Abstract
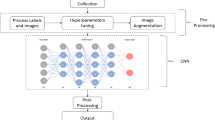
The satellite images have been employed in building extraction to aid urban planning, tax assessment, disaster management, etc. The number of buildings and building types is huge in urban areas, which puts more burden on human experts to extract buildings in satellite images. Hence, building extraction from satellite images using deep learning (DL) has become an emerging research domain in recent decades. The performance of the DL model depends on training parameters, the depth of the model, and the memory required to preserve the model. In this work, a Memory-Efficient Residual Dilated Convolutional Network (MRDCN) has been proposed to extract buildings effectively with reduced number of training parameters and with lesser memory consumption. The model is trained using the Massachusetts buildings dataset and implemented using PyTorch in Kaggle platform. The trained model has been tested using both Massachusetts and AIRS Dataset. The simulation results prove that the proposed model uses 31.64% less memory than the existing dilated residual network. It is evident from the results that the MRDCN is able to extract the buildings with better accuracy and an Intersection of Union with minimal memory consumption than the existing standard UNet, SegNet, ResUNet, and Dilated ResUNet models.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maggiori, E.; Tarabalka, Y.; Charpiat, G.; Alliez, P.: Convolutional neural networks for large-scale remote-sensing image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 55(2), 645–657 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2016.2612821
Bachofer, F.; Braun, A.; Adamietz, F.; Murray, S.; d’Angelo, P.; Kyazze, E.; Mumuhire, A.P.; Bower, J.: Building stock and building typology of Kigali, Rwanda. Data 4(3), 105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/data4030105
**, X.: Segmentation-based image processing system. US Patent, 20 (2009).
Huang, B.; Zhao, B.; Song, Y.: Urban land-use map** using a deep convolutional neural network with high spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 214, 73–86 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.04.050
Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, H.: Unsupervised deep feature learning for urban village detection from high-resolution remote sensing images. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 83(8), 567–579 (2017). https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.83.8.567
Banan, A.; Nasiri, A.; Taheri-Garavand, A.: Deep learning-based appearance features extraction for automated carp species identification. Aquacult. Eng. 89, 102053 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaeng.2020.102053
Chen, C.; Zhang, Q.; Kashani, M.H.; Jun, C.; Bateni, S.M.; Band, S.S.; Dash, S.S.; Chau, K.-W.: Forecast of rainfall distribution based on fixed sliding window long short-term memory. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 16, 248–261 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2021.2009374
Lin, H.; Gharehbaghi, A.; Zhang, Q.; Band, S.S.; Pai, H.T.; Chau, K.-W.; Mosavi, A.: Time series-based groundwater level forecasting using gated recurrent unit deep neural networks. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 16, 1655–1672 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2022.2104928
Xu, Y.; **e, Z.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Z.: Road extraction from high-resolution remote sensing imagery using deep learning. Remote Sens. 10(9), 1461 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091461
Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, R.; Chen, D.; Ke, Y.; Peethambaran, J.; Chen, C.; Sun, L.: Multilevel building detection framework in remote sensing images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 11(10), 3688–3700 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2866284
Milletari, F.; Navab, N. and Ahmadi, S.A.: V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 fourth Int Conf on 3D vision (3DV), pp. 565–571 (2016)
Dixit, M.; Chaurasia, K.; Mishra, V.K.: Dilated-ResUnet: a novel deep learning architecture for building extraction from medium resolution multi-spectral satellite imagery. Expert Syst. Appl. 184, 115530 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115530
Guercke, R.; Sester, M.: Building footprint simplification based on hough transform and least squares adjustment. In: Proceedings of the 14th Workshop of the ICA commission on Generalisation and Multiple Representation, Paris, France, 30 (2011).
Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T.: UNet: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: MICCAI 2015: 18th Int Conf Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv, Munich, Germany Part III 18, pp. 234–241 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R.: Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2481–2495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit, 2117–2125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.106
Pinheiro, P.O.; Collobert, R.; Dollár, P.: Learning to segment object candidates. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 28 (2015).
