 3:467–475
Kiran BVB, Harish G (2013) Effect of resin and thickness on tensile properties of laminated composites. Am Int J Res Sci Technol Eng Math 5:128–134
American Standard of Testing Materials (ASTM): D790-10 (2010) Standard test methods for flexural properties of unreinforced and reinforced plastics and electrical insulating materials. ASTM International 146–154
American Standard of Testing Materials (ASTM): D256-10 (2010) Standard test methods for determining the Izod pendulum impact resistance of plastics. ASTM International 1–20
American Standard of Testing Materials (ASTM): D785-08 (2008) Standard test methods of test for Rockwell hardness of plastic and electrical insulating materials. ASTM International 274–279
Rathnakar G, Shivanand HK (2012) Effect of thickness on flexural properties of epoxy based glass fiber reinforced laminate. Int J Sci Technol 2:409–412
Reis PNB, Ferreira JAM, Antunes FV, Costa JDM (2007) Flexural behaviour of hybrid laminated composites. Compos A 38:1612–1620
Khatri SC, Koczak MJ (1996) Thick-section AS4-graphite/E-glass/PPS hybrid composites: Part II. Flexural response. Compos Sci Technol 56:473–482
Kiran BVB, Harish G (2014) Influence of resin and thickness of laminate on flexural properties of laminated composites. Int J Eng Sci Innov Technol 3:279–287
Zhou S, Zhang Q, Wu C, Huang J (2013) Effect of carbon fiber reinforcement on the mechanical and tribological properties of polyamide6/polyphenylene sulfide composites. Mater Des 44:493–499
Ning H, Vaidya U, Janowski GM, Husman G (2007) Design, manufacture and analysis of a thermoplastic composite frame structure for mass transit. Compos Struct 80:105–116
Belingardi G, Cavatorta MP, Frasca C (2006) Bending fatigue behavior of glass–carbon/epoxy hybrid composites. Compos Sci Technol 66:222–232
Saad NA, Hamza MS, Hamzah AF (2014) Experimental and numerical simulation of impact fracture toughness of polyphenylene sulfide basis composite material. Material Engineering, University of Babylon, Iraq
Vieille B, Casado VM, Bouvet C (2013) About the impact behavior of woven-ply carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic- and thermosetting-composites: a comparative study. Compos Struct 101:9–21
Valach J, Kytyr D, Doktor T, Sekyrova K, Kralik V, Nemecek J (2011) Comparison of mechanical properties of CFRP laminate obtained from full-scale test and extrapolated from local measurement. Chemické Listy 105:729–732
Dhal JP, Mishra SC (2013) Processing and properties of natural fiber-reinforced polymer composite. J Mater 2013:1–6
Devendra K, Rangaswamy T (2013) Strength characterization of E-glass fiber reinforced epoxy composites with filler materials. J Min Mater Character Eng 1:353–357
Bora MO, Coban O, Avcu E, Fidan S, Sınmazçelik T (2013) The effect of TIO2 filler content on the mechanical, thermal, and tribological properties of TiO2/PPS composites. Polym Compos 34:1591–1599
Díez-Pascual AM, Guan J, Simard B, Gómez-Fatou MA (2012) Poly(phenylene sulphide) and poly(ether ether ketone) composites reinforced with single-walled carbon nanotube buckypaper: I–Structure, thermal stability and crystallization behaviour. Compos A 43:997–1006
Diez-Pascual AM, Naffakh M (2012) Tuning the properties of carbon fiber-reinforced poly(phenylene sulphide) laminates via incorporation of inorganic nanoparticles. Polymer 53:2369–2378
Chipara M, Lozano K, Hernandez A, Chipara M (2008) TGA analysis of polypropylene-carbon nanofibers composites. Polym Degrad Stab 93:871–876
Wani V, Mahilal M, Jain S, Singh PP, Bhattacharya B (2012) Studies on the influence of testing parameters on dynamic and transient properties of composite solid rocket propellants using a dynamic mechanical analyzer. J Aerosp Technol Manag 4:443–452
Lee TH, Boey FYC, Loh NH (1993) Characterization of a fibre-reinforced PPS composite by dynamic mechanical analysis: effect of aspect ratio and static stress. Compos Sci Technol 49:217–223
Kanagaraj S, Fonseca A, Guedes RM, Oliveira MSA, Simoes JAO (2011) Thermo-mechanical behaviour of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene-carbon nanotubes composites under different cooling techniques. Defect Diffus Forum 312:331–340
Komalan C, George KE, Kumar PAS, Varughese KT, Thomas S (2007) Dynamic mechanical analysis of binary and ternary polymer blends based on nylon copolymer/EPDM rubber and EPM grafted maleic anhydride compatibilizer. Express Polym Lett 1:641–653
Abdellaoui H, Bensalah H, Echaabi J, Bouhfid R, Qaiss A (2015) Fabrication, characterization and modelling of laminated composites based on woven jute fibres reinforced epoxy resin. Mater Des 68:104–113
Díez-Pascual AM, Ashrafi B, Naffakh M, González-Domínguez JM, Johnston A, Simard B, Martínez MT, Gómez-Fatou MA (2011) Influence of carbon nanotubes on the thermal, electrical and mechanical properties of poly(ether ether ketone)/glass fiber laminates. Carbon 49:2817–2833
Davies IJ, Ishikawa T, Shibuya M, Hirokawa T (1999) Optical microscopy of a 3-D woven SiC/SiC-based composite. Compos Sci Technol 59:429–437
Bernasconi A, Cosmi F, Hine PJ (2012) Analysis of fibre orientation distribution in short fibre reinforced polymers: a comparison between optical and tomographic methods. Compos Sci Technol 72:2002–2008
Sreekala MS, George J, Kumaran MG, Thomas S (2002) The mechanical performance of hybrid phenol-formaldehyde-based composites reinforced with glass and oil palm fibres. Compos Sci Technol 62:339–353
Koschinski I, Reichert KH (1988) Preparation of carbon fibre reinforced poly(phenylene sulfide) by in situ polymerization. Die Makromolekulare Chemie Rapid Commun 9:291–298
Quintelier J, Samyan P, Beats PD, Ost W, Van Paepegem W (2005) Wear of steel against carbon fibre reinforced PPS. Tribol Ind 27:29–35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S.M., Gull, N., Munawar, M.A. et al. Polyphenylene sulphide/carbon fiber composites: study on their thermal, mechanical and microscopic properties. Iran Polym J 25, 475–485 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-016-0439-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-016-0439-3