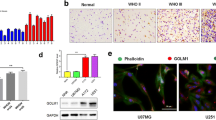
Abstract
Glioma occurs due to multi-gene abnormalities. Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1), as a transmembrane protein, involves in glioma proliferation, invasion, and migration, as well as tumor angiogenesis. The cytoplasmic protein, GAIP/RGS19-interacting protein (GIPC1), could regulate the clathrin-vesicles trafficking and recycling. Here, we show that NRP-1 co-localizes and co-immunoprecipitates with GIPC1, and the C-terminal SEA-COOH motif of NRP-1 interacts specially with the named from three proteins: PSD-95 (a 95 kDa protein involved in signaling at the post-synaptic density), DLG (the Drosophila melanogaster Discs Large protein) and ZO-1 (the zonula occludens 1 protein involved in maintenance of epithelial polarity) (PDZ) domain of GIPC1 in glioma cells. Knockdown of GIPC1 by small interfering RNA (siRNA) significantly reduces the proliferation and invasion of glioma cells in vitro and increases its apoptosis. Furthermore, si-GIPC1 prevents the action of adaptor proteins adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain and leucine zipper containing 1 (APPL1) and p130Cas and inhibits the downstream kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS)–ERK signaling pathway. This study demonstrated that NRP-1/GIPC1 pathway plays a vital role in glioma progression, and it is a potential important target for multi-gene combined therapeutics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raymond E, Brandes AA, Dittrich C, Fumoleau P, Coudert B, Clement PM, et al. Phase II study of imatinib in patients with recurrent gliomas of various histologies: a European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor Group Study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2008;26(28):4659–65. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.16.9235.
Minniti G, Muni R, Lanzetta G, Marchetti P, Enrici RM. Chemotherapy for glioblastoma: current treatment and future perspectives for cytotoxic and targeted agents. Anticancer Res. 2009;29(12):5171–84.
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ. Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(3):166–93. doi:10.3322/caac.20069.
Marin-Valencia I, Yang C, Mashimo T, Cho S, Baek H, Yang XL, et al. Analysis of tumor metabolism reveals mitochondrial glucose oxidation in genetically diverse human glioblastomas in the mouse brain in vivo. Cell Metab. 2012;15(6):827–37. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.05.001.
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V, Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 2010;17(1):98–110. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.020.
Latil A, Bieche I, Pesche S, Valeri A, Fournier G, Cussenot O, et al. VEGF overexpression in clinically localized prostate tumors and neuropilin-1 overexpression in metastatic forms. Int J Cancer. 2000;89(2):167–71.
Parikh AA, Fan F, Liu WB, Ahmad SA, Stoeltzing O, Reinmuth N, et al. Neuropilin-1 in human colon cancer: expression, regulation, and role in induction of angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2004;164(6):2139–51. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63772-8.
Lantuejoul S, Constantin B, Drabkin H, Brambilla C, Roche J, Brambilla E. Expression of VEGF, semaphorin SEMA3F, and their common receptors neuropilins NP1 and NP2 in preinvasive bronchial lesions, lung tumours, and cell lines. J Pathol. 2003;200(3):336–47. doi:10.1002/path.1367.
Stephenson JM, Banerjee S, Saxena NK, Cherian R, Banerjee SK. Neuropilin-1 is differentially expressed in myoepithelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells in preneoplastic and neoplastic human breast: a possible marker for the progression of breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2002;101(5):409–14. doi:10.1002/ijc.10611.
Fukasawa M, Matsushita A, Korc M. Neuropilin-1 interacts with integrin beta1 and modulates pancreatic cancer cell growth, survival and invasion. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6(8):1173–80.
Chu WM, Song XM, Yang XM, Ma L, Zhu J, He MY, et al. Neuropilin-1 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by stimulating nuclear factor-kappa B and is associated with poor prognosis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9(7), e101931. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0101931.
Osada H, Tokunaga T, Nishi M, Hatanaka H, Abe Y, Tsugu A, et al. Overexpression of the neuropilin 1 (NRP1) gene correlated with poor prognosis in human glioma. Anticancer Res. 2004;24(2B):547–52.
Chen LK, Miao W, Tang XY, Zhang HP, Wang SY, Luo FH, et al. The expression and significance of neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) on glioma cell lines and glioma tissues. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013;9(4):559–63. doi:10.1166/jbn.2013.1624.
Chen LK, Miao W, Tang XY, Zhang HP, Wang SY, Luo FH, et al. Inhibitory effect of neuropilin-1 monoclonal antibody (NRP-1 MAb) on glioma tumor in mice. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013;9(4):551–8. doi:10.1166/jbn.2013.1623.
Bielenberg DR, Pettaway CA, Takashima S, Klagsbrun M. Neuropilins in neoplasms: expression, regulation, and function. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(5):584–93. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.11.024.
Pellet-Many C, Frankel P, Jia H, Zachary I. Neuropilins: structure, function and role in disease. Biochem J. 2008;411:211–26. doi:10.1042/Bj20071639.