Bai, M.; Urtasun R.: Deep watershed transform for instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. pp. 5221–5229 (2017).https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.305
Prathap, G.; Afanasyev, I.: Deep learning approach for building detection in satellite multispectral imagery. Int. J. Intell. Syst. (IS) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/IS.2018.8710471
He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.: Mask R-CNN. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., pp. 2961–2969 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.322
Hu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; He, X.: Roof confusion removal for accurate vegetation extraction in the urban environment. In: Int Workshop on Earth Obs and Remote Sens Appl, pp. 1–7. IEEE (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/EORSA.2008.4620309
Yang, J.; Wang, Y.H.: Towards automatic building extraction variational level set model using prior shape knowledge. IEEE Int. Conf. Signal Image Process. Appl. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/IASP.2012.6424990
Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S.: Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically map** urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 24(3), 583–594 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160304987
Kumar, A.; Pandey, A.C.; Jeyaseelan, A.T.: Built-up and vegetation extraction and density map** using WorldView-II. Geocarto Int. 27(7), 557–568 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2012.657695
Huang, X.; Yuan, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.: A new building extraction postprocessing framework for high-spatial-resolution remote-sensing imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 10(2), 654–668 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2587324
Khatriker, S.; Kumar, M.: Building footprint extraction from high resolution satellite imagery using segmentation. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 42, 123–128 (2018). https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-5-123-2018
Hu, L.; Zheng, J.; Gao, F.: A building extraction method using shadow in high resolution multispectral images. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. (IGARSS) 1862, 1865 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2011.6049486
Shi, W.; Mao, Z.; Liu, J.: Building extraction from high-resolution remotely sensed imagery based on multi-subgraph matching. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 46, 2003–2013 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0868-x
Gavankar, N.L.; Ghosh, S.K.: Automatic building footprint extraction from high-resolution satellite image using mathematical morphology. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 51, 182–193 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/22797254.2017.1416676
Turlapaty, A.; Gokaraju, B.; Du, Q.; Younan, N.H.; Aanstoos, J.V.: A hybrid approach for building extraction from spaceborne multi-angular optical imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 5(1), 89–100 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2011.2179792
Avudaiammal, R.; Elaveni, P.; Selvan, S.; Rajangam, V.: Extraction of buildings in urban area for surface area assessment from satellite imagery based on morphological building index using SVM classifier. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 48, 1325–1344 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01161-0
Senaras, C.; Ozay, M.; Vural, F.T.Y.: Building detection with decision fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 6(3), 1295–1304 (2013)
Manno-Kovacs, A.; Sziranyi, T.: Orientation-selective building detection in aerial images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 108, 94–112 (2015)
Holloway, J.; Mengersen, K.: Statistical machine learning methods and remote sensing for sustainable development goals: a review. Remote Sens. 10(9), 1365 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091365
Mo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Liao, Y.: Review the state-of-the-art technologies of semantic segmentation based on deep learning. Neurocomputing 493, 626–646 (2022)
Zhu, X.X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; **a, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F.: Deep learning in remote sensing: a comprehensive review and list of resources. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 5(4), 8–36 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/MGRS.2017.2762307
Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. ar**v:1409.1556 (2014)
Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.: Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conf on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 31 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v31i1.11231
He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Huang, X.; Zhang, L.: A Multidirectional and multiscale morphological index for automatic building extraction from multispectral GeoEye-1 imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 77(7), 721–732 (2011). https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.77.7.721
Chen, B.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Shim, H.J.; Shi, Y.-Q.: An improved splicing localization method by fully convolutional networks. IEEE Access 6, 69472–69480 (2018)
