Abstract
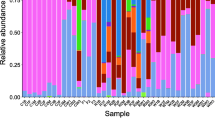
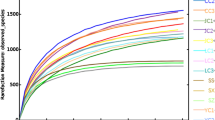
Intertidal mudflats are unique, highly productive ecosystems. Boleophthalmus pectinirostris and Periophthalmus magnuspinnatus are common fish species that are distributed in the intertidal mudflats of the Yangtze Estuary in China. They perform important ecological functions and have different feeding strategies. Herein, we studied the intestinal microbial diversity and structure of wild B. pectinirostris and P. magnuspinnatus with different sexes and feeding strategies during their breeding season. Gut samples of B. pectinirostris and P. magnuspinnatus individuals (female:male ratio = 1:1) were collected and subjected to high-throughput DNA sequencing. The results showed Proteobacteria was the most dominant phylum in all the four sample groups: 73.5% in the males and 52.6% in the females of B. pectinirostris and 40.2% in the males and 40.9% in the females of P. magnuspinnatus. Aeromonas, Shewanella, Halomonas, and Acinetobacter of the phylum Proteobacteria were dominant genera in all the sample groups and accounted for 62.13% of the ten dominant genera. The diversity of the intestinal microflora in the omnivorous P. magnuspinnatus was significantly higher (P < 0.05) than that in the herbivorous B. pectinirostris. Beta diversity, including PCoA and UPGMA of unweighted UniFrac distances, showed that B. pectinirostris samples were clustered together, and P. magnuspinnatus samples were clustered together, implying the effect of the feeding habits on the microbial community structure is more considerable than that of sex.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baeck GW, Takita T, Yang HY (2008) Lifestyle of Korean mudskipper Periophthalmus magnuspinnatus with reference to a congeneric species Periophthalmus modestus. Ichthyol Res 55:43–52
Beaz-Hidalgo R, Figueras MJ (2013) Aeromonas spp. whole genomes and virulence factors implicated in fish disease. J Fish Dis 36:371–388
Bolnick DI, Snowberg LK, Hirsch PE, Lauber CL, Org E, Parks B, Lusis AJ, Knight R, Caporaso JG, Svanbäck R (2014) Individual diet has sex-dependent effects on vertebrate gut microbiota. Nat Commun 5:4500
Brillet C (1969) Etude du comportement constructeur des poissons amphibies Periophtalmidæ. FRA 4:496
Brown K, Decoffe D, Molcan E, Gibson DL (2012) Diet-induced dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota and the effects on immunity and disease. Nutrients 4:1552–1553
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Cottrell MT, Wood DN, Yu L, Kirchman DL (2000) Selected chitinase genes in cultured and uncultured marine bacteria in the α- and γ-subclasses of the proteobacteria. Applied & Environmental Microbiology 66:1195
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Christopher Q, Rob K (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479
Filippo CD, Cavalieri D, Paola MD, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P (2010) Impact of diet in sha** gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:14691
Flint HJ, Bayer EA, Rincon MT, Lamed R, White BA (2008) Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:121–131
Freire AC, Basit AW, Choudhary R, Piong CW, Merchant HA (2011) Does sex matter? The influence of gender on gastrointestinal physiology and drug delivery. Int J Pharm 415:15
González JM, Moran MA (1997) Numerical dominance of a group of marine bacteria in the alpha-subclass of the class Proteobacteria in coastal seawater. Applied & Environmental Microbiology 63:4237–4242
Ishimatsu A, Yoshida Y, Itoki N, Takeda T, Lee HJ, Graham JB (2007) Mudskippers brood their eggs in air but submerge them for hatching. J Exp Biol 210:3946–3954
Zeehan J, Gianluca P, Yuliadi Z (2016) Description of a new species of Periophthalmus (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from the Lesser Sunda Islands. Raffles B Zool 64:278–283
Jabari L, Khelifi E, Gannoun H, Fardeau ML, Godon JJ, Hamdi M (2016) Effect of salinity and temperature on the bacterial diversity shift of anaerobic batch cultures treating abattoir wastewater. Desalination & Water Treatment 57:13909–13915
Jiang Y, **e C, Yang G, Gong X, Chen X, Xu L, Bao B (2011) Cellulase-producing bacteria of Aeromonas are dominant and indigenous in the gut of Ctenopharyngodon idellus (Valenciennes). Aquac Res 42:499–505
Lee HJ, Martinez CA, Hertzberg KJ, Hamilton AL, Graham JB (2005) Burrow air phase maintenance and respiration by the mudskipper Scartelaos histophorus (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae). J Exp Biol 208:169–177