Tran TS, Kolodkin AL, Bharadwaj R. Semaphorin regulation of cellular morphology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:263–92. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010605.093554.
Hamerlik P, Lathia JD, Rasmussen R, Wu QL, Bartkova J, Lee M, et al. Autocrine VEGF-VEGFR2-neuropilin-1 signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell viability and tumor growth. J Exp Med. 2012;209(3):507–20. doi:10.1084/jem.20111424.
Glinka Y, Stoilova S, Mohammed N, Prud’homme GJ. Neuropilin-1 exerts co-receptor function for TGF-beta-1 on the membrane of cancer cells and enhances responses to both latent and active TGF-beta. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32(4):613–21. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq281.
Hu B, Guo P, Bar-Joseph I, Imanishi Y, Jarzynka MJ, Bogler O, et al. Neuropilin-1 promotes human glioma progression through potentiating the activity of the HGF/SF autocrine pathway. Oncogene. 2007;26(38):5577–86. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210348.
Snuderl M, Batista A, Kirkpatrick ND, Ruiz de Almodovar C, Riedemann L, Walsh EC. Targeting placental growth factor/neuropilin 1 pathway inhibits growth and spread of medulloblastoma. Cell. 2013;152(5):1065–76. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.036.
Pellet-Many C, Frankel P, Evans IM, Herzog B, Junemann-Ramirez M, Zachary IC. Neuropilin-1 mediates PDGF stimulation of vascular smooth muscle cell migration and signalling via p130Cas. Biochem J. 2011;435(3):609–18. doi:10.1042/BJ20100580.
West DC, Rees CG, Duchesne L, Patey SJ, Terry CJ, Turnbull JE, et al. Interactions of multiple heparin binding growth factors with neuropilin-1 and potentiation of the activity of fibroblast growth factor-2. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(14):13457–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.M410924200.
Cai HB, Reed RR. Cloning and characterization of neuropilin-1-interacting protein: a PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1 domain-containing protein that interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of neuropilin-1. J Neurosci. 1999;19(15):6519–27.
Wang L, Mukhopadhyay D, Xu XL. C terminus of RGS-GAIP-interacting protein conveys neuropilin-1-mediated signaling during angiogenesis. FASEB J. 2006;20(9):1513. doi:10.1096/fj.05-5504fje.
Wang L, Zeng HY, Wang P, Soker S, Mukhopadhyay D. Neuropilin-1-mediated vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent endothelial cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(49):48848–60. doi:10.1074/jbc.M310047200.
Prahst C, Heroult M, Lanahan AA, Uziel N, Kessler O, Shraga-Heled N, et al. Neuropilin-1-VEGFR-2 complexing requires the PDZ-binding domain of neuropilin-1. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(37):25110–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.C800137200.
De Vries L, Lou XJ, Zhao G, Zheng B, Farquhar MG. GIPC, a PDZ domain containing protein, interacts specifically with the C terminus of RGS-GAIP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(21):2340–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.21.12340.
Katoh M. Functional proteomics, human genetics and cancer biology of GIPC family members. Exp Mol Med. 2013;45:e26. doi:10.1038/emm.2013.49.
Choi JS, Paek AR, Kim SY, You HJ. GIPC mediates the generation of reactive oxygen species and the regulation of cancer cell proliferation by insulin-like growth factor-1/IGF-1R signaling. Cancer Lett. 2010;294(2):254–63. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.02.007.
Kirikoshi H, Katoh M. Expression of human GIPC1 in normal tissues, cancer cell lines, and primary tumors. Int J Mol Med. 2002;9(5):509–13.
Yavelsky V, Rohkin S, Shaco-Levy R, Tzikinovsky A, Amir T, Kohn H, et al. Native human autoantibodies targeting GIPC1 identify differential expression in malignant tumors of the breast and ovary. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:247. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-8-247.
Muders MH, Vohra PK, Dutta SK, Wang E, Ikeda Y, Wang L, et al. Targeting GIPC/synectin in pancreatic cancer inhibits tumor growth. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(12):4095–103. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2837.
Wang L, Lau JS, Patra CR, Cao Y, Bhattacharya S, Dutta S, et al. RGS-GAIP-interacting protein controls breast cancer progression. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8(12):1591–600. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0209.
Muders MH, Dutta SK, Wang L, Lau JS, Bhattacharya R, Smyrk TC, et al. Expression and regulatory role of GAIP-interacting protein GIPC in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66(21):10264–8. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2321.
Cuddapah VA, Robel S, Watkins S, Sontheimer H. A neurocentric perspective on glioma invasion. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014;15(7):455–65. doi:10.1038/nrn3765.
Koul D, Parthasarathy R, Shen RJ, Davies MA, Jasser SA, Chintala SK, et al. Suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 gene expression and invasion in human glioma cells by MMAC/PTEN. Oncogene. 2001;20(46):6669–78. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204799.
Paw I, Carpenter RC, Watabe K, Debinski W, Lo HW. Mechanisms regulating glioma invasion. Cancer Lett. 2015;362(1):1–7. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.03.015.