Shao, Z.; Tang, P.; Wang, Z.; Saleem, N.; Yam, S.: Sommai, Chatpong: BRRNet: a fully convolutional neural network for automatic building extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 12(6), 1050 (2020)
Yi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, T.: Semantic segmentation of urban buildings from VHR remote sensing imagery using a deep convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 11(15), 1774 (2019)
Wei, S.; Ji, S.; Meng, L.: Toward automatic building footprint delineation from aerial images using CNN and regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 58(3), 2178–2189 (2019)
Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C., Reid, I.: Refinenet: multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1925–1934 (2017)
Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Liang, K.; Yu, Y.: Fastfcn: rethinking dilated convolution in the backbone for semantic segmentation. ar**v:1903.11816 (2019)
Xu, Y.; Wu, L.; **e, Z.; Chen, Z.: Building extraction in very high-resolution remote sensing imagery using deep learning and guided filters. Remote Sens. 10(1), 144 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010144
Duan,Y.; Sun, L.: Buildings extraction from remote sensing data using deep learning method based on improved UNet network. In: Int Geosci Remote Sens. Symp. pp. 3959–3961. IEEE (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8899798
Li, W.; He, C.; Fang, J.; Zheng, J.; Fu, H.; Yu, L.: Semantic segmentation-based building footprint extraction using very high-resolution satellite images and multi-source GIS data. Remote Sens. 11(4), 403 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11040403
Schuegraf, P.; Bittner, K.: Automatic building footprint extraction from multi-resolution remote sensing images using a hybrid FCN. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 8(4), 191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8040191
Yang, H.L.; Yuan, J.; Lunga, D.; Laverdiere, M.; Rose, A.; Bhaduri, B.: Building extraction at scale using convolutional neural network: map** of the united states. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 11(8), 2600–2614 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2835377
Khan, S.D.; Alarabi, L.; Basalamah, S.: An encoder–decoder deep learning framework for building footprints extraction from aerial imagery. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 48(2), 1273–1284 (2023)
Hurtado, J.V.; Valada, A.: Semantic scene segmentation for robotics. In: Deep learning for robot perception and cognition, pp. 279–311. Academic Press (2022)
Bouvrie, J.: Notes on convolutional neural networks (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2014.09.007
Hamaguchi, R.; Fujita, A.; Nemoto, K.; Imaizumi, T.; Hikosaka, S.: Effective use of dilated convolutions for segmenting small object instances in remote sensing imagery. In: IEEE Winter Conf Appl Comput Vis (WACV), pp. 1442–1450 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2018.00162
Mnih, V.: Machine Learning for Aerial Image Labeling. University of Toronto (Canada), Toronto (2013)
Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wu, G.; Guo, Z.; Waslander, S.L.: TEMPORARY REMOVAL: aerial imagery for roof segmentation: a large-scale dataset towards automatic map** of buildings. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 147(A5), 42–55 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.11.011
Burgan, H.: Comparison of different ANN (FFBP GRNN F) algorithms and multiple linear regression for daily streamflow prediction in Kocasu River-Turkey. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 31(5), 4699–4708 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge ISRO RESPOND Programme and Director, Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS) Dehradun for funding, guidance and support to this work. Authors extend their thanks to the management of St. Joseph’s College of Engineering, Chennai, for their support for this study.
Funding
This is a collaborative sponsored research work between Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS), Dehradun, and St. Joseph’s College of Engineering, Chennai. It is funded by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Department of Space, Government of India, under RESPOND-BASKET 2021 Project scheme of India, Grant No. ISRO/RES/4/687/21-22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. AR, Dr VS were responsible for the conceptualization and idea of the project. Mr. SVG performed statistical analysis, coding, and implementation. Dr AR, Dr SA, and Dr MLMJ were responsible for the whole framing, streamlining of the research project and have rigorously drafted the manuscript or revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors have substantial contributions toward concept and design, or analysis and interpretation of data; all have been involved in drafting the manuscript and Dr. VS has given the final approval for this version to be published. Each author has participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the content. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential of interest among the author(s).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramalingam, A., George, S.V., Srivastava, V. et al. Semantic Segmentation-Based Building Extraction in Urban Area Using Memory-Efficient Residual Dilated Convolutional Network. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08593-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08593-z