Ley RE, Hamady M, Lozupone C, Turnbaugh PJ, Ramey RR, Bircher JS, Schlegel ML, Tucker TA, Schrenzel MD, Knight R (2008) Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 320:1647–1651
Li XM, Zhu YJ, Yan QY, Ringø E, Yang DG (2014) Do the intestinal microbiotas differ between paddlefish (Polyodon spathala) and bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) reared in the same pond? J Appl Microbiol 117:1245–1252
Li T, Long M, Ji C, Shen Z, Gatesoupe FJ, Zhang X, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Zhao Y, Liu X (2016) Alterations of the gut microbiome of largemouth bronze gudgeon (Coreius guichenoti) suffering from furunculosis. Sci Rep 6:30606
Liao C, Yu D, Chen Y, Reichard M, Liu H (2014) Reproductive behaviour of female rosy bitterling Rhodeus ocellatus in response to a female-biased operational sex ratio. Behaviour 151:755–768
Magoč T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Mrázek J, Strosová L, Fliegerová K, Kott T, Kopecný J (2008) Diversity of insect intestinal microflora. Folia Microbiol 53:229–233
Muegge BD, Kuczynski J, Knights D, Clemente JC, González A, Fontana L, Henrissat B, Knight R, Gordon JI (2011a) Diet drives convergence in gut microbiome functions across mammalian phylogeny and within humans. Science (New York, NY) 332:970–974
Muegge BD, Kuczynski J, Knights D, Clemente JC, González A, Fontana L, Henrissat B, Knight R, Gordon JI (2011b) Diet drives convergence in gut microbiome functions across mammalian phylogeny and within humans. Science 332:970
Murdy EO (1989) A taxonomic revision and cladistic analysis of the oxudercine gobies (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae). Records of the Australian Museum Supplement 11:1–93
Ravi V (2013) Food and feeding habits of the mudskipper, Boleophthalmus boddarti (Pallas, 1770) from Pichavaram Mangroves, Southeast Coast of India. International Journal of Marine Science 3:98–104
Romero J, Navarrete P (2006) 16S rDNA-based analysis of dominant bacterial populations associated with early life stages of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Microb Ecol 51:422–430
Sanders JG, Beichman AC, Roman J, Scott JJ, Emerson D, Mccarthy JJ, Girguis PR (2015) Baleen whales host a unique gut microbiome with similarities to both carnivores and herbivores[J]. Nat Commun 6:8285
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Applied & Environmental Microbiology 75:7537
Sekirov I, Russell SL, Antunes LC, Finlay BB (2010) Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol Rev 90:859
Stephens WZ, Burns AR, Stagaman K, Wong S, Rawls JF, Guillemin K, Bohannan BJM (2016) The composition of the zebrafish intestinal microbial community varies across development. ISME J 10:644
Sullam KE, Essinger SD, Lozupone CA, O'Connor MP, Rosen GL, Knight R, Kilham SS, Russell JA (2012) Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: a meta-analysis. Mol Ecol 21:3363
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied & Environmental Microbiology 73:5261
Ward NL, Steven B, Penn K, Methé BA, Iii WHD (2009) Characterization of the intestinal microbiota of two Antarctic notothenioid fish species. Extremophiles 13:679–685
Yang KY, Lee SY, Williams GA (2003) Selective feeding by the mudskipper ( Boleophthalmus pectinirostris ) on the microalgal assemblage of a tropical mudflat. Mar Biol 143:245–256
Yun JH, Roh SW, Whon TW, Jung MJ, Kim MS, Park DS, Yoon C, Nam YD, Kim YJ, Choi JH (2014) Insect gut bacterial diversity determined by environmental habitat, diet, developmental stage, and phylogeny of host. Applied & Environmental Microbiology 80:5254–5264
Zhu Y, Zhang Q (1993) On feeding habits and histological structure of digestive tract of the mudskipper, Boleophthalmus pectinirostris, in intertidal zone of Jiulong River Estuary. J Oceanography Taiwan Strait 12:225–232
Funding
This work was financially supported by the NSFC (31600334).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of East China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, R., Wang, S., Zhao, F. et al. Comparative study on intestinal bacterial communities of Boleophthalmus pectinirostris and Periophthalmus magnuspinnatus with different sexes and feeding strategies. Ann Microbiol 68, 123–133 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1324-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1324-4