Abstract
Background
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease, characterized by chronic hyperglycemia that increases the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Objective
The aim of this study was to investigate the risk factors of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and establish an accurate and simple prediction model for its development.
Methods
The data of 435 patients with T2DM were collected from September 2021 to March 2022 at the First People’s Hospital of Lin** District. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression and stepwise backward regression were used to screen variables, and multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to establish a nomogram prediction model.
Results
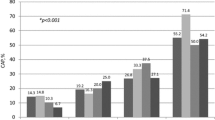
The results showed that the risk factors of T2DM with carotid atherosclerosis included male sex, elderly age, long course of disease, hypertension, cerebral infarction, alcohol drinking, and high level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The models showed good discrimination with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.862 (95%CI: 0.827–0.898) and 0.871 (95%CI: 0.837–0.905) and a good calibration. The cutoff value of the net reclassification improvement was − 0.0134 (95%CI: − 0.0897 to 0.0496, p = 0.703), and the integrated discrimination improvement was − 0.0163 (95%CI: − 0.0291 to − 0.0036, p = 0.012), indicating that there is no significant difference in the accuracy of the two prediction models, but the prediction probability of model A is slightly worse than that of model B.
Conclusion
Two prediction models were developed to assist with the early screening of carotid atherosclerosis in T2DM patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
References
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119.
American Diabetes Association. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(Suppl 1):S111–34.
Braunwald E. Diabetes, heart failure, and renal dysfunction: the vicious circles. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2019;62(4):298–302.
Lee SH, Hwang SM, Kang DH, Yang HJ. Brain education-based meditation for patients with hypertension and/or type 2 diabetes: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(19):e15574.
Henning RJ. Type-2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Future Cardiol. 2018;14(6):491–509.
Wu Y, He J, Sun X, Zhao YM, Lou HY, Ji XL, et al. Carotid atherosclerosis and its relationship to coronary heart disease and stroke risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(39):e8151.
American Diabetes Association. 2 Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(Suppl 1):S14–31.
Zhong P, Lu Z, Li T, Lan Q, Liu J, Wang Z, et al. Association between regular blood pressure monitoring and the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture: a Multicenter Retrospective Study with Propensity Score Matching. Transl Stroke Res. 2022;13(6):983–94.
Wood AM, Kaptoge S, Butterworth AS, Willeit P, Warnakula S, Bolton T, et al. Risk thresholds for alcohol consumption: combined analysis of individual-participant data for 599 912 current drinkers in 83 prospective studies. Lancet. 2018;391(10129):1513–23.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(33):3021–104.
Utazirubanda JC, Leon T, Ngom P. Variable selection with Group LASSO approach: application to Cox regression with frailty model. Commun Stat Simul Comput. 2021;50(3):881–901.
Zhang Z. Variable selection with stepwise and best subset approaches. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4(7):136.
Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, DeMatteo RP. Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(4):e173–80.
Wei L, Champman S, Li X, Li X, Li S, Chen R, et al. Beliefs about medicines and non-adherence in patients with stroke, diabetes mellitus and rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study in China. BMJ Open. 2017;7(10):e017293.
Sanchez-Pinto LN, Venable LR, Fahrenbach J, Churpek MM. Comparison of variable selection methods for clinical predictive modeling. Int J Med Inform. 2018;116:10–7.
Guo F, Zhou T, Tang J, Dong M, Wei Q. Related risk factors between subclinical carotid atherosclerosis and diabetic retinopathy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus in China. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021;129(4):283–8.
Kulkarni NB, Ganu MU, Godbole SG, Deo SS. Effect of age and blood pressure on surrogate markers of atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(6):BC08-11.
Veerasamy M, Ford GA, Neely D, Bagnall A, MacGowan G, Das R, et al. Association of aging, arterial stiffness, and cardiovascular disease: a review. Cardiol Rev. 2014;22(5):223–32.
Sugiura T, Dohi Y, Takagi Y, Yoshikane N, Ito M, Suzuki K, et al. Impacts of lifestyle behavior and shift work on visceral fat accumulation and the presence of atherosclerosis in middle-aged male workers. Hypertens Res. 2020;43(3):235–45.
Rosoff DB, Davey Smith G, Mehta N, Clarke TK, Lohoff FW. Evaluating the relationship between alcohol consumption, tobacco use, and cardiovascular disease: a multivariable Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2020;17(12):e1003410.