Tan GJ, Peng ZK, Lu JP, Tang FQ. Cathepsins mediate tumor metastasis. World J Biol Chem. 2013;4(4):91–101. doi:10.4331/wjbc.v4.i4.91.
Eisele G, Weller M. Targeting apoptosis pathways in glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2013;332(2):335–45. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.12.012.
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P, Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, et al. Classification of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16(1):3–11. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.150.
Palumbo S, Miracco C, Pirtoli L, Comincini S. Emerging roles of microRNA in modulating cell-death processes in malignant glioma. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(3):277–86. doi:10.1002/jcp.24446.
Varsano T, Dong MQ, Niesman I, Gacula H, Lou X, Ma T, et al. GIPC is recruited by APPL to peripheral TrkA endosomes and regulates TrkA trafficking and signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(23):8942–52. doi:10.1128/Mcb.00305-06.
Varsano T, Taupin V, Guo LX, Baterina OY, Farquhar MG. The PDZ protein GIPC regulates trafficking of the LPA(1) receptor from APPL signaling endosomes and attenuates the cell’s response to LPA. PLoS One. 2012;7(11), e49227. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049227.
Barrett A, Pellet-Many C, Zachary IC, Evans IM, Frankel P. p130Cas: a key signalling node in health and disease. Cell Signal. 2013;25(4):766–77. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.12.019.
Frankel P, Pellet-Many C, Lehtolainen P, D’Abaco GM, Tickner ML, Cheng LL, et al. Chondroitin sulphate-modified neuropilin 1 is expressed in human tumour cells and modulates 3D invasion in the U87MG human glioblastoma cell line through a p130Cas-mediated pathway. EMBO Rep. 2008;9(10):983–9. doi:10.1038/embor.2008.151.
Wang YX, Kaiser CE, Frett B, Li HY. Targeting mutant KRAS for anticancer therapeutics: a review of novel small molecule modulators. J Med Chem. 2013;56(13):5219–30. doi:10.1021/jm3017706.
Neuzillet C, Hammel P, Tijeras-Raballand A, Couvelard A, Raymond E. Targeting the Ras-ERK pathway in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013;32(1–2):147–62. doi:10.1007/s10555-012-9396-2.
Guttmann-Raviv N, Kessler O, Shraga-Heled N, Lange T, Herzog Y, Neufeld G. The neuropilins and their role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Cancer Lett. 2006;231(1):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2004.12.047.
Pan Q, Chanthery Y, Liang WC, Stawicki S, Mak J, Rathore N, et al. Blocking neuropilin-1 function has an additive effect with anti-VEGF to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 2007;11(1):53–67. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.018.
Valdembri D, Caswell PT, Anderson KI, Schwarz JP, Konig I, Astanina E, et al. Neuropilin-1/GIPC1 signaling regulates alpha5beta1 integrin traffic and function in endothelial cells. PLoS Biol. 2009;7(1), e25. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000025.
Wang L, Dutta SK, Kojima T, Xu X, Khosravi-Far R, Ekker SC, et al. Neuropilin-1 modulates p53/caspases axis to promote endothelial cell survival. PLoS One. 2007;2(11), e1161. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001161.
Ballmer-Hofer K, Andersson AE, Ratcliffe LE, Berger P. Neuropilin-1 promotes VEGFR-2 trafficking through Rab11 vesicles thereby specifying signal output. Blood. 2011;118(3):816–26. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-01-328773.
Naccache SN, Hasson T, Horowitz A. Binding of internalized receptors to the PDZ domain of GIPC/synectin recruits myosin VI to endocytic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(34):12735–40. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605317103.
Miaczynska M, Christoforidis S, Giner A, Shevchenko A, Uttenweiler-Joseph S, Habermann B, et al. APPL proteins link Rab5 to nuclear signal transduction via an endosomal compartment. Cell. 2004;116(3):445–56. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00117-5.
Defilippi P, Di Stefano P, Cabodi S. p130Cas: a versatile scaffold in signaling networks. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16(5):257–63. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2006.03.003.
Seerapu HR, Borthakur S, Kong N, Agrawal S, Drazba J, Vasanji A, et al. The cytoplasmic domain of neuropilin-1 regulates focal adhesion turnover. FEBS Lett. 2013;587(21):3392–9. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.08.040.
Li SQ, Mattar P, Dixit R, Lawn SO, Wilkinson G, Kinch C, et al. RAS/ERK signaling controls proneural genetic programs in cortical development and gliomagenesis. J Neurosci. 2014;34(6):2169–90. doi:10.1523/Jneurosci.4077-13.2014.
Repasky GA, Chenette EJ, Der CJ. Renewing the conspiracy theory debate: does Raf function alone to mediate Ras oncogenesis? Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14(11):639–47. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2004.09.014.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EWT, Chang F, et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Cell Res. 2007;1773(8):1263–84. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.001.
Acknowledgments
Our study has been kindly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81471780).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Chen, L., Sun, K. et al. Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1)/GIPC1 pathway mediates glioma progression. Tumor Biol. 37, 13777–13788 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5138-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5138-3