Kamarck TW, Li X, Wright AGC, Muldoon MF, Manuck SB. Ambulatory blood pressure reactivity as a moderator in the association between daily life psychosocial stress and carotid artery atherosclerosis. Psychosom Med. 2018;80(8):774–82.
Hinterdobler J, Schott S, ** H, Meesmann A, Steinsiek AL, Zimmermann AS, et al. Acute mental stress drives vascular inflammation and promotes plaque destabilization in mouse atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(39):4077–88.
Clarkson TB. Estrogen effects on arteries vary with stage of reproductive life and extent of subclinical atherosclerosis progression. Menopause. 2018;25(11):1262–74.
Sasaki Y, Ikeda Y, Miyauchi T, Uchikado Y, Akasaki Y, Ohishi M. Estrogen-SIRT1 axis plays a pivotal role in protecting arteries against menopause-induced senescence and atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2020;27(1):47–59.
Hurtubise J, McLellan K, Durr K, Onasanya O, Nwabuko D, Ndisang JF. The different facets of dyslipidemia and hypertension in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2016;18(12):82.
Leong XF, Ng CY, Jaarin K. Animal models in cardiovascular research: hypertension and atherosclerosis. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:528757.
Poznyak AV, Sadykhov NK, Kartuesov AG, Borisov EE, Melnichenko AA, Grechko AV, et al. Hypertension as a risk factor for atherosclerosis: cardiovascular risk assessment. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:959285.
Ni T, Fu Y, Zhou W, Chen M, Shao J, Zhou W, et al. Carotid plaques and neurological impairment in patients with acute cerebral infarction. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(1):e0226961.
Kianoush S, Yakoob MY, Al-Rifai M, DeFilippis AP, Bittencourt MS, Duncan BB, et al. Associations of cigarette smoking with subclinical inflammation and atherosclerosis: ELSA-Brasil (The Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health). J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6(6):e005088.
Stein JH, Smith SS, Hansen KM, Korcarz CE, Piper ME, Fiore MC, et al. Longitudinal effects of smoking cessation on carotid artery atherosclerosis in contemporary smokers: the Wisconsin Smokers Health Study. Atherosclerosis. 2020;315:62–7.
Mahajan H, Choo J, Masaki K, Fujiyoshi A, Guo J, Hisamatsu T, et al. Association of alcohol consumption and aortic calcification in healthy men aged 40–49 years for the ERA JUMP Study. Atherosclerosis. 2018;268:84–91.
Kim MK, Shin J, Kweon SS, Shin DH, Lee YH, Chun BY, et al. Harmful and beneficial relationships between alcohol consumption and subclinical atherosclerosis. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;24(7):767–76.
Zheng Y, Yu B, Alexander D, et al. Metabolomic patterns and alcohol consumption in African Americans in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99(6):1470–8.
Du R, Li M, Wang X, Wang S, Li S, Tian H, et al. LDL-C/HDL-C ratio associated with carotid intima-media thickness and carotid plaques in male but not female patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;511:215–20.
Inukai T, Yamamoto R, Suetsugu M, Matsumoto S, Wakabayashi S, Inukai Y, et al. Small low-density lipoprotein and small low-density lipoprotein/total low-density lipoprotein are closely associated with intima-media thickness of the carotid artery in type 2 diabetic patients. J Diabetes Complications. 2005;19(5):269–75.
Huang J, Gu JX, Bao HZ, Li SS, Yao XQ, Yang M, et al. Elevated serum small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol may increase the risk and severity of coronary heart disease and predict cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Dis Markers. 2021;5597028.
Kozakova M, Morizzo C, Fraser AG, Palombo C. Impact of glycemic control on aortic stiffness, left ventricular mass and diastolic longitudinal function in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017;16(1):78.
Vergès B. Is reduction of hyperglycemia associated with a cardiovascular benefit. Presse Med. 2018;47(9):764–8.
Taylor R, Al-Mrabeh A, Sattar N. Understanding the mechanisms of reversal of type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(9):726–36.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the help of all patients and researchers who contributed to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XHC and JCS analyzed the data, drew the diagrams, and drafted the article. YLH and HHM performed data analysis and generated graphs. XHC and BL obtained the clinical data and revised the manuscript. XHC and ZHJ contributed to the design of the research and helped to write the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by Ethical Committee of The first People’s Hospital of Lin** District in Hangzhou, China. All research was performed in accordance with relevant guidelines. Informed consent was obtained from all participants and/or their legal guardians.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Shi, J., Hu, Y. et al. Study on risk factors of carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus and development of prediction model. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-024-01355-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-024-01355-z